How to lyse bacterial cells?
How do you Lyse bacterial cells? The freeze-thaw method is commonly used to lyse bacterial and mammalian cells. The technique involves freezing a cell suspension in a dry ice/ethanol bath or freezer and then thawing the material at room temperature or 37°C.
What is the difference between lysis and lysate?
Overview of Cell Lysis and Protein Extraction
- Structure and diversity of cells. All cells have a plasma membrane, a protein-lipid bilayer that forms a barrier separating cell contents from the extracellular environment.
- Cell lysis and protein extraction. ...
- Recommended reading. ...
What causes lysis of red blood cells?
- red meat, such as beef.
- organ meat, such as kidney and liver.
- dark, leafy, green vegetables, such as spinach and kale.
- dried fruits, such as prunes and raisins.
- beans.
- legumes.
- egg yolks.
Do bacterial cells have lysosomes?
The bacteria do have a complex cell wall and with the question of do bacteria have lysosomes the bacteria have no membrane bound organelles and thus no lysosomes as well but do have granules. The cell wall of prokaryotes has peptidoglycan and also has many small ribosomes inside the cytoplasm.
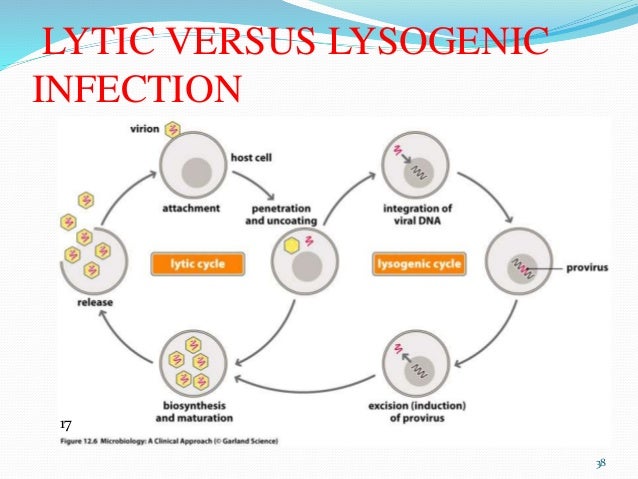
What does bacteria lysis mean?
(LY-sis) In biology, lysis refers to the breakdown of a cell caused by damage to its plasma (outer) membrane. It can be caused by chemical or physical means (for example, strong detergents or high-energy sound waves) or by infection with a strain virus that can lyse cells.
What is the process of lysis?
Lysis refers to the breaking down of the cell, often by viral, enzymic, or osmotic mechanisms that compromise its integrity. A fluid containing the contents of lysed cells is called a "lysate". Cell lysis is used to break open cells to avoid shear forces that would denature or degrade sensitive proteins and DNA.
What is released during lysis of bacteria?
The release of phage progeny from an infected bacterium is necessary for the spread of infection. Only helical phages are secreted from a cell without causing its destruction. The release of remaining phages is correlated with bacterial lysis and death.
What is the purpose of the lysis?
The word lysis comes from the greek word for “loosen.” Cell lysis is the process of rupturing the membrane or walls of a cell. The purpose of a cell lysis buffer is to use a chemical mixture to disrupt the exterior environment of a cell in a way that causes it to break open and release its contents.
How do you lyse bacteria?
The freeze-thaw method is commonly used to lyse bacterial and mammalian cells. The technique involves freezing a cell suspension in a dry ice/ethanol bath or freezer and then thawing the material at room temperature or 37°C.
What happens to bacterial cells during the cell lysis step?
Chemical lysis methods use lysis buffers to disrupt the cell membrane. Lysis buffers break the cell membrane by changing the pH. Detergents can also be added to cell lysis buffers to solubilize the membrane proteins and to rupture the cell membrane to release its contents.
How do bacteriophages lyse bacteria?
In canonical lysis, a phage encoded protein, the holin, accumulates harmlessly in the cytoplasmic membrane until triggering at an allele-specific time to form micron-scale holes. This allows the soluble endolysin to escape from the cytoplasm to degrade the peptidoglycan.
What would be the purpose of lysing the host cell?
Viruses can be released from the host cell by lysis, a process that kills the cell by bursting its membrane and cell wall if present. This is a feature of many bacterial and some animal viruses.
Does lysis mean to burst?
The bursting of a cell membrane is called "lysis."
What is lysis solution made of?
Cell lysis buffer for RNA extraction is highly denaturing and is usually composed of phenol and guanidine isothiocyanate.
What are the different methods of cell lysis?
5 Common Cell Disruption MethodsMechanical Homogenization.Ultrasonic Homogenization.Pressure Homogenization.Temperature Treatments.Osmotic and Chemical Lysis.
