
Behaviorism in the Education Theory
- Introduction. In education field, behaviorism is also a philosophy of mind with certain assumptions about human nature as well as about the essential workings of the mind.
- Theory of Behaviorism. ...
- S-R Learning Thesis. ...
- Learning Process and Behaviorism. ...
- Conclusion. ...
- Works Cited. ...
What is behaviourism and how to use it in the classroom?
Behaviorism as a Philosophy of Education Behaviorism is a branch of psychology that, when applied to a classroom setting, focuses on conditioning student behavior with various types of behavior reinforcements and consequences called operant conditioning.... It has increasingly become part of the educational process.
How does education use behaviorism?
Behaviorism as an educational learning theory led to the development of several aspects of instruction and learning production, some of which we still use in classrooms today, including direct instruction, lecture, behavioral objective as classroom management, behavioral reward system, positive reinforcement, and individualized instruction, among other notions.
How is Behaviorism used in the classroom?
How to Use Behaviorism in a Classroom
- Incorporate Behaviorism into Course Design. The Office for Teaching and Learning and Wayne State University suggest that using weighted grades for homework assignments, exams and class participation is an effective ...
- Implement a Classroom Reward System. ...
- Team Up With Other Teachers for Support. ...
- Apply Behaviorism to Classroom Teaching and Discipline. ...
What is about the behaviorism theory of learning?
The Behaviorist Method Behaviorism, also known as behavioral psychology, is a learning theory that holds that all behaviors are learnt by contact with the environment, which is referred to as conditioning. As a result, behavior is just a reaction to external stimuli.
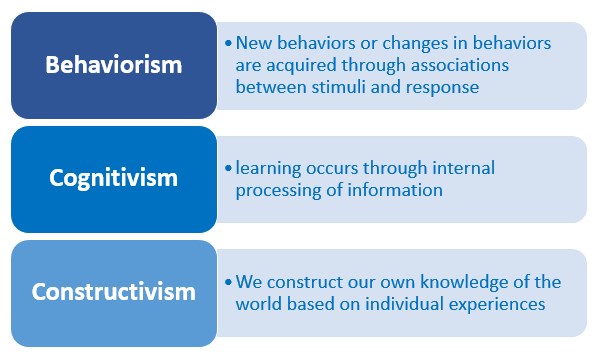
How do teachers use behaviorism?
You can find countless ways to apply behaviorism theory in the classroom to elicit and maintain desired student behavior. Examples of behavior modification techniques include praise, reward systems, continual feedback, positive reinforcement and non-punitive discipline.
What is behaviorism example?
An example of behaviorism is when teachers reward their class or certain students with a party or special treat at the end of the week for good behavior throughout the week. The same concept is used with punishments. The teacher can take away certain privileges if the student misbehaves.
How is behaviorism used in the classroom?
Behaviourism in the modern classroom Rewarding students for working well with commendations or praise points (even with vocal praise) is a behaviourist approach. This conditions students to behave or to strive for better work using the same operant conditioning techniques championed by Skinner.
What is Behaviourism explain?
Behaviorism is a theory of learning based on the idea that all behaviors are acquired through conditioning, and conditioning occurs through interaction with the environment. Behaviorists believe that our actions are shaped by environmental stimuli. 1.
How does behaviorism apply to every day life?
Behaviorism is a holistic theory of development that can be seen everywhere in our daily lives. It focuses on the concept that the environmental experiences can shape us and create the person that we are today. Pavlov, Watson, and Skinner all focused on behaviorism and its effects.
How is behaviorism used today?
Behaviorist principles are sometimes used today to treat mental health challenges, such as phobias or PTSD; exposure therapy, for example, aims to weaken conditioned responses to certain feared stimuli. Applied behavior analysis (ABA), a therapy used to treat autism, is based on behaviorist principles.
How does Behaviourism explain human Behaviour?
Behaviourists explain behaviour in terms of (1) the stimuli that elicit it and (2) the events that caused the person to learn to respond to the stimulus that way. Behaviourists use two processes to explain how people learn: classical conditioning and operant conditioning.
What are the three types of behaviorism?
There are three types of behaviorism:Methodological= behavior should be studied without connection to mental states (just behavior)Psychological= Human and animal behavior is explained based on external, physical stimuli. ... Analytical/Logical=Certain behaviors will arise from particular mental states and beliefs.
What are the benefits of behaviorism?
