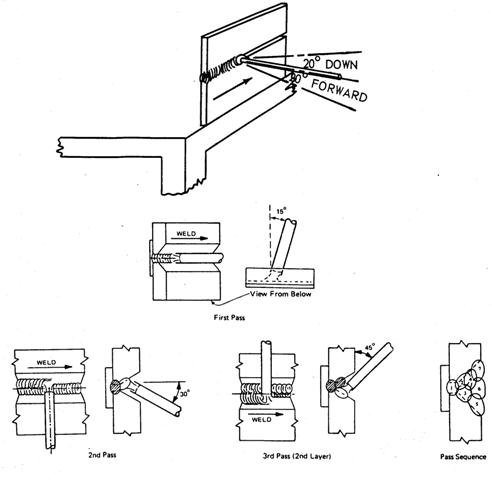
How to start an arc welder?
- Strike the arc. This is the process of creating an electric arc between the electrode and the workpiece. ...
- Move the arc to create a bead. The bead is the metal from the melting electrode flowing together with molten metal from the base metal to fill the space between ...
- Shape the weld bead. ...
- Chip and brush the weld between passes. ...
What is the best arc welder?
Top 5 Arc Welders Reviewed
- Amico Power. Amico’s Power is the first machine in our review, and it shows quite a lot of promise regarding performance and versatility.
- Amico Tig Welder. Dimensions: 16.6 x 7.5 x 11.8″ Weight: 15.5lbs ... ...
- Forney Easy Weld. Dimensions: 24.6 x 12.6 x 18.5″ Weight: 32.6lbs ... ...
- Hitbox. Dimensions: 12.4 x 5.3 x 10.5″ Weight: 9.5lbs ... ...
- Lotos Combo Welder. ...
Which is better, arc welding or MIG welding?
MIG welds are known to be more pleasing to the eye and would not require a lot of touch-ups. This will be highly different from arc welds that will require a lot of cleanups before they can look presentable. Arc welding will usually have a lot more sparks and debris which can make the welds not very appealing.
What are the advantages of arc welding?
Arc Welding Advantages and Disadvantages. Advantages of Arc Welding: 1. Good Impact Strength. The weld connection generated during the arc welding technique has a high impact strength. It can withstand heavier loads. Many businesses choose arc welding over other procedures due to its high impact strength. 2. High Welding Performance

What is basic welding?
Welding is a fabrication process whereby two or more parts are fused together by means of heat, pressure or both forming a join as the parts cool. Welding is usually used on metals and thermoplastics but can also be used on wood.
What are the basic arc welding circuit?
Basic Arc Welding Circuit An alternating current (AC) or direct current (DC) power source, fitted with whatever controls may be needed, is connected by a work cable to the work-piece and by a “hot” cable to an electrode holder of some type, which makes an electrical contact with the welding electrode.
What is arc welding explain?
Arc welding is a process where an electrode welding rod is attached to the welding torch which connects to a portable welding machine. When the power source is turned on, the electrode becomes live. By touching the rod to the base metal, the current will move through the rod and complete the electrical circuit.
What are the 4 types of arc welding?
The four main types of welding are: Gas Metal Arc Welding (GMAW/MIG), Gas Tungsten Arc Welding (GTAW/TIG), Shielded Metal Arc Welding (SMAW), and Flux Cored Arc Welding (FCAW).
What are the 5 basic weld types?
There are five basic welding joint types commonly used in the industry, according to the AWS:Butt joint welding.Tee joint welding.Corner joint welding.Lap joint welding.Edge joint welding.
Why is it called arc welding?
Arc welding is a type of welding process using an electric arc to create heat to melt and join metals. A power supply creates an electric arc between a consumable or non-consumable electrode and the base material using either direct (DC) or alternating (AC) currents.
What are the types of arc?
Minor Arcs (two capital letters) Arcs that have a degree measure of less than 180 degrees.Major Arc (three capital letters) Arcs that have a degree measure greater than 180 degrees.Semi Circle (three capital letters) Arcs that have a degree measure equal to 180 degrees.
What are 3 advantages of arc welding?
Advantages of arc weldingAffordable cost for equipment and doesn't need much due to the lack of gas.Portability; very easy to transport.Versatile and works well on metal that's dirty.Shielding gas not necessary, meaning the process can be completed in all types of weather (including wind or rain)
What is the process of arc?
