
A blind or blinded experiment is a scientific experiment where some of the people involved are prevented from knowing certain information that might lead to conscious or subconscious bias on their part, thus invalidating the results.
What is an example of a double blind study?
What experiments can be double blind?
- Medication Experiments. A double-blind experiment is beneficial when testing a specific medication. …
- Taste Testing. We have all seen the commercials where the individual is asked to determine which beverage tastes better. …
- Computer Generated Survey. …
- Forensic Application.
What is a double blind method?
What is a Double Blind Test?
- Basics of Clinical Trials. A double blind test works well in determining the overall effectiveness of a certain medication on groups of people.
- Blinding. Double blind testing typically involves the use of a placebo. ...
- Double Blinding. ...
What is a double blind technique?
Double-Blind Procedure (also known as Double Blind Control) This is one type of experimental procedure in which both the patient and the staff are ignorant (blind) as to the condition (or group) that the participant is in. This would make it impossible for the participant or researcher to know if the participant is receiving the treatment (for example a drug) or a placebo.
What is a randomized double blind study?
What is a Double-Blind Study? In a randomized double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of a medical treatment, some of the participants are given the treatment, others are given fake treatment (placebo), and neither the researchers nor the participants know which is which until the study ends (they are thus both “blind”).
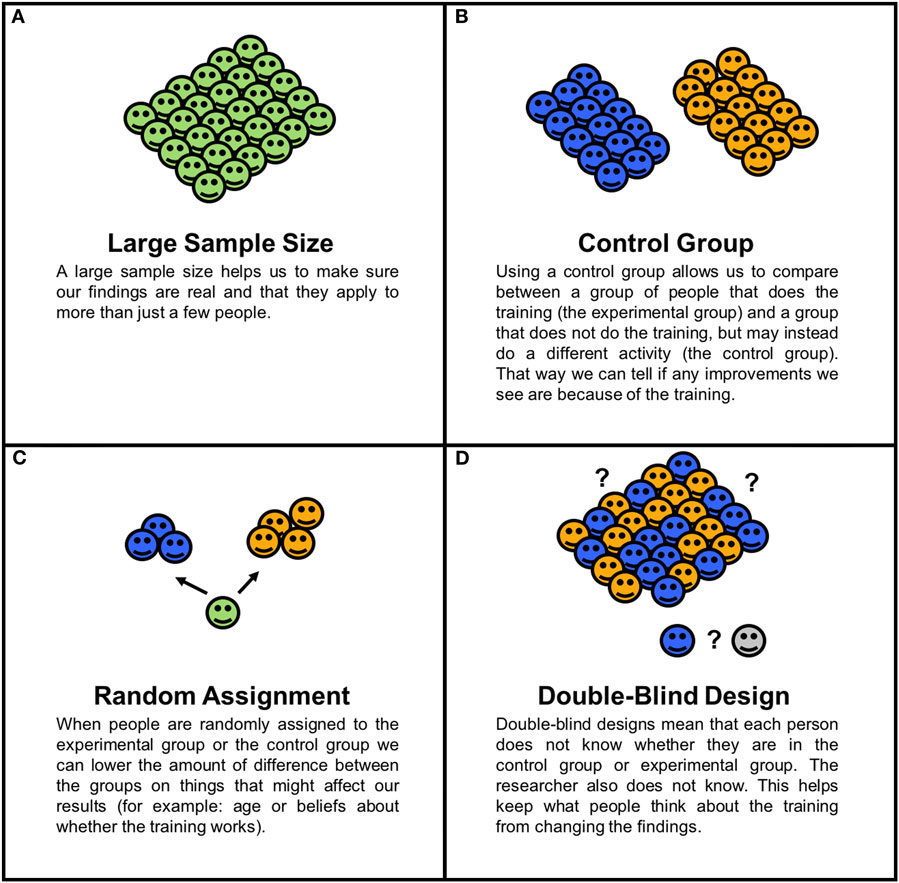
What is an example of a blind experiment?
Example: Yogurt Tasting The researchers know which yogurt containers are low-fat and which are high-fat, but participants are not told. This is an example of a single-blind study because the researchers know which participants are in the low- and high-fat groups but the participants do not know.
Why is blindness important in an experiment?
Good blinding can reduce or eliminate experimental biases that arise from a participants' expectations, observer's effect on the participants, observer bias, confirmation bias, and other sources.
What is blind experiment biology?
A type of clinical trial in which neither the participants nor the researcher knows which treatment or intervention participants are receiving until the clinical trial is over. This makes results of the study less likely to be biased.
What is a blind experimental design?
A blind or blinded experiment is a scientific experiment where some of the people involved are prevented from knowing certain information that might lead to conscious or subconscious bias on their part, thus invalidating the results.
Why are trials blinded?
Blinding is used in trials to reduce bias by ensuring that knowledge of which intervention a given trial participant received does not influence the judgments of trial participants or investigators.
How does blinding affect bias?
Blinding of outcome assessors reduces detection bias. Outcome assessors (study nurses or investigators) who are aware of the actual treatment may unconsciously or intentionally alter their assessment. Particularly, in case of soft endpoints, e.g. pain blinding of outcome assessors is important.