One of the major benefits of behaviorism is that it allowed researchers to investigate observable behavior in a scientific and systematic manner. However, many thinkers believed it fell short by neglecting some important influences on behavior.
Who is the father of behaviorism?
Behaviorism was formally established with the 1913 publication of John B. Watson 's classic paper, "Psychology as the Behaviorist Views It." 3 It is best summed up by the following quote from Watson, who is often considered the "father" of behaviorism: "Give me a dozen healthy infants, well-formed, and my own specified world to bring them up in ...
What is the one dimensional approach to understanding human behavior?
Many critics argue that behaviorism is a one-dimensional approach to understanding human behavior. Critics of behaviorism suggest that behavioral theories do not account for free will and internal influences such as moods, thoughts, and feelings. 9
What is behavioral psychology?
Strengths and Weaknesses. Influencers and Impact. Behaviorism, also known as behavioral psychology, is a theory of learning based on the idea that all behaviors are acquired through conditioning. Conditioning occurs through interaction with the environment.
What are the therapeutic techniques used in behavioral therapy?
Effective therapeutic techniques such as intensive behavioral intervention, behavior analysis, token economies, and discrete trial training are all rooted in behaviorism. These approaches are often very useful in changing maladaptive or harmful behaviors in both children and adults. 8
How did Freud think behaviorism failed?
Freud, for example, felt that behaviorism failed by not accounting for the unconscious mind's thoughts, feelings, and desires that influence people's actions. Other thinkers, such as Carl Rogers and the other humanistic psychologists, believed that behaviorism was too rigid and limited, failing to take into consideration personal agency.
When did behavioral psychology become popular?
From about 1920 through the mid-1950s, behaviorism grew to become the dominant school of thought in psychology. Some suggest that the popularity of behavioral psychology grew out of the desire to establish psychology as an objective and measurable science.
How do behaviorists teach?
Behaviorist teaching methods tend to rely on so-called “skill and drill” exercises to provide the consistent repetition necessary for effective reinforcement of response patterns. Other methods include question (stimulus) and answer (response) frameworks in which questions are of gradually increasing difficulty; guided practice; and regular reviews of material. Behaviorist methods also typically rely heavily on the use of positive reinforcements such as verbal praise, good grades, and prizes. Behaviorists assess the degree of learning using methods that measure observable behavior such as exam performance. Behaviorist teaching methods have proven most successful in areas where there is a “correct” response or easily memorized material. For example, while behaviorist methods have proven to be successful in teaching structured material such as facts and formulae, scientific concepts, and foreign language vocabulary, their efficacy in teaching comprehension, composition, and analytical abilities is questionable.
What is the method of behaviorism?
Their methodology was primarily introspective, relying heavily on first-person reports of sensations and the constituents of immediate experiences. Behaviorists such as J. B. Watson and B. F. Skinner rejected introspectionist methods as being subjective and unquantifiable. Instead, they focused on objectively observable, quantifiable events and behavior. They argued that since it is not possible to observe objectively or to quantify what occurs in the mind, scientific theories should take into account only observable indicators such as stimulus-response sequences. According to Skinner (1976, 23), “The mentalistic problem can be avoided by going directly to the prior physical causes while bypassing intermediate feelings or states of mind. The quickest way to do this is to … consider only those facts which can be objectively observed in the behavior of one person in its relation to his [or her] prior environmental history.” Radical behaviorists such as Skinner also made the ontological claim that facts about mental states are reducible to facts about behavioral dispositions.
How do behaviorists assess learning?
Behaviorists assess the degree of learning using methods that measure observable behavior such as exam performance. Behaviorist teaching methods have proven most successful in areas where there is a “correct” response or easily memorized material.
How do behaviorists explain motivation?
Just as receiving food pellets each time it pecks at a button teaches a pigeon to peck the button, pleasant experiences cause human learners to make the desired connections between specific stimuli and the appropriate responses. For example, a student who receives verbal praise and good grades for correct answers (positive reinforcement) is likely to learn those answers effectively; one who receives little or no positive feedback for the same answers (negative reinforcement) is less likely to learn them as effectively. Likewise, human learners tend to avoid responses that are associated with punishment or unpleasant consequences such as poor grades or adverse feedback.
What is the behaviorist argument that someone knows Shakespeare?
So, for instance, the behaviorist would argue that to say that that someone knows Shakespeare is to say that they have a certain behavioral repertoire with respect to Shakespeare (152).
What is knowledge in behavior?
