What is Bitbit synchronization?
Bit Synchronization: This layer helps to allow synchronization of all bits which are delivered with clock, and this clock has ability to manage both receiver and sender that is producing synchronization on bit level.
What is bit level synchronization in data transmission?
In data transmission sender and receiver should be synchronized at the bit level. Means that sender's and receiver's clock must be synchronized. This is done by physical layer Kanwar Home Study Guides Science Math and Arithmetic History Literature and Language Technology Health
What does the physical layer do in a computer network?
The physical layer provides the encoding of signals if required. It also provides the bit synchronization for the transmission of bits in both synchronous and asynchronous transmission. The physical layer does not character synchronization and frame synchronization. They are the responsibility of the data link layer.
What is meant by synchronisation?
- Answers The process of maintaining one operation in step with another. In data transmission sender and receiver should be synchronized at the bit level. Means that sender's and receiver's clock must be synchronized. This is done by physical layer Kanwar
What is the importance of bit synchronizer?
Bit and Frame Synchronization techniques are used in order to ensure that signals transmitted from one participant of the communication can be correctly decoded by the receiver.
What is the synchronization explain in detail?
Synchronization is the coordination of events to operate a system in unison. For example, the conductor of an orchestra keeps the orchestra synchronized or in time. Systems that operate with all parts in synchrony are said to be synchronous or in sync—and those that are not are asynchronous.
What is Carrier synchronization?
Carrier synchronization is one of the key components in digital communication systems. Briefly, carrier synchronization concerns the estimation and compensation of the carrier frequency and phase differences between the transmitted signal and the corresponding received signal.
What are two types of synchronization?
There are two types of synchronization: full and incremental.
What are two methods of synchronization?
Types of SynchronizationProcess Synchronization.Thread Synchronization.
What is timing and synchronization?
Time synchronization refers to the distribution of time across clocks in a network. Time synchronization is one way of achieving phase synchronization.
What is carrier and symbol synchronization?
Carrier and symbol synchronization are the key prerequisite for the accurate reception of the Quadrature Phase Shift Keying (QPSK) signal. The traditional synchronization methods have some intrinsic problems, such as slow speed, difficult to design the coefficients for the loop filter.
What is frequency synchronization?
Phase synchronisation is usually applied to two waveforms of the same frequency with identical phase angles with each cycle. However it can be applied if there is an integer relationship of frequency, such that the cyclic signals share a repeating sequence of phase angles over consecutive cycles.
What is synchronization explain the synchronization in Python with example?
The threading module provided with Python includes a simple-to-implement locking mechanism that allows you to synchronize threads. A new lock is created by calling the Lock() method, which returns the new lock. The acquire(blocking) method of the new lock object is used to force threads to run synchronously.
What is synchronization in mobile computing?
Synchronization in Mobile computing systems: Defined as the process of maintaining the availability of data generated from the source and. maintaining consistency between the copies pushed from the data source and local cached or hoarded.
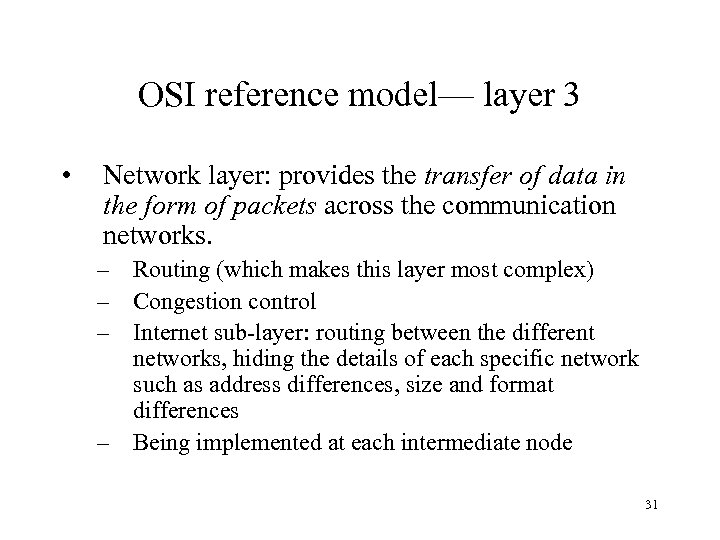
What is the physical layer of a network?
