What is the function of the arachnoid mater?
The arachnoid mater makes arachnoid villi, small protrusions through the dura mater into the venous sinuses of the brain, which allow CSF to exit the subarachnoid space and enter the blood stream.
Where is the arachnoid layer attached to the meninges?
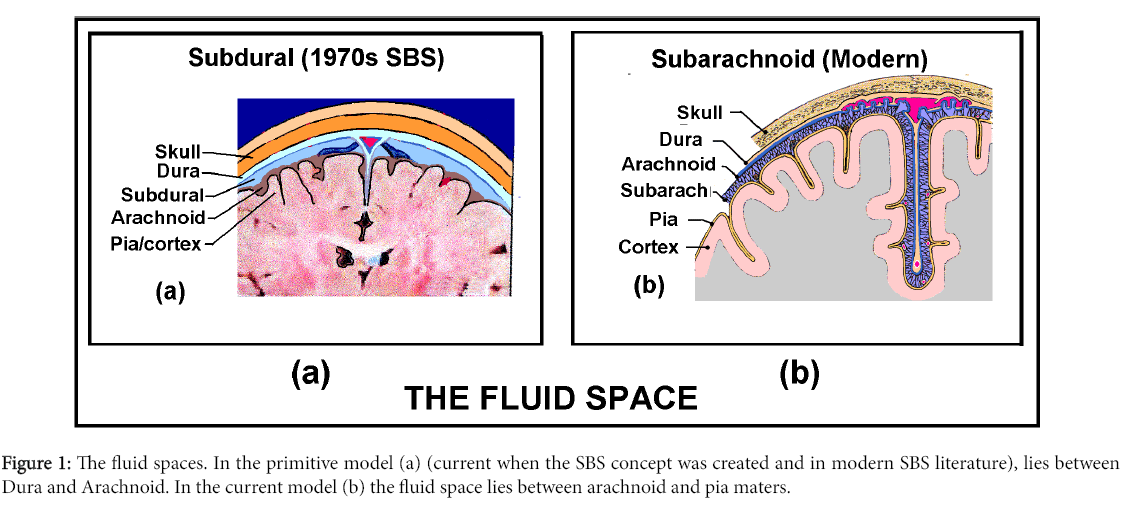
It is interposed between the two other meninges, the more superficial and much thicker dura mater and the deeper pia mater, from which it is separated by the subarachnoid space. The delicate arachnoid layer is attached to the inside of the dura and surrounds the brain and spinal cord.
Does the arachnoid line the brain?
It does not line the brain down into its sulci (folds), as does the pia mater, with the exception of the longitudinal fissure, which divides the left and right cerebral hemispheres. Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) flows under the arachnoid in the subarachnoid space, within a meshwork of trabeculae which span between the arachnoid and the pia.
What is between the dura mater and arachnoid?
Sandwiched between the dura and arachnoid maters lie some veins that connect the brain's venous system with the venous system in the dura mater. The arachnoid mater covering the brain is referred to as the "arachnoidea encephali," and the portion covering the spinal cord as the "arachnoidea spinalis.".

What is between the arachnoid mater and the pia mater?
Between your arachnoid mater and pia mater is the subarachnoid space, which contains cerebrospinal fluid that helps cushion your brain.
Which separates arachnoid mater and dura mater?
The dura mater and arachnoid mater are separated from each other by a gap called subdural space. Hence, the correct answer is option (B). Note: The bony skull, three meninges, and the cerebrospinal fluid together protect the delicate brain and spinal cord.
What structure lies between the pia and arachnoid mater in the spine?
The spinal subarachnoid space is located between the arachnoid and pia mater and is filled with CSF. Arachnoid trabeculae extend between these two layers within the subarachnoid space to give the subarachnoid space its characteristic spiderweb appearance.
How are the pia mater dura mater and arachnoid mater related?
Three layers of membranes known as meninges protect the brain and spinal cord. The delicate inner layer is the pia mater. The middle layer is the arachnoid, a web-like structure filled with fluid that cushions the brain. The tough outer layer is called the dura mater.