Behaviorists such as Watson and Skinner construe knowledge as a repertoire of behaviors. Skinner argues that it is not the case that we use knowledge to guide our action; rather, “knowledge is action, or at least rules for action” (152). It is a set of passive, largely mechanical responses to environmental stimuli.
Which method of teaching has proven most successful in areas where there is a “correct” response or easily memorized?
Behaviorist teaching methods have proven most successful in areas where there is a “correct” response or easily memorized material.
How can behaviorism be applied to the classroom?
The principles of psychological behaviorism can be applied to the classroom to guide student behavior and learning. Explore an overview of how behaviorism applies to teaching, including practical examples of reinforcement, punishment, and extinction. Updated: 09/30/2021
What is behaviorism psychology?
Lesson Summary. Behaviorism is the psychological philosophy that people's behaviors are driven by rewards and punishments. There are essentially four types of rewards and punishments for behaviors: Positive reinforcement, which involves giving someone something they want.
What does behavioral theory believe about behavior?
Remember that behaviorists believe that people learn behaviors through rewards and punishments, so perhaps Mr. Greene can use some of the behavioral philosophy to help him with Cynthia. There are two major categories of responses to a person's behavior, according to behavioral theory.
What does extinction do in behaviorism?
In behaviorism, extinction decreases the chances of a response to something by withdrawing reinforcement of the behavior. In other words, if Mr. Greene stops rewarding Cynthia's behavior, that behavior will become extinct. Think of extinction kind of like a reset button.
What did behavioralists study?
Behaviorists were interested only in observable behaviors, and they did all sorts of studies to see how different rewards and punishments affected people's behaviors. Let's take a look at how Mr. Greene, and teachers like him, can apply behavioral principles to their classrooms.
What is a negative punishment?
He could also take away something that the student does want, which is called a negative punishment. For example, he can ban Cynthia from going on a school field trip because she doesn't obey the rules. He's punishing her bad behavior by taking away something she wants (the field trip).
What is Cynthia's behavior?
Behaviorism. Cynthia is a problem student. She doesn't do her homework, and when she does, it's only half-finished. She acts out in class, refusing to follow the rules and cracking jokes at the teacher's expense. Her teacher, Mr. Greene, is at his wit's end.
What is behaviorism in learning?
This learning theory states that behaviors are learned from the environment, and says that innate or inherited factors have very little influence on behavior. A common example of behaviorism is positive reinforcement. A student gets a small treat if they get 100% on their spelling test.
Why do teachers use behaviorism?
Teachers use behaviorism to show students how they should react and respond to certain stimuli. This needs to be done in a repetitive way, to regularly remind students what behavior a teacher is looking for. Positive reinforcement is key in the behavioral learning theory. Without positive reinforcement, students will quickly abandon their responses ...
What is constructivism?
Learn about constructivism and how this learning theory impacts education.
Why is positive reinforcement important in behavioral learning?
Teachers often work to strike the right balance of repeating the situation and having the positive reinforcement come to show students why they should continue that behavior. Motivation plays an important role in behavioral learning.
What is stimulus response?
A stimulus is given, for example a bell rings, and the response is what happens next, a dog salivates or a pellet of food is given. Behavioral learning theory argues that even complex actions can be broken down into the stimulus-response.
How can teachers implement behavioral learning strategies in their classroom?
Teachers can implement behavioral learning strategy techniques in their classroom in many ways, including: Drills. Teachers may practice skills using drill patterns to help students see the repetition and reinforcement that behavioral learning theory uses. Question and answer.
Why is it important to learn classroom management?
Every teacher knows that they will usually have a student in class who is difficult to manage and work with. Their behavior is usually hard to control and it can be extra work to get them to pay attention and stop distracting others. If you’re studying to become a teacher, your courses will help you learn classroom management techniques that will prepare you for difficult students. Additionally, it’s extremely valuable to learn about learning theories and recognize that there are different methods and thoughts about how people learn.
Why is behaviorism important?
One reason behaviorism rose to prominence in the 1920s is that it implies human behavior is predictable. People often expect, or hope, that others will behave in a predictable fashion, even if that isn’t always the case. On a social level, behavioral predictability builds confidenceand trust—and behaviors and attitudes that deviate too far from the established norm or that are erratic and unpredictable are often considered unacceptable. Thus, the idea that one can predict how another person will behave or elicit a standard response using operant conditioning was enticing to generations of psychologists. And though behaviorism is no longer a dominant school of thought in psychology, it hasn’t been entirely discounted—many modern approaches incorporate behaviorist elements with some success.
