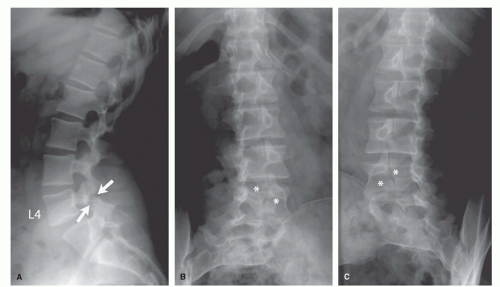
What does bilateral L5 pars defects mean?
A pars defect means that the lower and upper portion of the vertebrae (spine bones) can become separated during repeated stress and strain. This can happen on one side (unilateral) or both sides (bilateral) of the spine.
How is L5 pars defect treated?
Most patients with pars defect do not require surgery and can experience relief with medications and rest. Anti-inflammatory medications and muscle relaxers are commonly used to treat pain. Often, a lumbar corset back brace is prescribed for the acute phase of the injury.
Can bilateral pars fracture heal?
In the typical bilateral pars fracture, healing without a brace and without reduced activity has a very poor repair rate. Even with the best healing fractures (unilateral and hypertrophic), healing with a brace and three to six months of reduced activity has a success rate hovering about 50%.
How do you fix bilateral pars defect?
The defect is repaired by placing a strong titanium screw through the pars in order to bridge the two sides of the fracture back together, allowing for healing and stabilization. A bone graft may also be used for further support of the area. A pars repair will often take 3 hours in the operating room.
What happens if pars defect is left untreated?
If the fracture of the pars interarticularis is not treated, this fracture can worsen, eventually causing one of the vertebra to slide forward. This worsened condition is known as spondylolisthesis.
Is a pars defect a broken back?
A pars defect or spondylolysis is a stress fracture of the bones of the lower spine. These fractures typically occur due to overuse. They can be on one or both sides of the vertebrae. It is a common cause of low back pain in children and adolescents.
Can a chiropractor help pars defect?
The treatment for pars defect or lumbar stress fracture involves four phases. Chiropractors adopt a conservative approach to treating lumbar stress fractures. Along with massage, heat or ice therapy, chiropractors use spinal stabilisation, spinal adjustments and suggest lifestyle changes for the treatment.
Is a pars fracture painful?
Those with a pars fracture may feel pain and stiffness in the lower back that is worsened with activity and improves with rest. Hyperextension (abnormal stretching) of the lower back will usually aggravate the area as it overloads the pars fracture.
How long does a pars fracture take to heal?
Typically, the average recovery rate of Pars Fracture can be anything from between 6-12 weeks. Recovery is the most important aspect for the initial stages of a pars stress fracture.
How long does a fractured l5 take to heal?
This takes most of the pressure off the fractured vertebral body, and allows the vertebrae to heal. It also protects the vertebra and stops further collapse of the bone. Vertebral fractures usually take about three months to fully heal.
How long does a l5 stress fracture take to heal?
Restoration of normal function including return to sports Consequences of the Injury Just like any bone fracture, stress fractures in the low back need time to heal. This means resting from all sporting and impact activities until there is little, to no pain. This usually takes 4-8 weeks, but may take longer.
How common is a pars defect?
The pars interarticularis is a thin bone segment joining two vertebrae. It is the most likely area to be affected by repetitive stress. This condition is fairly common and is found in one out of every 20 people.
Can a pars defect heal on its own?
One of the good things about a pars defect is that because the area is small, it does tend to heal well when the area is given enough rest and protection. In fact, most patients with a pars defect do not need surgery and can experience a full recovery with the assistance of a few conservative measures.
Can pars defect be fixed?
Some people need surgery to stabilize the spine. A pars repair surgery fixes the pars fracture without needing to perform a spinal fusion (where surgeons fuse the two vertebrae together to form one bone). In pars repair, surgeons remove scar tissue from the fracture area.
How serious is a pars defect?
Diagnosis of Pars Stress Fracture Most people with a pars defect do not require surgery with anti-inflammatory medications, Physiotherapy and recovery the recommended means of dealing with a pars stress fracture. Typically, the average recovery rate of Pars Fracture can be anything from between 6-12 weeks.
