What is the bank of Canada interest rate now?
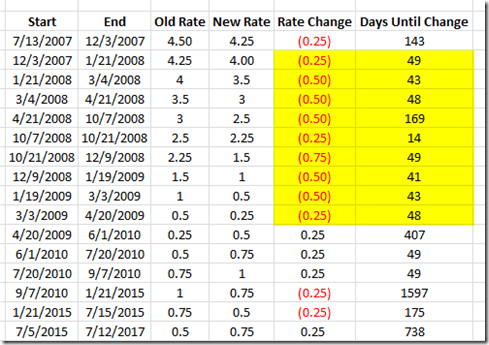
The Bank of Canada rate then dropped from 1.25% to 0.75% in 2015. 2018-Present: Low Inflation and COVID-19. Despite widespread economic growth, 2018 and 2019 were marked by continued low inflation, preventing the Bank of Canada from raising rates any higher than 1.75%.
How does the BOC’s key interest rate affect the Canadian dollar?
If the Canadian central bank has set a new target for the level of the key interest rate this will usually also lead to a change in the interest rates for loans, mortgages and savings. It can also have an effect on the exchange rate of the Canadian dollar. This page shows the current and historic value of the BOC’s key interest rate.
What are the other central banks’ interest rates?
Summary of other central banks’ interest rates central bank interest rate region percentage date BoE interest rate Great Britain 0.100 % 03-19-2020 BOC interest rate Canada 0.250 % 03-27-2020 PBC interest rate China 3.850 % 04-20-2020 ECB interest rate Europe 0.000 % 03-10-2016 6 more rows ...
Will interest rates rise in Canada in 2020?
However, the massive amounts of debt raised by both federal and provincial Canadian governments will pose a barrier to any further increases in interest rates. The Federal government alone is expected to borrow $713 billion CAD in 2020, more than double the amount raised in 2019.

What is the Bank of Canada interest rate?
The Bank of Canada today increased its target for the overnight rate to 1½%, with the Bank Rate at 1¾% and the deposit rate at 1½%. The Bank is also continuing its policy of quantitative tightening (QT).
What is the Bank of Canada's key policy rate?
1%Bank of Canada increases policy interest rate by 50 basis points, begins quantitative tightening. The Bank of Canada today increased its target for the overnight rate to 1%, with the Bank Rate at 1¼% and the deposit rate at 1%.
What does key interest rate mean?
The key policy rate, also known as the target for the overnight rate, is the interest rate the Bank of Canada wants commercial banks to charge when lending each other money overnight so they settle balances at the end of each day.
What is the interest rate paid by the Bank of Canada on deposits?
Bank of Canada will hold current level of policy rate until inflation objective is sustainably achieved, continues quantitative easing. The Bank of Canada today held its target for the overnight rate at the effective lower bound of ¼ percent, with the Bank Rate at ½ percent and the deposit rate at ¼ percent.
Will mortgage rates go up in 2021?
After mortgage rates hit an all-time low in January of this year, they quickly increased and have since dropped back down closer to their record lows. But many experts forecast that rates will rise by the end of 2021. As the economy begins to reopen, the expectation is for mortgage and refinance rates to grow.
What's the new interest rate today?
Current mortgage and refinance ratesProductInterest rateAPR30-year fixed-rate5.084%5.170%20-year fixed-rate4.706%4.814%15-year fixed-rate4.242%4.390%10-year fixed-rate3.796%4.049%5 more rows
What is the most important interest rate?
The federal funds rate is one of the most important interest rates in the U.S. economy. That's because it affects monetary and financial conditions, which in turn have a bearing on critical aspects of the broader economy including employment, growth, and inflation.
Will Bank of Canada raise rates in 2022?
We said in April that we expect inflation to average almost 6% in the first half of 2022 before easing to about 2½% in the second half of 2023 and returning to the 2% target in 2024.
Which Bank has the highest interest rate for fixed deposit in Canada?
Motive Financial, the online banking division of Canadian Western Bank, offers the highest regular interest rate on this list. As such, your eligible deposits are held at Canadian Western Bank, and protected by the Canada Deposit Insurance Corporation (CDIC; see details below).
When did the Bank of Canada adopt the new interest rate system?
Summary of Consultation Results. On 19 September 2000, the Bank of Canada published details of its plan to adopt a new system of eight “fixed” or pre-specified dates each year for announcing any changes to the official interest rate that it uses to implement monetary policy.