How do you know if your study is blind?
Explanation: A double blind experiment requires that both researchers and test subjects are unaware of who is receiving the treatment and who is receiving the placebo. If only one group is unaware, it is a single blind experiment. If both groups are aware, the experiment is not blinded.
How does blindness affect language development?
They lack visual references and have reduced integration of information from their parents. More recent studies have found that the language of visually impaired children is more self-oriented and that the word meanings are more limited than for normally sighted children (Anderson et al 1984).
How does blindness affect social development?
Visual impairment may limit social interaction and have a negative impact on individuals' socioemotional development (Rosemblum, 1998). Children with visual impairments may present with more emotional and behavioural difficulties than their sighted peers (Harris & Lord, 2016; Pinquart & Pfeiffer, 2014).
How does blindness affect memory?
Whereas sighted individuals to some extent rely on visual cues for remembering different types of sensory information, blind individuals clearly cannot. Research has shown that visual deprivation may result in a more developed ability to remember non-visual information.
How does blindness and low vision affect learning?
The presence of a visual impairment can potentially impact the normal sequence of learning in social, motor, language and cognitive developmental areas. Reduced vision often results in a low motivation to explore the environment, initiate social interaction, and manipulate objects.
History
The French Academy of Sciences originated the first recorded blind experiments in 1784: the Academy set up a commission to investigate the claims of animal magnetism proposed by Franz Mesmer.
Single-blind trials
Single-blind describes experiments where information that could introduce bias or otherwise skew the result is withheld from the participants, but the experimenter will be in full possession of the facts.
Double-blind trials
Not to be confused with double bind, a type of dilemma in communication.
Triple-blind trials
A triple-blind study is an extension of the double-blind design; the committee monitoring response variables is not told the identity of the groups. The committee is simply given data for groups A and B.
Usage
Double-blinding is relatively easy to achieve in drug studies, by formulating the investigational drug and the control (either a placebo or an established drug) to have identical appearance (color, taste, etc.).
What is Blinding in Research?
Blinding, in research, mentions to a practice where the study population or the stakeholders involved in research are not permitted from knowing certain information or treatment, which may somehow influence the study findings.
What is an unblinded trial?
Unblinded or open level. Unblinding a trial is a necessary process to safeguard participants in the event of medical or safety reasons. The process of unblinding is planned and included in the study protocol. Potential lower efficiency.
What are the different types of blinding?
Different Types of Blinding: There are basically three different types of blinding used in researches: 1. Single blinding or single-masked: In single blinding, only a single stakeholder i.e. either the participant or the investigator is not informed of the nature of treatment the participant is receiving. A trial is called single-blind ...
What is double blinding in psychology?
Double-blinding or double-masked: Double-blinded study is defined as a study, in which both study population/participant and data collectors/investigators/researchers are not aware of the kind or nature of the treatment given and who receive the treatment. ...
Why is double blind important?
Double blind. It prevents research outcomes from being ‘biased’ and not influenced by knowledge of the participant and the researcher. It is a basic tool to prevent conscious and unconscious bias in research. It avoids deception in the research process. Lack of adequate demographic controls.
What is triple blinding?
Triple blinding: A clinical trial or experiment in which neither the subject nor the person governing treatment nor an individual measuring the response to the treatment is aware of the particular treatment received by the subject is known as triple blind.
Who is blinded in triple blinding?
In triple blinding, the study participant, the data investigator or data collector and the data analyzer- all are blinded.
What is blind experiment?
Blind Experiment is an experiment in which certain information that could introduce bias in the results is held back from the Subjects or Researchers or the committee monitoring the experiment or any combination of them.
What is single blind study?
1. Single-Blind Study: Information that could introduce bias is concealed from participants (subjects) only and experimenters are not withheld from the information. However this kind of experiment faces a risk of experimenter’s bias where researchers can influence behavior of the participants consciously or subconsciously.
What is the purpose of blindfolding?
The main purpose of Blind Experiment is to prevent bias whether intentional or unconscious. Similarly in Blind Experiment, the participants (Subjects or Researchers or monitoring committee) are kept ignorant of information that could introduce bias in the results. Bias can cause various errors to creep into the experiment leading to incorrect results. They are of three types:
Need for Blind Experiment
Consider an example to understand why blind experiments are important. A food company has developed a new cereal. It has a similar appearance and taste to another popular cereal, but this cereal has fewer calories, less sugar, and more nutrients.
Single-Blind Procedure
In a single-blind procedure, the researchers get a group of volunteer participants. They are told of the possible risks and potential benefits but also that they won't know which group they are placed in. The participants must all sign consent forms agreeing to the experiment.
Single-Blind Study Example
Another example of a single-blind study is trying a new hand lotion. Each participant would be assigned to either the control or the experimental group. The control group would get a known hand lotion, while the experimental group would try the new hand lotion.
What is blind testing?
Blind testing is the experimentation on participants who are “blind” (unaware) of whether or not they are in the experimental or control group. They also are usually unaware of what the independent and dependent variables are. The experimental group is the group exposed to the independent variable. The independent variable is the variable ...