What is the space outside the dura mater called?
The space between the spinal dura mater and the periosteum of the vertebral column is called the epidural space. It is filled with loose connective and adipose tissues, and traversed by the anterior and posterior internal vertebral venous plexuses.
What are the two layers of the dura mater?
The dura mater is composed of two layers: the periosteal/endosteal layer and the meningeal layer. The dural venous sinuses are between these two layers. The dura folds to form septa that create the falx cerebri, tentorium cerebelli, falx cerebelli, and diaphragma sellae.
What are the spaces between the meninges?
The meninges separate three spaces called the epidural space, subarachnoid space, and the subdural space. Each of these spaces contains some important blood vessels, rupture of which can cause headache. The epidural space is a potential space located between the inner surface of the skull and the tightly adherent dura.
What are the 3 layers of meninges and where is each located which one contains the CSF fluid?
The middle layer of meninges is arachnoid, a thin layer resembling a cobweb with numerous threadlike strands attaching it to the innermost layer. The space under the arachnoid, the subarachnoid space, is filled with cerebrospinal fluid and contains blood vessels. The pia mater is the innermost layer of meninges.
Where is epidural space located?
The epidural space is the area between the dura mater (a membrane) and the vertebral wall, containing fat and small blood vessels. The space is located just outside the dural sac which surrounds the nerve roots and is filled with cerebrospinal fluid.
What are the 3 parts of the brain?
The brain can be divided into three basic units: the forebrain, the midbrain, and the hindbrain.
What connects the two hemispheres of the brain?
the corpus callosumThe two hemispheres are connected by a thick band of nerve fibres called the corpus callosum. The brain halves are able to communicate with each other via this 'bridge'.
What are the three meninges and two named spaces that surround the brain in order from superficial to deep outermost to innermost )?
From superficial to deep, they are: Dura mater. Arachnoid mater. Pia mater.
What does dura mater separate?
The dura mater of the brain is composed of two layers, an outer periosteal layer that connects to the inside of the skull, and a deep meningeal layer. In certain areas these two layers separate and the meningeal layer forms folds that extend into the brain forming physical partitions in the brain.
What part of the dura mater is between cerebrum and cerebellum?
tentorium cerebelliThe tentorium cerebelli exists between and separates the cerebellum and brainstem from the occipital lobes of the cerebrum. The falx cerebri, which separates the two hemispheres of the brain, is located in the longitudinal cerebral fissure between the hemispheres.
What is subdural space?
The subdural space is a potential intracranial space situated between the arachnoid and dura. Fluid can collect in the subdural space and in the subarachnoid space.
Which dural folds covers and separates cerebellum from the cerebrum?
The tentorium cerebelliThe tentorium cerebelli is the dural fold that separates the cerebrum from the cerebellum.
What is the causative vessel of brain trauma?
The causative vessel is usually the middle meningeal artery, tearing as a consequence of brain trauma. Subdural – venous blood collects between the dura and the arachnoid mater. It results from damage to cerebral veins as they empty into the dural venous sinuses.
What are the three meninges?
There are three layers of meninges, known as the dura mater, arachnoid mater and pia mater. These coverings have two major functions: Provide a supportive framework for the cerebral and cranial vasculature. Acting with cerebrospinal fluid to protect the CNS from mechanical damage.
What is the function of cerebrospinal fluid?
It contains cerebrospinal fluid, which acts to cushion the brain. Small projections of arachnoid mater into the dura (known as arachnoid granulations) allow CSF to re-enter the circulation via the dural venous sinuses. By TeachMeSeries Ltd (2021) Fig 3 – Coronal section of the skull, meninges and cerebrum.
What is the outermost layer of the meninges?
The dura mater is the outermost layer of the meninges and is located directly underneath the bones of the skull and vertebral column. It is thick, tough, and inextensible. The dura mater consists of two layered sheets of connective tissue: Periosteal layer – lines the inner surface of the bones of the cranium.
