
What is diphtheria?
What is diphtheria? Diphtheria is an infection caused by the bacterium Corynebacterium diphtheriae . Signs and symptoms usually start 2 – 5 days after exposure and range from mild to severe. Symptoms often come on gradually, beginning with a sore throat and fever.
What type of bacteria causes diphtheria?
A type of bacteria called Corynebacterium diphtheriae causes diphtheria. The condition is typically spread through person-to-person contact or through contact with objects that have the bacteria on them, such as a cup or used tissue.
What is the hallmark sign of diphtheria?
Diphtheria typically causes a sore throat, fever, swollen glands and weakness. But the hallmark sign is a sheet of thick, gray material covering the back of your throat, which can block your airway, causing you to struggle for breath.

What causes black diphtheria?
Diphtheria is a serious infection caused by strains of bacteria called Corynebacterium diphtheriae that make a toxin. It is the toxin that can cause people to get very sick.
What are the main causes of diphtheria?
Diphtheria is caused by the bacterium Corynebacterium diphtheriae. The bacterium usually multiplies on or near the surface of the throat or skin.
What is diphtheria called now?
Over the period of time, it was called Microsporon diphtheriticum, Bacillus diphtheriae, and Mycobacterium diphtheriae. Current nomenclature is Corynebacterium diphtheriae.
What are the 5 types of diphtheria?
Respiratory and cutaneous diphtheria are caused by toxic strains of the bacteria Corynebacterium diphtheriae and Corynebacterium ulcerans and very rarely Corynebacterium pseudotuberculosis....Diphtheriaclassical respiratory diphtheria.laryngeal diphtheria.nasal diphtheria and.cutaneous diphtheria (skin lesions).
What diphtheria smells like?
Infectious diseases were known by their characteristics odors--scrofula as smelling like stale beer; typhoid, like freshly baked brown bread; rubella, like plucked feathers; and diphtheria, as "sweetish." Anosmics might be banned from medical school.
What organs does diphtheria affect?
Diphtheria is a contagious infection caused by a bacterium called Corynebacterium diphtheriae. The bacterium releases a toxin that causes a buildup of grey tissue in your throat, leading to problems with swallowing and breathing.
Is diphtheria an STD?
While classical respiratory diphtheria is transmitted by droplets, cutaneous diphtheria often results from minor trauma. This report concerns the first case of sexually transmitted diphtheria in a patient with non-gonococcal urethritis after orogenital contact.
Can diphtheria be cured?
Antibiotics, such as penicillin or erythromycin, help kill bacteria in the body, clearing up infections. Antibiotics lessen the time that someone with diphtheria is contagious. An antitoxin. If a doctor suspects diphtheria, he or she will request a medication that counteracts the diphtheria toxin in the body.
Can you get diphtheria even if vaccinated?
FACT: You cannot get diphtheria from the vaccine. infected person's nose, throat, eyes and/or skin lesions. FACT: Nearly one out of every 10 people who get diphtheria will die from it.
Does diphtheria cause death?
Diphtheria is a serious infection caused by strains of bacteria called Corynebacterium diphtheriae that make toxin. It can lead to difficulty breathing, heart rhythm problems, and even death.
Who is the most common victim of diphtheria?
Children under 5 and adults over 60 years old are particularly at risk for getting it. People living in crowded or unclean conditions, those who aren't well nourished, and children and adults who don't have up-to-date immunizations are also at risk.
What is the survival rate of diphtheria?
The overall case-fatality rate for diphtheria is 5%–10%, with higher death rates (up to 20%) among persons younger than 5 and older than 40 years of age. Cutaneous diphtheria infection rarely results in severe disease.
What are the two main way of transmission of diphtheria?
Diphtheria is transmitted from person to person through close contact with the discharge from an infected person's eyes, nose, throat or skin.
Where is diphtheria most commonly found?
The most common sites of diphtheria infection are the pharynx and the tonsils. Infection at these sites is usually associated with substantial systemic absorption of toxin. The onset of pharyngitis is gradual. Early symptoms include malaise, sore throat, anorexia, and low-grade fever (less than 101°F).
Is diphtheria caused by poor hygiene?
Because of widespread vaccination (immunization) of children, diphtheria is now rare in many parts of the world. Risk factors for diphtheria include crowded environments, poor hygiene, and lack of immunization.
Who is the most common victim of diphtheria?
Children under 5 and adults over 60 years old are particularly at risk for getting it. People living in crowded or unclean conditions, those who aren't well nourished, and children and adults who don't have up-to-date immunizations are also at risk.
What is diphtheria?
Diphtheria: Diphtheria is a bacterial infection of the upper airway caused by Corynebacterium diphtheriae. This disease was historically associated with severe i... Read More
What causes diphtheria?
