SPSS SPSS Statistics is a software package used for interactive, or batched, statistical analysis. Long produced by SPSS Inc., it was acquired by IBM in 2009. The current versions are named IBM SPSS Statistics.SPSS
Full Answer
What is the population proportion for binomial test in SPSS?
For running a binomial test in SPSS, see SPSS Binomial Test. population proportion is likely to be x. For example, is 50% -a proportion of 0.50- of the entire Dutch population familiar with my brand? We asked a simple random sample of N = 10 people if they are. Only 2 of those -a proportion of 0.2- or 20% know my brand.
What is a binomial test used for?
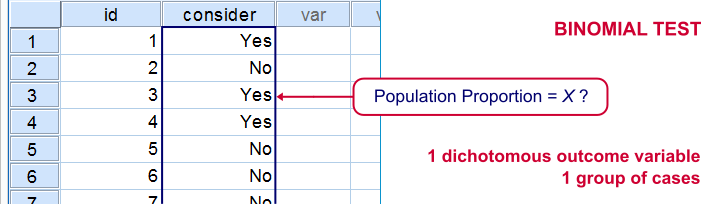
SPSS binomial test is used for testing whether a proportion from a single dichotomous variable is equal to a presumed population value.
What is the difference between A binomial and a Z-test?
A z-test allows us to compute a confidence interval for our sample proportion. We can easily estimate statistical power for a z-test but not for a binomial test. A z-test is computationally less heavy, especially for larger sample sizes. * I suspect that most software actually reports a z-test as if it were a binomial test for larger sample sizes.
How do I perform a statistical test in SPSS?
Where P is the proportion of people who selected cats. Determine if the hypotheses are one- or two-tailed. These hypotheses are two-tailed as the null is written with an equal sign. Specify the α level: α = .05 Perform the statistical test. First, scroll in the SPSS Data Editor until you can see the first row of the variable that you just recoded.

What is a binomial test in SPSS?
The Binomial test procedure compares the observed frequencies of the two categories of a dichotomous variable to the frequencies that are expected under a binomial distribution with a specified probability parameter. By default, the probability parameter for both groups is 0.5.
What is a binomial test used for?
The binomial test is a one-sample test used to assess whether an observed proportion derived from a single random sample differs from an expected parametric proportion. It can be used to assess outcomes of encounters in behavioural studies.
What type of test is a binomial test?
probability testThe binomial test of significance is a kind of probability test that is based on various rules of probability. It is used to examine the distribution of a single dichotomous variable in the case of small samples. It involves the testing of the difference between a sample proportion and a given proportion.
What is a binomial distribution test?
In statistics, the binomial test is an exact test of the statistical significance of deviations from a theoretically expected distribution of observations into two categories using sample data.
Is binomial test parametric or nonparametric?
non-parametricThe binomial test is a non-parametric statistical procedure for determining whether the frequency distribution of nominal scaled, dichotomous variables corresponds with an assumed distribution.
How do I run a binomial test in SPSS?
0:013:56SPSS - Binomial test - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipGet from data indicates that we'll use the first one as accounting. And successor will use yes asMoreGet from data indicates that we'll use the first one as accounting. And successor will use yes as success click on OK and in the output.
What is a one-sample binomial test?
The one-sample binomial test makes statistical inference about the proportion parameter by comparing it with a hypothesized value. The methods for estimating the power for such a test are either the normal approximation or the binomial enumeration. Select a test assumption Estimate setting (Sample size or Power).
Is binomial test the same as Z test?
We can always use a 2-sided z-test. However, a binomial test is always 1-sided unless P0 = 0.5. A z-test allows us to compute a confidence interval for our sample proportion. We can easily estimate statistical power for a z-test but not for a binomial test.
How do you find the p-value in a binomial test?
0:033:48Finding the P Value Using The Binomial Distribution - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipUsing the binomial distribution instead of their normal distribution the p-value that will result isMoreUsing the binomial distribution instead of their normal distribution the p-value that will result is going to be an exact value for the p-value.
How do you verify a binomial experiment?
We have a binomial experiment if ALL of the following four conditions are satisfied:The experiment consists of n identical trials.Each trial results in one of the two outcomes, called success and failure.The probability of success, denoted p, remains the same from trial to trial.The n trials are independent.
What is binomial term?
Binomial is a polynomial with only terms. For example, x + 2 is a binomial, where x and 2 are two separate terms. Also, the coefficient of x is 1, the exponent of x is 1 and 2 is the constant here. Therefore, A binomial is a two-term algebraic expression that contains variable, coefficient, exponents and constant.
Why do we use t tests?
A t-test is a statistical test that is used to compare the means of two groups. It is often used in hypothesis testing to determine whether a process or treatment actually has an effect on the population of interest, or whether two groups are different from one another.
Is binomial test the same as Z test?
We can always use a 2-sided z-test. However, a binomial test is always 1-sided unless P0 = 0.5. A z-test allows us to compute a confidence interval for our sample proportion. We can easily estimate statistical power for a z-test but not for a binomial test.
What is a one sample binomial test?
The one-sample binomial test makes statistical inference about the proportion parameter by comparing it with a hypothesized value. The methods for estimating the power for such a test are either the normal approximation or the binomial enumeration. Select a test assumption Estimate setting (Sample size or Power).
What is a binomial distribution in statistics?
The binomial distribution is a probability distribution used in statistics that states the likelihood that a value will take one of two independent values under a given set of parameters or assumptions.
What's a binomial in math?