How do you know if your cell is lysed?
You can visualize lysis through a microscope, which will let you know early on if your buffer is working the way it's supposed to. Other ways to monitor the release of proteins are by using a Bradford, Lowry or other assays.
What is lysis in a lab?
Cell lysis is used in laboratories to break open cells and purify or further study their contents. Lysis in the laboratory may be affected by enzymes or detergents or other chaotropic agents. Mechanical disruption of cell membranes, as by repeated freezing and thawing, sonication, pressure, or filtration may also be referred to as lysis. Many laboratory experiments are sensitive to the choice of lysis mechanism; often it is desirable to avoid mechanical shear forces that would denature or degrade sensitive macromolecules, such as proteins and DNA, and different types of detergents can yield different results. The unprocessed solution immediately after lysis but before any further extraction steps is often referred to as a crude lysate.
What is the unprocessed solution immediately after lysis but before any further extraction steps?
The unprocessed solution immediately after lysis but before any further extraction steps is often referred to as a crude lysate. For example, lysis is used in western and Southern blotting to analyze the composition of specific proteins, lipids, and nucleic acids individually or as complexes.
What is a fluid that contains the contents of lysed cells called?
A fluid containing the contents of lysed cells is called a lysate. In molecular biology, biochemistry, and cell biology laboratories, cell cultures may be subjected to lysis in the process of purifying their components, as in protein purification, DNA extraction, RNA extraction, or in purifying organelles . Many species of bacteria are subject ...
What is the process of a cell burst that causes excess water to move into the cell?
Cytolysis . Cytolysis occurs when a cell bursts due to an osmotic imbalance that has caused excess water to move into the cell. Cytolysis can be prevented by several different mechanisms, including the contractile vacuole that exists in some paramecia, which rapidly pump water out of the cell.
What is the contraction of cells in plants?
Plasmolysis is the contraction of cells within plants due to the loss of water through osmosis. In a hypertonic environment, the cell membrane peels off of the cell wall and the vacuole collapses. These cells will eventually wilt and die unless the flow of water caused by osmosis can stop the contraction of the cell membrane.
What is the term for the breaking down of the membrane of a cell?
Lysis ( / ˈlaɪsɪs / LY-sis; Greek λύσις lýsis, "a loosing" from λύειν lýein, "to unbind") is the breaking down of the membrane of a cell, often by viral, enzymic, or osmotic (that is, "lytic" / ˈlɪtɪk / LIT-ək) mechanisms that compromise its integrity. A fluid containing the contents of lysed cells is called a lysate.

Overview
Lysis is the breaking down of the membrane of a cell, often by viral, enzymic, or osmotic (that is, "lytic" /ˈlɪtɪk/ LIT-ik) mechanisms that compromise its integrity. A fluid containing the contents of lysed cells is called a lysate. In molecular biology, biochemistry, and cell biology laboratories, cell cultures may be subjected to lysis in the process of purifying their components, as in protein purification, DNA extraction, RNA extraction, or in purifying organelles.
Cytolysis
Cytolysis occurs when a cell bursts due to an osmotic imbalance that has caused excess water to move into the cell.
Cytolysis can be prevented by several different mechanisms, including the contractile vacuole that exists in some paramecia, which rapidly pump water out of the cell. Cytolysis does not occur under normal conditions in plant cells because plant cells have a strong cell wall that contains t…
Oncolysis
Oncolysis is the destruction of neoplastic cells or of a tumour.
The term is also used to refer to the reduction of any swelling.
Plasmolysis
Plasmolysis is the contraction of cells within plants due to the loss of water through osmosis. In a hypertonic environment, the cell membrane peels off of the cell wall and the vacuole collapses. These cells will eventually wilt and die unless the flow of water caused by osmosis can stop the contraction of the cell membrane.
Immune response
Erythrocytes' hemoglobin release free radicals in response to pathogens when lysed by them. This can damage the pathogens.
Applications
Cell lysis is used in laboratories to break open cells and purify or further study their contents. Lysis in the laboratory may be affected by enzymes or detergents or other chaotropic agents. Mechanical disruption of cell membranes, as by repeated freezing and thawing, sonication, pressure, or filtration may also be referred to as lysis. Many laboratory experiments are sensitive to the choice of lysis mechanism; often it is desirable to avoid mechanical shear forces that would d…
Methods
This method uses chemical disruption. It is the most popular and simple approach. Chemical lysis chemically deteriorates/solubilizes the proteins and lipids present within the membrane of targeted cells.
This method uses ultrasonic waves to generate areas of high and low pressure which causes cavitation and in turn, cell lysis. Though this method usually comes out clean, it fails to be cost e…
See also
• Cell disruption
• Cell unroofing
• Crenation
• Hemolysis
• Lysogenic