Infection: Infection, usually in the throat, with cornybacterium diphtheriae produced a toxin that causes the signs and symptoms of diphtheria. Dpt vaccination p... Read More
How serious is diphtheria?
Pulmonary v serious: Respiratory diptheria is very serious and leads to death in 5-10% of infected individuals. Dpt vaccination protects.
How is diphtheria transmitted?
Droplets/drainage: Diptheria is spread by contact with respiratory tract droplets from a respiratory carrier or drainage from skin lesions from a person with cutaneous d... Read More
Can you die from diphtheria?
In many cases, YES: Otherwise, whoever has diphtheria can die, or while dying, can actively spread the disease to other people.
Where is diphtheria most common?
About a million cases a year are believed to have occurred before the 1980s. Diphtheria currently occurs most often in sub-Saharan Africa, India, and Indonesia. In 2015, it resulted in 2,100 deaths, down from 8,000 deaths in 1990. In areas where it is still common, children are most affected.
How long does it take for a diphtheria to show symptoms?
Signs and symptoms may vary from mild to severe. They usually start two to five days after exposure. Symptoms often come on fairly gradually, beginning with a sore throat and fever.
How is C. diphtheriae spread?
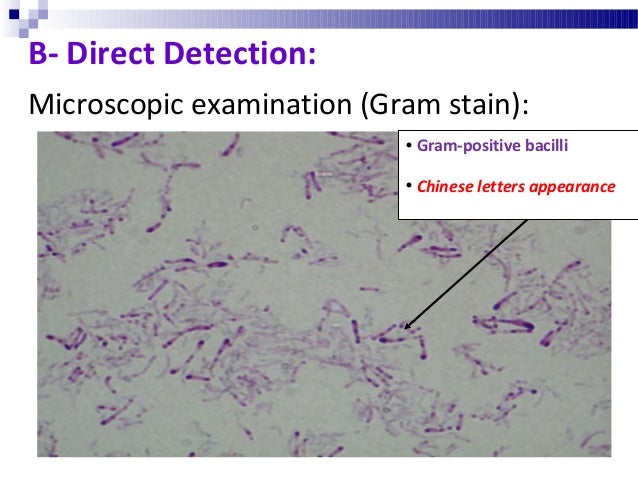
Diphtheria is usually spread between people by direct contact or through the air. It may also be spread by contaminated objects. Some people carry the bacterium without having symptoms, but can still spread the disease to others. The three main types of C. diphtheriae cause different severities of disease. The symptoms are due to a toxin produced by the bacterium. Diagnosis can often be made based on the appearance of the throat with confirmation by microbiological culture. Previous infection may not protect against future infection.
What is a dense, grey pseudomembrane covering the tonsils?
An adherent, dense, grey pseudomembrane covering the tonsils is classically seen in diphtheria.
How many people died from diphtheria in 2013?
In children under five years and adults over 40 years, the fatality rate may be as much as 20%. In 2013, it resulted in 3,300 deaths, down from 8,000 deaths in 1990.
When should diphtheria be treated empirically?
Empirical treatment should generally be started in a patient in whom suspicion of diphtheria is high.
When did the diphtheria epidemic start?
In 1735, a diphtheria epidemic swept through New England.
How does diphtheria spread?
Causes and Spread to Others 1 Diphtheria is an infection caused by strains of bacteria called Corynebacterium diphtheriae that make toxin. 2 Diphtheria spreads from person to person, usually through respiratory droplets, like from coughing or sneezing. It can also spread by touching open sores or ulcers of someone with a diphtheria skin infection.
What causes a thick, gray coating on the throat?
Diphtheria can infect the respiratory tract (parts of the body involved in breathing) and skin. In the respiratory tract, it causes a thick, gray coating to build up in the throat or nose. This coating can make it hard to breathe and swallow. Diphtheria skin infections can cause open sores or shallow ulcers. More.
What is the cause of diphtheria?
A type of bacteria called Corynebacterium diphtheriae causes diphtheria. The condition is typically spread through person-to-person contact or through contact with objects that have the bacteria on them, such as a cup or used tissue. You may also get diphtheria if you’re around an infected person when they sneeze, cough, or blow their nose.
How to tell if you have diphtheria?
Your doctor may believe that you have diphtheria if they see a gray coating on your throat or tonsils. If your doctor needs to confirm the diagnosis, they’ll take a sample of the affected tissue and send it to a laboratory for testing. A throat culture may also be taken if your doctor suspects diphtheria of the skin.
How long does it take for diphtheria to show up?
Signs of diphtheria often appear within two to five days of the infection occurring. Some people don’t experience any symptoms, while others have mild symptoms that are similar to those of the common cold. The most visible and common symptom of diphtheria is a thick, gray coating on the throat and tonsils. Other common symptoms include: a fever.