Why is behaviorism considered a classical theory?
Because behaviorism focuses on observable behavioral outputs, classical behaviorists argue that any task or behavior can be modified with the right conditioning, regardless of individual traits and thinking patterns. That conditioning may be neutral or may include consequences, such as rewards or punishments.
What is behaviorist therapy?
Behaviorist principles are sometimes used today to treat mental health challenges, such as phobias or PTSD; exposure therapy, for example, aims to weaken conditioned responses to certain feared stimuli. Applied behavior analysis (ABA), a therapy used to treat autism, is based on behaviorist principles. Behaviorism also shows up in organizational psychology, particularly in the use of rewards and punishments to modify employee behavior.
When did behaviorism start to decline?
Behaviorism began to decline in popularity when cognitive psychology, which prioritizes the study of internal mental processes such as attentionand memory, started to gain steam in the 1960s. Psychologists of the time were frustrated by the limits of behaviorism and felt that it was unable to truly explain the complex realities of human behavior. An influential critique by linguist Noam Chomskyis credited with dismantling much of behaviorism’s influence.
What are the criticisms of behaviorism?
Among the most common criticisms of behaviorism are that it is reductionist and that it ignores the complexity of human thought and emotion, as well as the possibility of free will. Some modern applications of behaviorism—most notably applied behavior analysis—have been criticized for modifying behavior at the expense of personal agency; some have suggested that the use of behaviorist techniques to treat autism, in particular, can be harmful.
What is the term for a form of learning in which an organism modifies its behavior in response to repeated rewards or?
Operant conditioning is a form of learning in which an organism modifies its behavior in response to repeated rewards or punishments. A child who touches a hot stove, for example, will be burned; that negative consequence will likely lead them to avoid touching hot stoves in the future.
What is behavioral predictability?
On a social level, behavioral predictability builds confidenceand trust. Behaviors and attitudes that deviate too far from the established norm or that are erratic and unpredictable are often considered unacceptable. At the same time, some people appreciate breaks in predictable routines.
What is behaviorism concerned with?
Behaviorism is only concerned with observable stimulus-response behaviors, as they can be studied in a systematic and observable manner.
What is behaviorism in psychology?
Behaviorism is primarily concerned with observable behavior, as opposed to internal events like thinking. Behavior is the result of stimulus–response (i.e., all behavior, no matter how complex, can be reduced to a simple stimulus – response features).
What is the theory of learning that states all behaviors are learned through interaction with the environment through a process called conditioning?
Behaviorist Approach. Behaviorism , also known as behavioral psychology, is a theory of learning which states all behaviors are learned through interaction with the environment through a process called conditioning. Thus, behavior is simply a response to environmental stimuli.
What is the difference between behaviorism and neobehaviorism?
Historically, the most significant distinction between versions of behaviorism is that between Watson's original 'methodological behaviorism,' and forms of behaviorism later inspired by his work, known collectively as neobehaviorism (e.g., radical behaviorism).
What is learning theory?
We learn new behavior through classical or operant conditioning (collectively known as 'learning theory').
What is the role of environmental factors in influencing behavior?
All behavior is learned from the environment: Behaviorism emphasizes the role of environmental factors in influencing behavior, to the near exclusion of innate or inherited factors. This amounts essentially to a focus on learning.
What are the contributions of behaviorism?
These include insights into learning, language development, and moral and gender development, which have all been explained in terms of conditioning. The contribution of behaviorism can be seen in some of its practical applications.
How can behaviorism be used in the classroom?
While often used as tools for classroom management , behaviorist principles can be broadly applied to change behaviors. Given that our goal is to encourage the use of better study strategies, any mechanism that can change behavior is worth considering.
Who wrote the manifesto Psychology as the Behaviorist View It?
In 1911, psychologist John Watson took key elements of observation and experimental rigor, but wrote a seminal paper, Psychology as the Behaviorist View It. In this manifesto, he explained that in order for psychology to be taken seriously as a science, the focus needed to turn toward objective, observable behaviors.
How can operant conditioning be used in a classroom?
It's easy to see how operant conditioning can be used for classroom management. There are many behaviors that need to be shaped (an operant term!) in order to have an orderly classroom. There are indeed some classroom behaviors that I need to shape in order to enhance learning. For example, students could receive negative punishment for having their phones out. This might mean that they do not receive their daily attendance points. Research indicates that cell phones pull attention (1), so we can use operant conditioning to increase attention and learning.