How common is a pars defect?
The pars interarticularis is a thin bone segment joining two vertebrae. It is the most likely area to be affected by repetitive stress. This condition is fairly common and is found in one out of every 20 people.
How to tell if you have a pars defect?
Symptoms of a pars defect are pain and stiffness in the center of the low back. Lumbar extension and twisting typically increases pain. Symptoms get worse with activity and go away with rest. Some may experience pain radiating down one or both legs. This pain comes from pressure and irritation on the nerves that exit the spinal canal near the fracture. Patients can even experience numbness, tingling, and weakness in their legs.
What is the term for a crack in the back of the spinal column?
Spondylolysis, also known as a pars defect, happens when a crack forms in the bony ring on the back of the spinal column. Most commonly, this occurs in the
Can a child have a pars defect?
Although pars defect can affect people of any age, children and adolescents are most susceptible. This is because their spines are still developing, and the pars is the weakest part of the vertebra. Placing extra strain on this area of the spine during childhood increases the chance that a pars defect will occur.
What is a Pars Defect?
The ‘pars’, which is actually called the ‘pars interarticularis’, is a small length of bone that joins the facet joints of one vertebra to the facet joints of the vertebra below it. There is a pars interarticularis on each side of the vertebrae at the back of the spine.
Where do pars defects occur?
About 80% of pars defects occur on both sides of the vertebra (bilateral) however they can also happen on only one side (unilateral).
What is the difference between spondylolysis and spondylolisthesis?
Therefore, spondylolysis refers to the separation of the pars interarticularis caused by a fracture/break where as spondylolisthesis refers to the slippping of one vertebra over another. This happens if the stress fracture weakens the bone so much that it is unable to maintain its correct position and the vertebra can start to slip out of place.
What does it mean when a pars fracture is non-union?
Non-union means the fracture is old and it has not healed.
What sports cause pars defect?
Typical sports are: Gymnastics, ballet dancers, rowers, weight lifting, fast bowlers in cricket, field athletics, rugby players and tennis players.
What is the best way to diagnose pars defect?
Imaging is used usually to confirm, or exclude, a diagnosis and this is generally in the form of standing X-rays, MRI and in the case of a pars defect, a CT scan is often performed.
Can a pars defect cause buttock pain?
Buttock pain – not always present. Stiffness in the low back and tightness in the hamstring muscles. If the pars defect has resulted in a Spondylolisthesis and there is spinal nerve irritation, then you may also have pain or altered sensations in your legs.
What is a pars defect?
Pars defect: Bilateral pars defect also commonly called spondylolysis is a stress fracture near the joint of the spine. This usually occurs in the lower lumbar spine and can be painful and cause instability. This defect often occurs during the teenage years but can persist into adulthood and become symptomatic later in life.
What is lumbar pars?
Lumbar Pars Defect: The defect is a stress fracture of the posterior portion of the spine that connects the facet joints and lamina with the anterior vertebral body at the level of the pedicle. This process is also known as a spondylolysis. It occurs in 5% of the general population but can be as high as 15% in certain athletes like gymnasts and football lineman due to the lumbar hyperextension.
What is the pars defect?
A pars defect is a condition affecting the lumbar (lower) spine. It affects an area of bone called the pars interarticularis. The pars interarticularis is a small segment of bone which joins the facet joints at the back of the spine.
Why does my pars break?
The break in the bone occurs due to undue pressure on the pars interarticularis which can be linked to activities which cause repeated stress and strain. These may include (but not limited to): Gymnastics, athletics, diving due to hyperextension and/or extreme twisting.
How to treat spondylolisthesis?
Whilst pain medications and physical therapies as well as exercises to gradually return to sport can help some may not heal or could have resulting neurological problems. These cases may require surgical intervention which include a decompression (to release and free up the nerves being compressed by the slippage) and spinal fusion (to stabilise the spine whilst the bone heals).
What is the condition where the upper vertebrae slip forward relative to the lower vertebrae?
Sometimes the upper vertebra slips forward relative to the lower one – this is referred to as spondylolisthesis. Neurological deficits are relatively rare with the most common symptoms being back pain and leg pain which limits the activity level of the patients.
