
What are some biological contaminants in water?
Feb 09, 2020 · Standing water, water-damaged materials or wet surfaces also serve as a breeding ground for molds, mildews, bacteria and insects. In this regard, what does biological pollution mean? Biological pollutants are substances in our environment which come from living organisms and can affect our health. They includethings such as pollen from trees and plants, …
What are four examples of biological contaminants?
Water pollution is any chemical, physical or biological change in the quality of water that has a harmful effect on any living thing that drinks or uses or lives (in) it. When humans drink polluted water it often has serious effects on their health. Water pollution can also make water unsuited for the desired use.
What are biological water pollutants?
Water pollution is defined as the presence in groundwater of toxic chemicals and biological agents that exceed what is naturally found in the water and may pose a threat to human health and/or the environment. Additionally, water pollution may consist of chemicals introduced into the water bodies as a result of various human activities.
What are the 10 causes of water pollution?
Feb 10, 2020 · Water pollution is any chemical, physical or biological change in the quality of water that has a harmful effect on any living thing that drinks or uses or lives (in) it. When humans drink polluted water it often has serious effects on their health. Water pollution can also make water unsuited for the desired use.
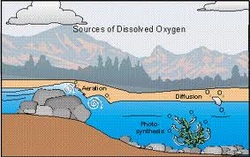
What do you mean by biological pollution of water?
Biological pollutants include bacteria, viruses, and parasites that are responsible for waterborne diseases, such as typhoid fever, cholera, dysentery, polio, hepatitis, and schistosomiasis. The presence of Coliform bacteria is indicator of recent fecal pollution.
What is meant by biological pollution?
Biological pollutants are substances in our environment which come from living organisms and can affect our health. They includethings such as pollen from trees and plants, insects or insect parts, certain fungi, some bacteria and viruses, and even animal hair, animal skin scales, saliva, and urine.
What causes biological pollution?
What are biological pollutants? Common indoor biological pollutants are: bacteria, molds, viruses, animal dander and saliva, dust mites, cockroach parts, and pollens. Biological pollutants can travel through the air and are not always easy to see. There are many sources for these pollutants.
What are biological effects of water pollution?
This can cause fish and other aquatic organisms to die. Toxic elements dissolved in water can make their way to humans through fish or other aquatic organisms. Water pollution also leaches chemicals into the soil that may impact the growth of plants or other food crops.
What are the example of biological pollutants?
Biological contaminants include bacteria, molds, mildew, viruses, animal dander and cat saliva, house dust, mites, cockroaches, and pollen (see more about Asthma triggers at www.epa.gov/asthma). There are many sources of these pollutants.Nov 8, 2021
What are examples of biological contamination?
Biological contaminants include bacteria, molds, mildew, viruses, animal danger and cat saliva, house dust mites, cockroaches, and pollen. There are many sources of these pollutants.Dec 7, 2021
What are the two types of biological pollution?
Biological contaminants include bacteria, viruses, animal dander and cat saliva, house dust, mites, cockroaches, and pollen. There are many sources of these pollutants.
What are the top 3 causes of water pollution?
Causes of Water PollutionRapid Urban Development.Improper Sewage Disposal.Fertilizer Run-Off.Oil Spills.Chemical Waste Dumping.Radioactive Waste Discharge.Oct 26, 2018
What are 5 effects of water pollution?
EFFECTS OF WATER POLLUTIONDestruction of biodiversity. Water pollution depletes aquatic ecosystems and triggers unbridled proliferation of phytoplankton in lakes — eutrophication —.Contamination of the food chain. ... Lack of potable water. ... Disease. ... Infant mortality.
What are biological pollutants?
They includethings such as pollen from trees and plants, insects or insect parts, certain fungi, some bacteria and viruses, and even animal hair, animal skin scales, saliva, and urine. Not all of these substances are harmful ...
Can hamsters be pets?
Animal dander (dead skin cells) and other animal-shed particles cause many allergies. Short-haired or non shedding animals (such as hamsters), may make better pets. Use “mite-proof” pillow and mattress covers: People who are allergic to dust mites can benefit from covering their bedding with special covers.
What are the organisms that absorb food?
Organisms which absorb their food through cell walls. Some are microscopic, like yeast that helps make bread rise. Others are large, such as the mushrooms we eat in salads. Molds that grow on bread, and mildew found in many bathrooms are also fungi.
Why are aquatic organisms more integrative than water?
Aquatic organisms could be more integrative of the biological pollution and useful than water since they already could filter and concentrate parasite in their tissues. Biological response of aquatic organism could be an alternative to water analysis based approach which has a poor sensitivity and representativeness.
What is ballast discharge?
Ballast discharges from ships are responsible for tar balls in the open oceans and seas, and can cause problems in navigating tanker routes. Nevertheless, the discharge of ballast water only accounts for a small percentage of oil pollution in the marine environment.
How does pollution affect the ecosystem?
