How is bilirubin released from the body?
Bilirubin is released from the destroyed red blood cells and passed on to the liver. The liver releases the bilirubin in fluid called bile. If the liver is not functioning correctly, the bilirubin will not be properly released.
What is bilirubin conjugated with in the liver?
In the liver, bilirubin is conjugated with glucuronic acid for solubilization and subsequent transport through the bile duct and elimination via the digestive tract.
How do you convert bilirubin to water soluble?
Conjugation of bilirubin to the water-soluble form involves the disruption of the hydrogen bonds, an essential process for its elimination by the liver and kidney. This is achieved by glucuronic acid conjugation of the propionic acid side chains of bilirubin.
What is the source of bilirubin?
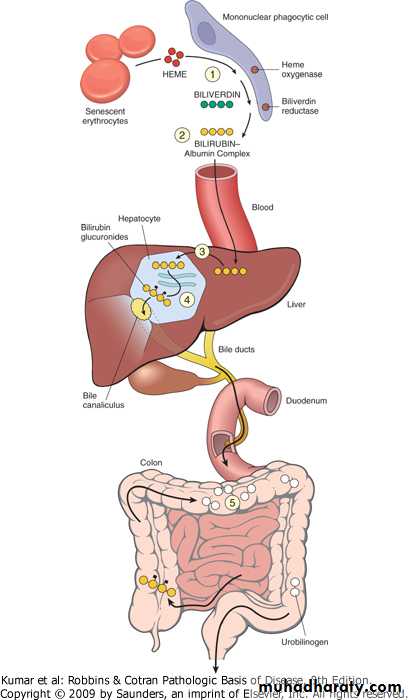
Roughly, 80% of bilirubin is made from the breakdown of hemoglobin in senescent red blood cells, and prematurely destroyed erythroid cells in the bone marrow. The remainder originates from the turnover of various heme-containing proteins found in other tissues, primarily the liver and muscles.
Where does bilirubin go after the liver?
Normally, conjugated bilirubin passes from the gallbladder or liver into the intestine. There, it is reduced by bacteria to mesobilirubinogen and urobilinogen. Some urobilinogen is reabsorbed back into the blood; the rest goes back to the liver or is excreted from the body in urine and fecal matter.
Does the liver convert bilirubin to urobilinogen?
Bilirubin and Urobilinogen Direct bilirubin is made in the hepatocyte, where bilirubin is conjugated with glucuronic acid. Conjugated bilirubin has a low molecular weight, is water soluble, and normally passes from the liver to the small intestine through the bile ducts, where it is converted to urobilinogen.
How is bilirubin removed from the liver?
Conjugated bilirubin is secreted into the bile canaliculus as part of bile and thus delivered to the small intestine. Bacteria in the intestinal lumen metabolize bilirubin to a series of other compounds which are ultimately eliminated either in feces or, after reabsortion, in urine.
What is the difference between urobilinogen and bilirubin?
Urobilinogen comes from bilirubin. Your body makes bilirubin during the normal process of breaking down old red blood cells. Your liver uses the bilirubin to make bile, a fluid that helps you digest food in your intestines. Some bile flows through ducts (small tubes) from your liver directly into your intestines.
Can unconjugated bilirubin be converted to urobilinogen?
The conjugated form is metabolized into the unconjugated form, and then into urobilinogen by bacteria in the intestine. Unconjugated bilirubin and urobilinogen are absorbed into the blood stream. The kidney filtrates conjugated bilurubin and urobilinogen into urine.
Where is urobilinogen formed?
Urobilinogen is formed by bacteria in the small intestine and in the colon. It is then reabsorbed by the small intestine and the colon and re-xcreted by the by the liver into the intestine almost entirely. A very small amount is therefore excreted into the urine: 0-4 mg/day.
What causes urobilinogen in urine?
Two situations can lead to an increase in urobilinogen levels in urine: a liver disease that disturbs the normal passage of urobilinogen through the liver and gallbladder (viral hepatitis, cirrhosis of the liver, obstruction of the gallbladder by gallstones, etc.), or a urobilinogen overload caused by the release of ...
How is urobilinogen converted to urobilin?
Some of the urobilinogen produced by the gut bacteria is reabsorbed and re-enters the enterohepatic circulation. These urobilinogens are oxidized and converted to urobilin. The urobilin is processed through the kidneys and then excreted in the urine, which causes the yellowish color in urine.
How is bilirubin formed and excreted?