In the electric arc process, two electrically conductive wires are continuously brought into contact with each other at a predetermined angle. An arc is struck between the two wires when a voltage is applied.
What is 5S in welding?
5S is a system to reduction waste, productivity optimization and quality through maintaining and organizing work-place [3]. The 5S concept consists of Sort (seiri), Set in Order (seiton), Shine (seiso), Standardise (seiketsu) and Sustain (shitsuke).
What are the 3 basic elements of welding?
Every welding process has the following three basic elements: Heat source. Filler metal. Shielding gas or flux.
Which arc welding is best?
Gas Tungsten Arc Welding (TIG) is probably the highest quality and most expensive of the arc welding processes. It is generally performed manually; however, there are some automatic applications.
What type of circuit is welding?
A typical arc welder requires a 220 volt circuit and does not require a dedicated neutral wire but does require a ground wire as always.
What are the 3 types of electric arc welding?
The four main types of arc welding are Gas Metal Arc Welding (GMAW), Gas Tungsten Arc Welding (GTAW), Shielded Metal Arc Welding (SMAW), and Flux-Coated Arc Welding (FCAW).
What are the 3 basic types of welding operations?
Three of the most common are Arc, MIG (Metal, Inert Gas) or GMAW (Gas, Metal Arc Welding), and TIG (Tungsten Inert Gas) welding. In order to know which process is best for the particular job you're working on, here's what you should know about each of them.
What is an arc in a circuit?
Electrical arcing is when electrical current jumps a gap in a circuit or between two electrodes (conductors of electricity). You may be familiar with this activity from the classic science experiment – Jacob's Ladder.
How does it work?
Arc welding is a fusion welding process used to join metals. An electric arc from an AC or DC power supply creates an intense heat of around 6500°F...
What are the different types of arc welding?
Arc welding can be categorised into two different types; consumable and non-consumable electrode methods. Consumable electrode methods include Meta...
Where is it used?
This common joining process is used across all industry sectors, including automotive, aerospace, oil and gas, power, and construction.
How Does it Work?
Arc welding is a fusion welding process used to join metals. An electric arc from an AC or DC power supply creates an intense heat of around 6500°F which melts the metal at the join between two work pieces.
What are the Different Types of Arc Welding?
This process can be categorised into two different types; consumable and non-consumable electrode methods.
What is tungsten welding?
Tungsten Inert Gas Welding (TIG) Also known as Gas Tungsten Arc Welding (GTAW) , uses a non-consumable tungsten electrode to create the arc and an inert shielding gas to protect the weld and molten pool against atmospheric contamination.
What is fusible flux?
A frequently-used process with a continuously-fed consumable electrode and a blanket of fusible flux which becomes conductive when molten , providing a current path between the part and the electrode. The flux also helps prevent spatter and sparks while suppressing fumes and ultraviolet radiation.
What is FCAW in electrical?
Created as an alternative to SMAW, FCAW uses a continuously fed consumable flux cored electrode and a constant voltage power supply, which provides a constant arc length. This process either uses a shielding gas or just the gas created by the flux to provide protection from contamination.
How does flux melt?
The flux melts as the wire consumable is fed into the molten pool, which creates a molten slag on top of the pool. Heat for melting the wire and plate edges is generated through the molten slag's resistance to the passage of the electric current.
What is arc welding?
Arc welding is a type of welding process using an electric arc to create heat to melt and join metals. A power supply creates an electric arc between a consumable or non-consumable electrode and the base material using either direct (DC) or alternating (AC) currents. This article is one of a series of TWI frequently asked questions (FAQs).
What is arc welding?
Arc Welding Basics: Arc welding is a unique category under MIG welding which involves the use of an electric arc to melt and join two pieces of metals. A good power supply is used to create this arc between the consumable/ non-consumable electrode and the base material. It can be created using both ‘alternating current’ (AC) as well as ‘direct current’ (DC).
What is a GMAW wire?
Flux-cored arc welding (FCAW) is a modified version of the GMAW technique. FCAW wire is actually a fine metal tube that is filled with powdered flux materials.
How many amps do you need for arc welding?
Higher the power you can afford to supply, the better results you can get in your weld. Most arc welding applications need a maximum of 225 Amps in general. A welding machine with lower amperage supplied can be used to weld thinner metals of around 1 inch of thickness also by using several passes to perfect the required bead size.