Why is classical conditioning limited?
Classical conditioning is fairly limited when it comes to shaping behavior, primarily because an automatic response must already exist. BF Skinner (a radical behavorist, famous for his assertion that there is no such thing as free will) pioneered research on a different form of learning - operant conditioning.
What are the consequences of adding a stimulus?
Thus, our four consequences are positive and negative reinforcement and positive and negative punishment. Here are some examples:
What is the dominant field of study in psychology?
Around the turn of the 20th century, introspection was the dominant field of study in psychology. Introspection involved rigorous methodology aimed at examining the contents of consciousness. Under tightly controlled experimental conditions, subjects observed and carefully recorded their current awareness.
Can behaviorists change behavior?
While often used as tools for classroom management, behaviorist principles can be broadly applied to change behaviors. Given that our goal is to encourage the use of better study strategies, any mechanism that can change behavior is worth considering. Please note that I am not a historian. Nor am I a behaviorist.

What Is Behaviorism?
History of Behaviorism
- Behaviorism was formally established with the 1913 publication of John B. Watson's classic paper, "Psychology as the Behaviorist Views It."3It is best summed up by the following quote from Watson, who is often considered the father of behaviorism: "Give me a dozen healthy infants, well-formed, and my own specified world to bring them up in and I'll guarantee to take any one …
Classical Conditioning
- Classical conditioning is a technique frequently used in behavioral training in which a neutral stimulus is paired with a naturally occurring stimulus. Eventually, the neutral stimulus comes to evoke the same response as the naturally occurring stimulus, even without the naturally occurring stimulus presenting itself. Throughout the course of three distinct phases of classical conditionin…
Operant Conditioning
- Operant conditioning, sometimes referred to as instrumental conditioning, is a method of learning that occurs through reinforcement and punishment. Through operant conditioning, an association is made between a behavior and a consequence for that behavior. This behavioral approach says that when a desirable result follows an action, the behavior becomes more likely to happen agai…
Uses For Behaviorism
- The behaviorist perspective has a few different uses, including some related to education and mental health.
Impact of Behaviorism
- Several thinkers influenced behavioral psychology.Among these are Edward Thorndike, a pioneering psychologist who described the law of effect, and Clark Hull, who proposed the drive theory of learning.13 There are a number of therapeutic techniques rooted in behavioral psychology. Though behavioral psychology assumed more of a background position after 1950, …
Criticisms of Behaviorism
- Many critics argue that behaviorism is a one-dimensional approach to understanding human behavior. They suggest that behavioral theories do not account for free will or internal influences such as moods, thoughts, and feelings.5 Freud, for example, felt that behaviorism failed by not accounting for the unconscious mind's thoughts, feelings, and desires, which influence people's …
A Word from Verywell
- While the behavioral approach might not be the dominant force that it once was, it has still had a major impact on our understanding of human psychology. The conditioning process alone has been used to understand many different types of behaviors, ranging from how people learn to how language develops. But perhaps the greatest contributions of behavioral psychology lie in its pra…
Background
View of Knowledge
- Behaviorists such as Watson and Skinner construe knowledge as a repertoire of behaviors. Skinner argues that it is not the case that we use knowledge to guide our action; rather, “knowledge is action, or at least rules for action” (152). It is a set of passive, largely mechanical responses to environmental stimuli. So, for instance, the behaviorist would argue that to say tha…
View of Learning
- From a behaviorist perspective, the transmission of information from teacher to learner is essentially the transmission of the response appropriate to a certain stimulus. Thus, the point of education is to present the student with the appropriate repertoire of behavioral responses to specific stimuli and to reinforce those responses through an effective reinforcement schedule (16…
View of Motivation
- Behaviorists explain motivation in terms of schedules of positive and negative reinforcement. Just as receiving food pellets each time it pecks at a button teaches a pigeon to peck the button, pleasant experiences cause human learners to make the desired connections between specific stimuli and the appropriate responses. For example, a student who receives verbal praise and g…
Implications For Teaching
- Behaviorist teaching methods tend to rely on so-called “skill and drill” exercises to provide the consistent repetition necessary for effective reinforcement of response patterns. Other methods include question (stimulus) and answer (response) frameworks in which questions are of gradually increasing difficulty; guided practice; and regular reviews...