Can pars defects be linked to degenerative changes in the spinal discs and facet joints?
Pars defects can also be linked to degenerative changes in the spinal discs and facet joints , which occurs with age.
What are the clinical presentations of Pars defect?
Two common clinical presentations of a pars defect include the imaging of an asymptomatic adolescent or adult in whom there is the incidental discovery of a pars defect. The second common presentation is an adolescent athlete involved in a sport requiring repetitive lumbar loading in extension and rotation, presenting with acute or insidious onset low back pain that is aggravated by continued lumbar loading. Although this history is typical, there is a broad differential diagnosis that might explain these symptoms. As such, the diagnosis of a pars interarticularis defect confirmation is only with radiographic support. Depending on the time of presentation and degree of injury, most cases of pars defects respond well to conservative treatment and relative rest from sport.
What causes pars defects?
The exact cause is still unclear. Currently, the most accepted theory is repetitive mechanical stress, specifically lumbar extension and rotation, which results in overuse or stress fracture to the pars interarticularis.[2] This theory garners support from the fact that, as noted below in epidemiology, the research observed zero cases of pars defects in 500 newborns and zero cases of pars defects in 143 non-ambulatory patients, suggesting this pathology develops as a result of repetitive axial loading over time. [1][3]Additionally, this theory is supported by the progression of unilateral pars defects into bilateral pars defects with age, again suggesting repetitive axial loading over time, both leading to the initial injury as well as disease progression.[4] As discussed, although generally thought to be the result of chronic repetitive stress to the pars region, these injuries can also occur due to a single acute overload injury. [5]
What is the best imaging for pars defects?
Plain radiographs can miss some lesions, especially acute injury. Other useful imaging modalities include CT, MRI, and bone scan. A bone scan is the most sensitive modality, and best detects early pars defects. This test should be utilized when there is high clinical suspicion for pars lesion, and initial imaging studies are equivocal. After plain radiographs, the imaging modality of choice is either MRI without contrast or CT scan without contrast. CT scan is the best imaging tool for determining fracture size and extent and is the most appropriate modality for follow-up assessment of healing. CT has the downside of additional radiation exposure, which is particularly concerning in the pediatric & adolescent population. Similar to a bone scan, MRI can be useful for early detection of acute lesions by the presence of bone marrow edema on T2 weighted sequences. Additionally, MRI has the benefit of no radiation exposure. MRI is somewhat limited, though, in its ability to adequately depict the cortical integrity of incomplete fractures. [19]
What is a single leg hyperextension test?
Physical exam ought to include single-leg hyperextension, otherwise known as the Stork test. The patient should be instructed to stand on one leg while simultaneously hyperextending the low back. A positive single-leg hyperextension test is elicited by the reproduction of pain during this maneuver, typically worse when standing on the leg ipsilateral to the side of the pars defect. This maneuver is the only potentially pathognomonic physical exam finding. [5]
How many categories are there in Pars defects?
Pars defects (spondylolysis) subdivide into five categories according to the Wiltse-Newman Classification[22]:
Which region of the vertebrae is most susceptible to chronic axial loading injury?
The pars interarticularis is most susceptible to chronic axial loading injury because it is a weak point in the vertebrae, and this region bears the highest stress load in extension/flexion.[6] The weakness of the pars region is multifactorial, with a hereditary and an acquired mechanical component. Mechanical factors include the physically narrow structure of the pars interarticularis as compared to other regions of the vertebrae. Furthermore, the pars in the lower lumbar vertebra characteristically have uneven trabeculation and cortication. The inherent mechanical flaws of the pars interarticularis in combination with the high-stress loads seen in the lower lumbar region render this region prone to stress fractures.
When does the pars interarticularis ossify?
Sagi et al. demonstrated, via histomorphic analysis, the pars interarticularis begins to ossify at 12 to 13 weeks gestation by endochondral ossification. In the lower lumbar vertebra, the ossification center originates in the pars region resulting in uneven distribution of trabeculation and cortication in this region. As a result of this uneven distribution of isthmic ossification, this region is potentially more susceptible to fatigue fracture. In contrast, in the upper lumbar vertebra, the ossification center arises at the end of the pedicle, which results in more uniform trabeculation throughout the pars. [14]