What happens when you weld for long hours?
Welding for long hours causes the welder to be exposed to bright sparks and light causing a condition in the eye known as ‘arc eye’. The ‘ultra-violet’ (UV) light coming out of it causes inflammation and sometimes can burn the retina of the eye directly.
Why is welding so slow?
Weld is slower compared to other processes due to the inexpensive and simple equipment available and the welder requires minimal training to proceed.
How much does a gas arc welding machine cost?
Arc welding machines are available for less than $200.
Why do we use protective welding clothing?
The risk of burns or skin rashes could be due to the exposure to heat and sparks for a large amount of time welding. Wearing protective welding clothing including heavy leather work shoes, protective full-sleeve jackets can be some of the best ways to avoid any sort of exposure to these flames, sparks, and fire. Moreover, we use a lot of shielding gas and compressed gases which themselves have high risks of fire and explosion.
How does a spray arc work?
Spray Arc - the drop is ejected from the molten metal at the electrode tip by an electric pinch propelling it to the molten pool (great for overhead welding) If an electrode is consumable, the tip melts under the heat of the arc and molten droplets are detached and transported to the work through the arc column.
How does a welding arc work?
In welding, the arc not only provides the heat needed to melt the electrode and the base metal, but under certain conditions must also supply the means to transport the molten metal from the tip of the electrode to the work. Several mechanisms for metal transfer exist. Two (of many) examples include: 1 Surface Tension Transfer® - a drop of molten metal touches the molten metal pool and is drawn into it by surface tension 2 Spray Arc - the drop is ejected from the molten metal at the electrode tip by an electric pinch propelling it to the molten pool (great for overhead welding)
How is spray arc ejected?
Spray Arc - the drop is ejected from the molten metal at the electrode tip by an electric pinch propelling it to the molten pool (great for overhead welding)
What is the purpose of an arc welding?
In welding, the arc not only provides the heat needed to melt the electrode and the base metal, but under certain conditions must also supply the means to transport the molten metal from the tip of the electrode to the work. Several mechanisms for metal transfer exist. Two (of many) examples include:
What is arc welding?
Arc welding is one of several fusion processes for joining metals. By applying intense heat, metal at the joint between two parts is melted and caused to intermix - directly, or more commonly, with an intermediate molten filler metal. Upon cooling and solidification, a metallurgical bond is created. Since the joining is an intermixture of metals, the final weldment potentially has the same strength properties as the metal of the parts. This is in sharp contrast to non-fusion processes of joining (i.e. soldering, brazing etc.) in which the mechanical and physical properties of the base materials cannot be duplicated at the joint.
Why does an arc need to be ignited?
Since there must be an ionized path to conduct electricity across a gap, the mere switching on of the welding current with an electrically cold electrode posed over it will not start the arc. The arc must be ignited. This is caused by either supplying an initial voltage high enough to cause a discharge or by touching the electrode to the work and then withdrawing it as the contact area becomes heated.
How does an AC power source work?
An AC or DC power source, fitted with whatever controls may be needed, is connected by a work cable to the workpiece and by a "hot" cable to an electrode holder of some type, which makes an electrical contact with the welding electrode.
What is Arc welding?
Let’s try to understand the arc welding basics along with the definition.
What is flux core welding?
It is a welding process that utilizes a continuously fed consumable flux cored electrode with a constant power supply for providing a consistent Arc length.
What is shielded metal arc welding?
Shielded metal arc welding is a welding activity in which the Arc is placed between the electrode flux coated metal rod and workpiece to form a weld pool.
What is consumable electrode welding?
In this type of electric arc welding, a consumable electrode is used to produce the joint between two materials at a time as the electrode is consumable, therefore each time , you have to use a new one to create the electric Arc.
What is tungsten inert gas welding?
Tungsten inert gas welding is a welding process that utilises a non-consumable tungsten electrode to produce an arc.
Why is arc welding so reliable?
Arc welding is very reliable for us because of its efficient, affordable and portability factor.
Which electrode should be continuously fed?
The consumable electrode should be continuously fed, and the fusible flux produces current conduction.
What temperature does an arc produce?
The electrode tip touches the workpiece and is withdrawn yet still within close contact. The arc produces a temperature of about 6500-degree centigrade at the tip. This heat melts both the base metal and the electrode producing a pool of molten metal sometimes called a creator.
How does an arc welding circuit work?