What was the original key interest rate?
Bank Rate . The original key interest rate was the Bank Rate . This is the minimum rate of interest that the Bank of Canada charges on one-day loans to financial institutions. Between March 1935 and November 1956, the Bank Rate was fixed, set directly by the Bank.
Why is the target for the overnight rate the most appropriate policy rate?
Because the target affects the interest rates that financial institutions charge each other from day to day, it usually affects other interest rates, such as mortgages and consumer loans. The target for the overnight rate is also the most appropriate policy rate for international comparisons; for example, with the target for ...
What is overnight rate?
The overnight rate is the interest rate at which major financial institutions borrow and lend one-day (or "overnight") funds among themselves; the Bank sets a target level for that rate. This target for the overnight rate is often referred to as the Bank's policy interest rate. Changes in the target for the overnight rate influence other interest ...
Does the Bank of Canada adjust its interest rate?
Over the years, the Bank of Canada has adjusted the way it sets its key interest rate .
What is the overnight rate in Canada?
This interest rate is also called the key policy rate or the overnight rate. It is the Canadian base rate at which banks and other financial institutions can borrow money for a period of 1 day (overnight). The Bank of Canada sets a target for the level of the rate: the target for the overnight rate. If the Canadian central bank has set a new target for the level of the key interest rate this will usually also lead to a change in the interest rates for loans, mortgages and savings. It can also have an effect on the exchange rate of the Canadian dollar.
What is the BOC?
The Bank of Canada (BOC) is the Canadian central bank. The BOC’s most important objective is to maintain the value of Canadian money by keeping inflation low and stable (between 1 and 3%). For an overview of current inflation in Canada, click here. The bank also strives for a stable, secure currency, financial stability and the most efficient management of public funds and public borrowings possible.
When will the Bank of Canada raise the rate?
The Bank of Canada expects a rate hike as early as the second half of 2022. While CPI inflation has reached the top of the Bank of Canada's inflation-control range, they believe that the inflation will be transitory and that "extraordinary monetary policy support" is still necessary for Canada's economic recovery.
What is the inflation target for the Bank of Canada?
Introduced in 1991, the inflation-control target sets a range of 1% – 3% as the ideal range for annual inflation, with the midpoint of 2% being the common target rate. This range is reviewed regularly with the latest review being in October 2016.
How does monetary policy affect fixed mortgage rates?
Changes in the key policy rate and monetary policy can also affect fixed mortgage rates. Fixed mortgage rates usually follow the yields of Government of Canada 5-Year bonds. A shift in monetary policy can lead to changes in the bond yields, which will then lead to changes in fixed mortgage rates.
When will variable mortgage rates be stable?
We expect variable mortgage rates to remain stable until 2021 with a rate hike in the second half of 2022. Variable mortgage rates are based on the Prime rate, which follows to the Bank of Canada target overnight rate. Our projections show that the BoC is unlikely to deviate from its current overnight rate of 0.25%. Consequently, Prime rates and variable mortgage rates are likely to also remain stable.
What is the overnight rate?
Everyday, the banks come together and make offers to borrow and lend money. The rate that they settle on is called the "overnight rate" because it's the interest rate for borrowing cash "overnight". The Bank of Canada is the "mom" of the group. The Bank of Canada has a "target overnight rate" and tries to keep the overnight rate close to the target. If the rate gets too low because there's too much money, the banks can lend their money to the Bank of Canada instead. If the rate gets too high because there's a shortage of money, the Bank of Canada acts as a "lender of last resort" and will lend out money.
What are the implications of negative rates?
Negative rates have significant implications for the financial sector as banks can't offload the costs of the negative rate onto their clients (imagine how popular a negative-rate savings account would be). According to a BoC paper from 2015, this can significantly compress margins for banks and other financial institutions as well as create market distortions. Due to these reasons and other effects of a negative interest rate policy, the Governor of the Bank of Canada, Tiff Macklem, has announced that he does not see negative interest rates as a viable option for the BoC.
How much debt will Canada have in 2020?
The Federal government alone is expected to borrow $713 billion CAD in 2020, more than double the amount raised in 2019. The 2021 Federal Budget shows a commitment to further deficit spending with a deficit of $154.7 billion this year. While much of Canada's debt is already owned by the Bank of Canada, it would be counter-productive to the aims of Canada's government to increase rates and tighten monetary policy while the government is deficit-spending to boost the economy.