A binomial is a polynomial with two terms. For example, x − 2 x-2 x−2 and x − 6 x-6 x−6 are both binomials. In this article, we'll review how to multiply these binomials.
What is the binomial test?
The binomial test, also known as the one-sample proportion test or test of one proportion, can be used to determine whether the proportion of cases (e.g., "patients", "potential customers", "houses", "coins") in one of only two possible categories (e.g. , patients at "high" or "low" risk of heart disease, potential customers who "likely" or "not likely" to purchase, houses with "subsidence" or "no evidence of sub sidence", the "heads" or "tails" showing after a coin is thrown) is equal to a pre-specified proportion (e.g., a proportion of 0.17 of patients having a low risk of heart disease).
What is the first step before using a binomial test?
The first step before analysing your data using a binomial test is to check whether it is appropriate to use this statistical test. After all, the binomial test will only give you valid/accurate results if your study design meets five assumptions that underpin a binomial test. If any of these five assumptions are not met, you cannot use a binomial test, but you may be able to use another statistical test instead. Therefore, before carrying out a binomial test, you need to check that your study design meets the following five assumptions:
What is the default display in SPSS?
Note: The Model Viewer is the default display in SPSS Statistics when carrying out an exact binomial test and exact Clopper-Pearson 95% CI. However, if you have changed the display options in SPSS Statistics (i.e., via the main menu under E dit > Optio n s...) from the Model Viewer to Pivot tables and charts, all of the results will be displayed in the initial IBM SPSS Statistics Viewer instead. However, even though the location where the results are displayed is different, the tables produced are the same.
What are some examples of dichotomous variables?
Examples of dichotomous variables that are nominal include gender (male or female), ethnicity (African American or Hispanic), transport type (bus or car), and degree type (undergraduate or postgraduate).
How to display confidence interval table?
To display the Confidence Interval Summary table, select from the drop-down options in the V iew: box. The Confidence Interval Summary table, shown below, will be displayed in the left-hand pane of the Model Viewer:
Where to enter dichotomous response variable?
The name of your dichotomous response variable should be entered in the cell under the column (e.g., " tv_advert " in row to represent our dichotomous response variable, advert_type ). There are certain "illegal" characters that cannot be entered into the cell. Therefore, if you get an error message and you would like us to add an SPSS Statistics guide to explain what these illegal characters are, please contact us.
Where is the hypothesis test summary table in SPSS?
The Hypothesis Test Summary table displayed in the IBM SPSS Statistics Viewer is also displayed in the left-hand pane of the Model Viewer above, as shown below:
What is a z-test?
A z-test is computationally less heavy, especially for larger sample sizes. *. I suspect that most software actually reports a z-test as if it were a binomial test for larger sample sizes. So when can we use a z-test instead of a binomial test?
What is the sample proportion of 0.5?
If the population proportion really is 0.5, we can find a sample proportion of 0.2. However, if the population proportion is only 0.1 (only 10% of all Dutch adults know the brand), then we may also find a sample proportion of 0.2. Or 0.9. Or basically any number between 0 and 1. The figure below illustrates the basic problem -I mean challenge - here.
Can a binomial test be 2 sided?
We can always use a 2-sided z-test. However, a binomial test is always 1-sided unless P 0 = 0.5.
Normal Approximation to the Binomial
As you know, you can use the normal approximation to the binomial distribution to find the probability that you would find a certain number of successes (or a more extreme number).
What if you were to use the correction for continuity?
If you used the correction for continuity (which is typically used for samples of size N=20 or less), you would use the score of 17.5 (the lower real limit of the interval containing 18) in the calculation of your z-value. Here is what you would get:

Binomial Test - Basic Idea
Binomial Test Assumptions
- First off, we need to assume independent observations. This basically means that the answer given by any respondent must be independent of the answer given by any other respondent. This assumption (required by almost all statistical tests) has been met by our data.
Binomial Distribution - Formula
- If 50% of some population knows my brand and I ask 10 people, then my sample could hold anything between 0 and 10 successes. Each of these 11 possible outcomes and their associated probabilities are an example of a binomial distribution, which is defined asP(B=k)=(nk)pk(1−p)n−kwhere 1. nis the number of trials (sample size); 2. kis the number of su…
Binomial Distribution - Chart
- Right, so we got the probabilities for our 11 possible outcomes (0 through 10 successes) and visualized them below. If a population proportion is 0.5 and we sample 10 observations, the most likely outcome is 5 successes: P(B = 5) ≈ 0.24. Either 4 or 6 successes are also likely outcomes (P ≈ 0.2 for each). The probability of finding 2 or fewer successes -like we did- is 0.055. This is our …
Binomial Test - Google Sheets
- We ran our example in this simple Google Sheet. It's accessible to anybody so feel free to take a look at it.
Binomial Test - SPSS
- Perhaps the easiest way to run a binomial test is in SPSS - for a nice tutorial, try SPSS Binomial Test. The figure below shows the output for our current example. It obviously returns the same p-valueof 0.109 as our Google Sheet. Note that SPSS refers to p as “Exact Sig. (2-tailed)”. Is there a non exact p-value too then? Well, sort of. Let's see how that works.
Binomial Test Or Z Test?
- Let's take another look at the binomial probability distribution we saw earlier. It kinda resembles a normal distribution. Not convinced? Take a look at the binomial distribution below. For a sample of N = 100, our binomial distribution is virtually identical to a normal distribution. This is caused by the central limit theorem. A consequence is that -for a larger sample size- a z-test for one propor…