Physical Layer is the bottom-most layer in the Open System Interconnection (OSI) Model which is a physical and electrical representation of the system. It consists of various network components such as power plugs, connectors, receivers, cable types, etc. Physical Layer sends data bits from one device (s) (like a computer) to another device (s).
Which layer maintains the data rate?
Physical Layer maintains the data rate (how many bits a sender can send per second).
Why is mesh topology so difficult to install?
Mesh Topology is difficult to install because it is more complex. Star Topology –. In star topology, the device should have a dedicated point-to-point connection with a central controller or hub. Star Topology is easy to install and reconnect as compared to Mesh Topology.
What is mesh topology?
Mesh Topology –. In a mesh topology, each and every device should have a dedicated point-to-point connection with each and every other device in the network. Here there is more security of data because there is a dedicated point-to-point connection between two devices.
What are the two types of configurations?
It provides two types of configuration Point to Point configuration and Multi-Point configuration.
What is the process of converting data into radio waves?
It provides an important aspect called Modulation, which is the process of converting the data into radio waves by adding the information to an electrical or optical nerve signal.
What is simplex mode?
Simplex mode –. In this mode, out of two devices, only one device can transmit the data, the other device can only receive the data. Example- Input from keyboards, monitors, TV broadcasting, Radio broadcasting, etc. Half Duplex mode –.
What is the physical layer of a network?
The physical layer is the lowest layer . This layer provides mechanical, electrical and other functional aids available to enable or disable, they maintain and transmit bits about physical connections. This may for example be electrical signals, optical signals (optical fiber, laser), electromagnetic waves (wireless networks) or sound. The techniques used are called technical transmission process. Devices and network components that are associated with the physical layer, for example, the antenna and the amplifier, plug and socket for the network cable, the repeater, the stroke, the transceiver, the T-bar and the terminator are (Terminator).
What is bit stream?
The bit stream may be grouped into code words or symbols and converted to a physical signal that is transmitted over a hardware transmission medium. The physical layer provides an electrical, mechanical, and procedural interface to the transmission medium.
What type of wave is used to transmit information?
This means the following: In computer networks today information is generally transmitted in the form of bit or symbol sequences. In copper cables and radio transmission, however, are modulated high frequency electromagnetic waves, the information carrier, in the optical waveguide light waves of a certain wavelength or different.
Which layer of OSI translates logical communications requests from the data link layer into hardware-specific operations?
Within the semantics of the OSI network architecture, the physical layer translates logical communications requests from the data link layer into hardware-specific operations to affect transmission or reception of electronic signals.
Which layer is the first and lowest layer?
In the seven-layer OSI model of computer networking, the physical layer or layer 1 is the first and lowest layer. The implementation of this layer is often termed PHY.
What is technical transmission?
This may for example be electrical signals, optical signals (optical fiber, laser), electromagnetic waves (wireless networks) or sound. The techniques used are called technical transmission process. Devices and network components that are associated with the physical layer, for example, the antenna and the amplifier, ...
Which layer provides encoding and synchronization?
Signal encoding and Synchronization. The physical layer provides the encoding of signals if required. It also provides the bit synchronization for the transmission of bits in both synchronous and asynchronous transmission. The physical layer does not character synchronization and frame synchronization. They are the responsibility of the data link ...
Why is the layer of a physical connection different from the physical transmission path?
The layer provides a physical connection different from the physical transmission path because it is at the bit level while the transmission path is at the electrical signal level. This physical connection can be a point to point physical connection or point to the multi-point physical connection, as shown in the figure −.
What is data link layer?
The data link layer hands over the physical service data unit (PSDU) with one bit in the serial transmission and "n" bits in parallel transmission. It can provide transparency of data, i.e., the bit sequences can be transmitted on a transmission channel through it without restricting them.
Why does the physical layer not have flow control?
Though the physical layer does not have any error control mechanism or flow control mechanism, it tries to deliver the data bits in the same sequence in which they were received from the data link layer. Because of the lack of error and flow controls, it can happen that some data bits and duplicated, altered or lost.
What is activation in a network?