Arc welding working or circuit diagram: An AC or DC power sources, fitted with whatever controls may be needed, is connected by work cable to the workpiece and by an electrode cable to electrode holder of some type, which makes electrical contact with the welding electrode. An arc is created across the gap when the energized circuit and.
What is arc welding?
Arc welding is a welding process that is used to join metal to metal by using electricity to create enough heat to melt metal, and the melted metals when the cool result in a binding of the metals.
What are the problems with arc welding?
A problem that arises in arc welding is the contamination of the metal with elements in the atmosphere (O, H, N, etc). There can also be a problem with the surface that is not clean. Gas shields: An inert gas is blown into the weld zone to drive away other atmospheric gases.
How much gap do you need to maintain when you touch a workpiece?
The workpiece is mounted there than before the electrode touches the workpiece we have to maintain a 2 to 3 mm gap because when you directly touch it, It might get sticks and do vibrates.
How can arc be controlled?
Arc is invisible, it can be controlled only by measuring arc voltage and current.
What happens when the creator solidifies behind the electrode?
The creator solidifies behind the electrode as it is moved along the joint. This result is a fusion bond.
What is a wire feeder?
A small built in wire feeder guides wire through the gun to the piece. For MIG welding or Flux-Cored welding, semiautomatic wire feeders are connected to a welding power source and are used to feed a spool of wire through the welding gun. Wire is only fed when the trigger is depressed. These units are portable.
What is a stick of wire?
A stick of electrode or cored wire that is designed not to fuse two pieces of metal together, but to add a layer of surface metal to a work-piece in order to reduce wear. An example of this is the shovel on an excavator. Heating the coated stick electrode and the base metal with an arc creates fusion of metals.
What is a welding consumable?
Welding Consumables. A short stick of welding filler metal consisting of a core of bare electrode covered by chemical or metallic materials that provide shielding of the welding arc against the surrounding air. It also completes the electrical circuit, thereby creating the arc. (Also known as SMAW, or Stick Metal Arc Welding.)
What is gas used for?
Gas is used for shielding. (Process is also known as GTAW, or Gas Tungsten Arc Welding.) Constant Voltage and Constant Current welders are used for MIG welding and are a semi-automated process when used in conjunction with a wire feeder. Wire is fed through a gun to the weld-joint as long as the trigger is depressed.
What is the difference between tungsten and gas welding?
A less intense current produces a finer, more aesthetically pleasing weld appearance. A tungsten electrode (non-consumable) is used to carry the arc to the workpiece. Filler metals are sometimes supplied with a separate electrode. Gas is used for shielding.
What is arc welding?
Arc welding is a method of joining two pieces of metal into one solid piece. To do this, the heat of an electric arc is concentrated on the edges of two pieces of metal to be joined. The metal melts, while the edges are still molten, additional melted metal is added. This molten mass then cools and solidifies into one solid piece.
Is cored wire a solid?
Cored wire is similar to MIG wire in that it is spooled filler metal for continuous welding. However, Cored wire is not solid, but contains flux internally (chemical & metallic materials) that provides shielding. Gas is often not required for shielding. (Process is also known as FCAW, or Flux-Cored Arc Welding.)

Description
Choosing The Right Arc Welder
- Using a welding machine with either AC/DC output is recommended for any general-purpose welding. DC output method produces less sticking of the weld puddle with the electrode giving us a better overall experience. We also obtain better vertical and overhead welding with restricted amounts of spatter production and distortion. Higher the power you can afford to supply, the bet…
Consumable Electrode Methods
- People who are whole-heartedly indulged in this profession of welding will be aware of the fact the most commonly referred to and used welding processes is shielded metal arc welding (SMAW) also known as ‘manual metal arc welding’ (MMAW). Electric current is passed between the base metal and the consumable electric rod which produces an arc. Generally, the electric rod is mad…
Safety Measures
- Without taking proper precautions, using welding equipment is a waste of time and resources and moreover a hazard to one’s life. Using the latest technological advancement in the equipment used along with proper measures before welding can be a great way to protect ourselves from any hazards. Heat, fire, and explosion hazard The risk of burns or skin rashes could be due to th…
Welding and Cancer
- Welding in general produces a large number of hazardous contaminants via the welding fumes and ultraviolet(UV) radiation produced. These toxic substances come under Group 1 carcinogens which cause cancer in human cells.