Pollution impacts may also undermine the resilience of ecosystems to other stressors such as elevated sea-surface temperatures and ocean acidification.
What is ocean governance?
Ocean governance relies on the precepts of ecologically sustainable development to manage the multiple uses in the coastal zone. The increasing reliance on aquaculture to provide food security and economic development has led to an increase in the use of nonnative target species grown as food sources.
How do floodplains affect humans?
Major human impacts include the destruction of floodplain habitats, channelization and snag removal, dewatering, and disconnection of floodplain and channel habitats. Impoundments are particularly destructive, as they result in large-scale changes to channel and floodplain habitats and disrupt the longitudinal continuity that characterizes rivers. Massive habitat changes associated with impoundments have predictable, negative impacts on many invertebrates and other consumer groups (Figure 10 ). Over half of the large river systems on the planet are affected by impoundments. In the contiguous United States, only ∼40 rivers that are longer than 125 miles remain unimpounded. Impoundments are less numerous on rivers in the tropics, but increasing interest in hydroelectric power threatens unimpounded rivers worldwide.
Where are jellyfish found?
Recently the jellyfish have been discovered in the Caspian Sea.
Can seafood be contaminated?
Hence, seafood can become contaminated and unhealthy for consumption. Not surprisingly, cholera outbreaks have been attributed to ship operations. Shellfish and drinking water can then be contaminated when the ship discharges its ballast water. To prevent marine bioinvasions, biosecurity strategies have been developed.
Why is water important?
Water is an important natural resource utilized for domestic, industrial, recreational, and agricultural purpose by human society. Quality of water is negatively affected by contamination of various pollutants.
What are the threats of biological pollutants?
Biological pollutants are the major threat to low-income countries as diseases caused by them are rapidly manifested and have important effects on children and the elderly, sometimes even resulting in fatalities.
How are suspended solids removed?
Suspended solids are removed by filtration and sedimentation. Soluble organics are removed by microbial action in the soil. Nitrogen is removed by sedimentation-filtration (e.g., particle-associated organic nitrogen), adsorption to soil, volatilization (e.g., NH4), uptake by crops, and biological denitrification.
Is water a chemical or physical property?
The chemistry of natural water is highly dependent on its geologic and hydrologic origins, as well as its biological contributions. The imparted chemical characteristics to natural water can be highly valued or a potential threat to public health.
What are the chemical properties of water?
Another crucial chemical property of water is its relative acidity or alkalinity. This chemical characteristic has a direct influence on the concentration of minor elements and trace elements. Many of the compounds found in natural water are the result of biosynthesis and biodegradation.
What are the two main groups of pollutants found in groundwater?
Pollutants found in groundwater can be classified into two broad groups: biological and chemical, and within the latter they can be further subclassified into two other groups: inorganic and organic.
What are the most common inorganic pollutants?
Inorganic pollutants include cations and anions, most of them naturally occurring in soils, sediments, and rocks. Cations include heavy metals, such as cadmium (Cd), chromium (Cr VI), lead (Pb), manganese (Mn), mercury (Hg), and nickel (Ni).
What are the causes of water pollution in India?
The key causatives of water pollution in India are: 1 Urbanization. 2 Deforestation. 3 Industrial effluents. 4 Social and Religious Practices. 5 Use of Detergents and Fertilizers. 6 Agricultural run-offs- Use of insecticides and pesticides.
What is water pollution?
Water pollution can be defined as the contamination of water bodies. Water pollution is caused when water bodies such as rivers, lakes, oceans, groundwater and aquifers get contaminated with industrial and agricultural effluents. When water gets polluted, it adversely affects all lifeforms that directly or indirectly depend on this source.
How much water does the Earth have?
The earth has more than two-thirds of its surface covered with water. This translates to just over 1 octillion litres (1,260,000,000,000,000,000,000 litres) of water distributed in the oceans, rivers, lakes and streams. That is a lot of water, however, less than 0.3% is accessible for human consumption.
Where is methylmercury dumping?
In 1932, a factory in Minamata City, Japan began dumping its industrial effluent – Methylmercury, into the surrounding bay and the sea. Methylmercury is incredibly toxic to humans and animals alike, causing a wide range of neurological disorders.
Is cadmium a toxic substance?
Cadmium and lead are some toxic substances, these pollutants upon entering the food chain through animals (fish when consumed by animals, humans) can continue to disrupt at higher levels. Humans are affected by pollution and can contract diseases such as hepatitis through faecal matter in water sources.
What are the symptoms of mercury poisoning?
Other affected people showed symptoms of acute mercury poisoning such as ataxia, muscle weakness, loss of motor coordination, damage to speech and hearing etc.
How much garbage is dumped in the ocean every year?
Nearly 6 billion kilograms of garbage is dumped every year in the oceans. Apart from industrial effluents and untreated sewage, other forms of unwanted materials are dumped into various water bodies. These can range from nuclear waste to oil spills – the latter of which can render vast areas uninhabitable.