Bilirubin is a waste product produced by the breakdown of red blood cells. Bilirubin is the end-product of heme metabolism; the liver is the site for bilirubin metabolism.
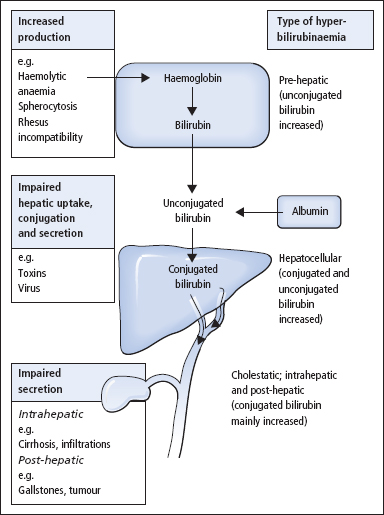
What happens to bilirubin with cholestatic or obstructive jaundice?
Cholestatic or obstructive jaundice occurs when liver cells are unable to transport bilirubin through the hepatic-bile capillary membrane because of damage in the liver. Obstructive jaundice can also occur when transport through the biliary tract is blocked because of anatomical obstructions such as gallstones or cancer.
How is bilirubin measured in the lab and what are the normal levels?
In the clinical laboratory, conjugated bilirubin is measured as direct bilirubin. If we take the total bilirubin and subtract the direct bilirubin, it provides the concentration of unconjugated bilirubin (also referred to as indirect bilirubin).
Recommended reading
Chalasani, N, Younossi, Z, Lavine, JE, et al. 2012. The diagnosis and management of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: practice guideline by the American Gastroenterological Association, American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases, and American College of Gastroenterology. Gastroenterology . 142: 1592–1609. PMID: 22656328
What is the function of bilirubin?
Bilirubin in the Body. One of the major functions of the liver is to break down old or damaged RBCs, and, in this process, bilirubin is produced. In turn, this substance is combined with others to make up bile, an essential fluid for digestion.
What is bilirubin in blood test?
Bilirubin is a brown and yellow fluid that’s a byproduct of the essential process of the breakdown of red blood cells (RBCs). This substance is a major component of bile, an important digestive fluid that’s cleaned from the blood by the liver. 1 .
What does it mean when your bilirubin is elevated?
Elevated Bilirubin Levels. Since the presence of excessive bilirubin in the bloodstream—a condition called hyperbilirubinemia —can mean significant health problems, it’s important to know the signs of this condition.
What happens if your liver is damaged?
If the liver is damaged, bilirubin may leak into the bloodstream, which can lead to jaundice, characterized by a yellowing of the skin and eyes , among other symptoms. As such, the bilirubin test, which measures these levels, helps doctors screen for diseases affecting the liver. Shidlovski / Getty Images.
Why is bilirubin measured?
Both forms of bilirubin—as well as total levels—are measured to help determine health status. Generally speaking, higher levels of this substance in the body are evidence of problems with liver disease (such as hepatitis), blood disorders, as well as blockages of bile ducts (the tubes that connect the liver to the small intestines). 2
What are the two important measures of bilirubin?
From the sample, practitioners focus on two important measures—the amount of direct bilirubin in the blood as well as overall (total) level in the blood. Based on what they see, they determine whether levels are normal or abnormal.
How many forms of bilirubin are there in the blood?
There are two forms of bilirubin observed in the bloodstream. Here’s a quick breakdown of each type: 2
What causes bilirubin to build up in the liver?
Liver dysfunction. Any condition that affects the function of your liver can cause bilirubin to build up in your blood. This is a result of your liver losing its ability to remove and process bilirubin from your bloodstream. Several things can affect the function of your liver, including: cirrhosis. liver cancer.
What is bilirubin?
Bilirubin is a yellowish substance in your blood. It forms after red blood cells break down, and it travels through your liver, gallbladder, and digestive tract before being excreted.
What causes high bilirubin?
Having high bilirubin can be a sign of several conditions. Your doctor will take your symptoms, as well as any other test results, into account to help narrow down a diagnosis.
What happens if bile ducts are blocked?
If these ducts become inflamed or blocked, bile can’t be properly drained. This can lead to an increased level of bilirubin.
What is the duct that connects the liver to the gallbladder?
Your bile ducts connect your liver to your gallbladder the opening of your small intestine, called the duodenum. They help to move bile, which contains bilirubin, from your liver and gallbladder into your intestines.