Activation means if a user initiates a data transmission at one end, then at the other end, the receiver is ready to receive the data message. It is a non-confirmed service. A physical layer after establishing the connection allows a half-duplex or full-duplex transmission of data.
What is the function of a physical layer?
The physical layer meets all these requirements out. The set of rules and procedures for interaction between physical layers are called Physical layer protocols. The layer provides a physical connection different from the physical transmission path because it is at the bit level while ...
Which layer is responsible for fault detection?
Fault Detection. The physical layer is also responsible for fault detections in the physical connection. If it detects any fault in the physical connection, it informs the data link layer.
What is bit synchronization?
Bit Synchronization: This layer helps to allow synchronization of all bits which are delivered with clock, and this clock has ability to manage both receiver and sender that is producing synchronization on bit level.
Which layer produces the transmission interface in between different network devices and transmission source?
Interface: Physical layer also produces the transmission interface in between different network devices and transmission source. Bit Rate Control: Physical layer can pre-defined transmission rate of flowing all bits such as how many bits can be sent in per second.
What is physical layer?
Definition: Physical layer is a layer 1 in the OSI model that plays major activity for interacting along with hardware components and signal mechanism system. This layer actually deals with making connection of two distinct station points.
What is line configuration?
Line Configuration: Physical layer allows establishing connection with different sources (medium) like as Point to Point configuration and Multipoint configuration.
What is a multiplexer?
Multiplexers: Multiplexer is a hardware component that has multiple analog and digital input signals and finally single output switch. Receivers: Receiver is a hardware device that is used for receiving signals like as analog electromagnetic signals or waves, or digital signals.
What is broadband signaling?
In the broadband signaling method, we can use only one line for sending and receiving signal via different frequencies for outgoing and incoming data, so it is known as “Frequency Division Multiplexing”. Its best example is “Television”.
Which layer delivers all frames to physical layer?
Physical layer delivers own services to Data link layer then DLL layer provides all frames to physical layer, and physical layer alters them into electrical pulse which like as binary form, and finally these binary data is moved to wired or wireless transmission media.
What is the physical signaling sublayer?
In a network using Open Systems Interconnection (OSI) architecture, the physical signaling sublayer is the portion of the physical layer that
What is the physical layer of OSI?
In the seven-layer OSI model of computer networking, the physical layer or layer 1 is the first and lowest layer; The layer most closely associated with the physical connection between devices. This layer may be implemented by a PHY chip.
What is a PHY device?
A PHY connects a link layer device (often called MAC as an acronym for medium access control) to a physical medium such as an optical fiber or copper cable. A PHY device typically includes both physical coding sublayer (PCS) and physical medium dependent (PMD) layer functionality.
What is Ethernet PHY?
More specifically, the Ethernet PHY is a chip that implements the hardware send and receive function of Ethernet frames; it interfaces between the analog domain of Ethernet's line modulation and the digital domain of link-layer packet signaling. The PHY usually does not handle MAC addressing, as that is the link layer 's job. Similarly, Wake-on-LAN and Boot ROM functionality is implemented in the network interface card (NIC), which may have PHY, MAC, and other functionality integrated into one chip or as separate chips.
What is a single pair Ethernet?
However, there now exists a new interface, called Single Pair Ethernet (SPE), which is able to utilize a single pair of copper wires while still communicating at the intended speeds. Texas Instruments DP83TD510E is an example of a PHY which uses SPE.
What are the topics associated with the physical layer?
Other topics associated with the physical layer include: bit rate; point-to-point, multipoint or point-to-multipoint line configuration; physical network topology, for example bus, ring, mesh or star network; serial or parallel communication; simplex, half duplex or full duplex transmission mode; and autonegotiation
What is line coding?
Line coding is used to convert data into a pattern of electrical fluctuations which may be modulated onto a carrier wave or infrared light. The flow of data is managed with bit synchronization in synchronous serial communication or start-stop signalling and flow control in asynchronous serial communication. Sharing of the transmission medium among multiple network participants can be handled by simple circuit switching or multiplexing. More complex medium access control protocols for sharing the transmission medium may use carrier sense and collision detection such as in Ethernet's Carrier-sense multiple access with collision detection (CSMA/CD).