Where does subdural blood come from?
Subdural - venous blood collects between the dura and the arachnoid mater. It results from damage to cerebral veins as they empty into the dural venous sinuses. The arachnoid mater is the middle layer of the meninges, lying directly underneath the dura mater.
What is the role of the meninges in the CNS?
Acting with cerebrospinal fluid to protect the CNS from mechanical damage. The meninges are often involved cerebral pathology , as a common site of infection (meningitis), and intracranial bleeds. In this article, we shall look at the anatomy of the three layers, and their clinical correlations.
What is the name of the gland that covers the hypophysial fossa of the sphen?
Diaphagma sellae – covers the hypophysial fossa of the sphenoid bone. It contains a small opening for passage of the stalk of the pituitary gland.
What is the term for the protective membranes that cover the brain and spinal cord?
9591. Anatomical terms of neuroanatomy. The arachnoid mater is one of the three meninges, the protective membranes that cover the brain and spinal cord. The arachnoid mater is a derivative of the neural crest mesectoderm in the embryo.
What is the name of the arachnoid mater?
The arachnoid mater is named after the Greek word arachne ("spider"), the suffix -oid ("in the image of"), and the Latin word mater ("mother"), because of the fine spider web -like appearance of the delicate fibres of the arachnoid ( arachnoid trabeculae) which extend down through the subarachnoid space and attach to the pia mater.
Where is the arachnoid mater located?
The arachnoid mater lies under the dura mater, and arteries and veins run on top of it.
Which layer of the arachnoid mater covers the internal cerebral veins?
There are two subdivisions of arachnoid mater surrounding the subarachnoid space, the dorsal layer and the ventral layer. The dorsal layer covers internal cerebral veins and fixes them to the surrounding tela choroidea.
Where does CSF circulate?
CSF circulates in the subarachnoid space (between arachnoid and pia mater). Cerebrospinal fluid is produced by the choroid plexus (inside the ventricles of the brain, which are in direct communication with the subarachnoid space so the CSF can flow freely through the nervous system).
Is the arachnoid mater vascular?
Unlike the dura mater, which receives a rich vascular supply from numerous arteries, the arachnoid mater and the deeper pia mater are generally non-vascular.
Does CSF line the brain?
It does not line the brain down into its sulci (folds), as does the pia mater, with the exception of the longitudinal fissure, which divides the left and right cerebral hemispheres. Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) flows under the arachnoid in the subarachnoid space, within a meshwork of trabeculae which span between the arachnoid and the pia.
What is the pia mater?
As we have seen, the pia mater is the deepest layer of the meninges, which means that it is the one that is furthest from the bones of the skull and the scalp.
Why is the spinal cord prone to deformation?
The consistency and shape of the spinal cord make this anatomical structure is prone to deformation. However, the pia mater helps prevent this from happening, since it ensures that everything stays in place and, at the same time, due to its function as a mold, it also prevents it from lengthening due to gravity.
What is the function of the Pia Mater?
The pia mater is responsible for providing physical support for the veins, arteries and capillaries that pass from the external environment to irrigate the tissues of the central nervous system. Thus, its presence neurons and glial cells can survive thanks to the combination of oxygen and nutrients that reaches them through the blood.
What is the function of the meninges?
The meninges are a series of tissues that line the central nervous system, offering both protection and support for the circulatory system to deliver blood to many of the areas occupied by neurons and glial cells.
What causes pia mater arachnoid?
This health problem associated with the pia mater and arachnoid can be caused by certain bacteria, viruses and fungi, sometimes after having suffered an injury to the area.
Which part of the body is responsible for ischemic accidents?
On the other hand, both the arachnoid and the pia mater and the dura mater can be the place where a blockage of blood vessels occurs, causing ischemic accidents and aneurysms of different severity.
What are the protective layers of the nervous system?
Specifically, both our brain and spinal cord depend on the protection of a series of protective layers known as meninges.