What is the cause of gallstones?
Gallstones happen when substances like cholesterol or bilirubin harden in your gallbladder. Your gallbladder is responsible for making bile, a digestive fluid that helps break down fats before they enter your intestines.
What does it mean when your bilirubin is high?
Or, with moderately high bilirubin, you may only have jaundice , a yellow cast to your eyes and skin. Jaundice is the main sign of high bilirubin levels. Other general signs of many of the illnesses that cause high bilirubin can include: abdominal pain or swelling. chills.
Where does bilirubin come from?
Bilirubin is derived from two main sources. Roughly, 80% of bilirubin is made from the breakdown of hemoglobin in senescent red blood cells , and prematurely destroyed erythroid cells in the bone marrow. The remainder originates from the turnover of various heme-containing proteins found in other tissues, primarily the liver and muscles. These proteins include myoglobin, cytochromes, catalase, peroxidase, and tryptophan pyrrolase. [4][5] About 4 mg/kg body weight of bilirubin is produced daily.
How is bilirubin transported?
Hepatic transport mechanisms: Bilirubin is taken up into the hepatocytes from the liver sinusoids by two different mechanisms: passive diffusion and receptor-mediated endocytosis. The process of passive diffusion is not energy-consuming and as a result, follows a concentration gradient making the flow bi-directional. Active transporter uptake of unconjugated bilirubin from the hepatic sinusoids is mediated by carrier proteins that are not well understood. A majority of the unconjugated bilirubin entering the hepatocytes is extracted in the periportal region. A fraction of conjugated and unconjugated bilirubin within the hepatocyte is transported back into the sinusoidal space, and this fraction is once again taken up downstream to the sinusoidal flow. The uptake is mediated by the 1A and 1B members of the organic anion transporting polypeptide family (OATP). These polypeptides are encoded by the genes: SLCO1B1and SLCO1B3. Conjugated bilirubin that escapes reuptake into the hepatocyte is excreted in the urine. Bilirubin binding to glutathione S-transferases, which by itself increases net uptake, minimizes the efflux of internalized bilirubin.
What is the binding affinity of bilirubin to albumin?
The binding affinity for albumin to bilirubin is extremely high, and under ideal conditions, no free (non-albumin bound) unconjugated bilirubin is seen in the plasma.
Why is bilirubinuria not detected in cholestasis?
An exception to this rule is when bilirubinuria is not detected in a patient with prolonged cholestasis and marked jaundice. This is due to the formation of delta bilirubin or conjugated bilirubin that is tightly bound to serum albumin.
How to measure unconjugated bilirubin?
Unconjugated bilirubin is measured by subtracting the direct-reacting fraction from total bilirubin. Potential sources of error include plasma lipids, drugs such as propranolol, and several other endogenous substances. These interfere with the diazo assay and can potentially produce an unreliable result.
How long does it take for bilirubin to be released from serum?
As the delta bilirubin is bound to albumin, its clearance from serum takes about 12-14 days (equivalent to the half-life of albumin) in contrast to the usual 2 to 4 hours (half-life of bilirubin). The process of conjugation alters the physicochemical properties of bilirubin giving it many special properties.
What is the yellow color of bilirubin?
However, the body has developed mechanisms for its safe detoxification and disposition. Bilirubin and its metabolites also provide the distinctive yellow color to bile and stool and a lesser degree, urine. This article will summarize the mechanism of heme metabolism and bilirubin synthesis.[1][2][3] Bilirubin is an important metabolite of heme ...
Where is bilirubin formed?
Bilirubin is formed in the reticuloendothelial system during the degradation of aged erythrocytes. The heme portion from hemoglobin and from other heme-containing proteins is removed, metabolized to bilirubin, and transported as a complex with serum albumin to the liver.
What is the bilirubin conjugate?
In the liver, bilirubin is conjugated with glucuronic acid for solubilization and subsequent transport through the bile duct and elimination via the digestive tract. 80 – 85% of bilirubin produced daily originates from haemoglobin released by the breakdown of senescent erythrocytes, the remaining 15 – 20% results from the breakdown ...
What causes bilirubin to increase?
Liver immaturity and several other diseases in which the bilirubin conjugation mechanism is impaired cause similar elevations of circulating unconjugated bilirubin. Bile duct obstruction or damage to hepatocellular structure causes increases in the levels of both conjugated (direct) and unconjugated (indirect) bilirubin in the circulation.