What are the signs of cutaneous diphtheria?
difficulty breathing or swallowing. changes in vision. slurred speech. signs of shock, such as pale and cold skin, sweating, and a rapid heartbeat. If you have poor hygiene or live in a tropical area, you may also develop cutaneous diphtheria, or diphtheria of the skin.
What is the most common symptom of diphtheria?
The most visible and common symptom of diphtheria is a thick, gray coating on the throat and tonsils. Other common symptoms include:
What is the gray substance that forms when you get infected?
Once you’re infected, the bacteria release dangerous substances called toxins. The toxins spread through your bloodstream and often cause a thick, gray coating to form in these areas of the body: nose. throat. tongue.
Can you get diphtheria from one person to another?
Although it spreads easily from one person to another, diphtheria can be prevent ed through the use of vaccines. Call your doctor right away if you believe you have diphtheria.
How does diphtheria occur?
Diphtheria is caused by bacteria adhering to the lining of the respiratory system. These bacteria generate a toxin which damages tissue cells of the respiratory system. Within two or three days, the tissue left behind forms a bulky, gray coating.
How many people die from diphtheria?
Vaccination is the best choice. Treatment for diphtheria is effective, but even with treatment, roughly 1 out of 10 people might die. For those without treatment, 1 out of 2 patients may die.
Why does diphtheria cause sores?
The bacterium releases a toxin that causes the accumulation of gray tissue in the throat, leading to problems with swallowing and breathing. In warmer climates, someone with diphtheria might also develop skin sores that will not heal and may be covered with the gray tissue.
How long is diphtheria contagious?
People with diphtheria are kept in isolation to prevent others from becoming infected. An infected person is no longer contagious around 48 hours after taking antibiotics. When treatment ends, tests will be run again to make sure the bacteria are gone.
What to do if you have diphtheria?
If you are diagnosed with, or suspected of having diphtheria, the doctor will start treatment right away. Treatment can start even before the lab test results are confirmed. Your doctor will prescribe diphtheria antitoxin to stop damage to organs and antibiotics, typically penicillin or erythromycin, to fight the infection.
How long does it take for diphtheria to show symptoms?
The length of time for symptoms to show can be anywhere from 1 to 10 days after exposure.
Is there a diphtheria problem in the US?
In other countries where vaccinations are not given, the disease still exists. Therefore, there is still a potential for diphtheria to cause problems in the U.S.
When was diphtheria first used?
Diphtheria vaccination first appeared in the 1890s, but only became widely used in the 1920s. During this interval medical scientists labored to create a safe and effective vaccine. Antitoxin introduced in 1890 provided immunity for only two weeks.
What was the only treatment for diphtheria?
Before Dr. O’Dwyer perfected his intubation techniques, tracheotomy presented the only viable treatment for diphtheria. This procedure involved cutting open the throat without anesthetic and inserting a tube directly into the trachea. Through this tube, an attendant could maintain consistent airflow by pushing air into the lungs. Although tracheotomy has been practiced for hundreds of years, operative complications persisted until the 1960s. During the early 19th century tracheotomy remained a last resort due to the lack of anesthesia, high risk of infection, and low success rate of the procedure.
Overview
Signs and symptoms
Transmission
Mechanism
Diagnosis
Diphtheria is an infection caused by the bacterium Corynebacterium diphtheriae. Most infections are asymptomatic or have a mild clinical course, but in some outbreaks more than 10% of those diagnosed with the disease may die. Signs and symptoms may vary from mild to severe and usually start two to five days after exposure. Symptoms often come on fairly gradually, beginning with a sor…
Prevention
The symptoms of diphtheria usually begin two to seven days after infection. They include fever of 38 °C (100.4 °F) or above; chills; fatigue; bluish skin coloration (cyanosis); sore throat; hoarseness; cough; headache; difficulty swallowing; painful swallowing; difficulty breathing; rapid breathing; foul-smelling and bloodstained nasal discharge; and lymphadenopathy. Within two to three d…
Treatment
Human-to-human transmission of diphtheria typically occurs through the air when an infected individual coughs or sneezes. Breathing in particles released from the infected individual leads to infection. Contact with any lesions on the skin can also lead to transmission of diphtheria, but this is uncommon. Indirect infections can occur, as well. If an infected individual touches a surface or object, the bacteria can be left behind and remain viable. Also, some evidence indicates diphthe…
Epidemiology
Diphtheria toxin (DT) is produced only by C. diphtheriae infected with a certain type of bacteriophage. Toxinogenicity is determined by phage conversion (also called lysogenic conversion); i.e, the ability of the bacterium to make DT changes as a consequence of infection by a particular phage. DT is encoded by the tox gene. Strains of corynephage are either tox (e.g., corynephage β) or tox (e.g., corynephage γ). The tox gene becomes integrated into the bacteria…