Why is blind testing inaccurate?
Another common misconception is that when a study is conducted with blind or double-blind testing, that study must automatically be completely accurate; this is incorrect, because blind testing does not make an experiment that lacks control completely valid.
Why are blind and double blind tests not intrusive?
Because blind and double-blind testing involves experimentation on participants who are unaware of their own exposer to an independent variable, they can lead people to worry about the safety of the participants ; both of these kinds of testing are, however, safe and not intrusive for the participants because of the Institutional Review Boards (IRBs) and debriefings that usually occur in blind and double-blind experiments. IRBs are committees that are put together to approve, monitor, and review studies in the scientific community that involve humans as the participants. These committees ensure the safety of the participants, so even though a participant is unaware of their exposer to an independent variable in a blind or double-blind study, they are no less safe than any other participant in a study not being conducted using blind or double-blind testing. Researchers often debrief the participants as well to let them know what was being tested, how it was being tested, and if that participant was in the experimental group. This way the participant is able to understand what happened, which removes any anxiety or ambiguity that may have occurred during the study.
How does double blind testing work?
Blind testing and double-blind testing are often thought of by the public as a way to simply eliminate a placebo effect from a study. A placebo effect is a phenomenon in which a fake treatment or stimulation, also known as a placebo, elicits a response from a participant simply because that participant expects that it will. Both blind testing and double-blind testing are effective at removing this bias because they can take advantage of the placebo effect itself. This can be beneficial when determining the effectiveness of a certain medication or drug. The participants are either exposed to the drug itself (experimental group) or they are exposed to a “fake drug,” which is the placebo (control group), so that all participants believe that they have taken and will experience effects from a drug. This makes the expectation of an effect constant across all groups, even if some of the groups did not receive the real drug, thus eliminating a possible bias from the placebo. An example of this is in the study of the effectiveness of nicotine patches on decreasing tobacco withdrawal symptoms and in helping users quit smoking (Daughton et al., 1990). In this study, participants were separated into three groups; one group was given patches that administered nicotine for 24 hours, one was given patches that administered nicotine for 18 hours, and one was given patches that administered no nicotine (placebo). The participants were then observed over 6 months, and it was determined that 22% of the people were able to refrain from smoking in the 24 hour group, 31% of people in the wakeful hours group, and 8% of people in the placebo group. Because the study was conducted using double-blind testing, and the participants all believed they were given nicotine, a valid conclusion about the effectiveness of the nicotine patches was able to be drawn from the comparison of the control (placebo) group and the two experimental groups.
Why is blind testing not valid?
Blind testing also does not make a study completely valid because it does not compensate for inadequate procedures. This is especially prevalent with blind tests that occur in experiments where the control group is a different size than the experimental group, such as in a study conducted to determine the effectiveness of a stent (tubular support placed into a blood vessel) that releases a drug versus a stent which did not (Pfisterer et al., 2006). This trial was conducted by dividing up the participants in a 2:1 ratio, meaning for every 2 participants in the experimental group (stent that released drugs), there was 1 participant in the control group (stent that did not release anything). The participants were randomly assigned to each group and were unaware of which type of stent they were receiving (blind test). The participants were then observed over a long period of time, the main observations being the health of their hearts as well as their life span. While the difference in size of control group versus the size of the experimental group was not as extreme in this instance (2:1), it still affects the validity of the results because in groups of different sizes, there is less variation in participants, so the results will be naturally different. This difference in results increases as the difference in size of control group verse experimental group increases. Blind testing cannot compensate for this because blind testing is not a method to remove or add variation.
What is the experimenter expectancy effect?
Similarly, the experimenter expectancy effect is another bias avoided by blind and double-blind testing in the scientific community. This bias also involves the researchers expectations, except here, the researchers expectations change the behavior of the participants. This can be seen in a study on the effect of researchers knowledge about ...
Why is double blind testing able to remove bias?
Double-blind testing is able remove this bias because it does not allow the researcher to have expectations for the behavior of a participant since they are unaware of the group the participant is in (control or experimental).
What is a blind scientific experiment?
A blind scientific experiment is where “some of the people involved are prevented from knowing certain information that might lead to conscious or subconscious bias on their part, thus invalidating the results.” Blind experiment
Why do we do double blind studies?
A double-blind study is one in which neither the participants nor the experimenters know who is receiving a particular treatment. This procedure is utilized to prevent bias in research results. Double-blind studies are particularly useful for preventing bias due to demand characteristics or the placebo effect. How Are Double-Blind Studies Used In Psychology?
Why is blinding useful?
Since bias may be unconscious or intended, blinding is useful because no dishonesty is implied through it. There are also ‘double blind experiments’ in which both the tester and the participant are masked from the experiment’s information. This basically eradicates bias as both have been blinded.
Why is it important to remove experimenter bias?
Because it helps to remove experimenter bias. If the experimenter doesn’t know which subject is being tested then that knowledge cannot interfere with the results.
What does "blind drug trials with a placebo" mean?
Its important that the participants dont know if the have been given the real drug or a placebo because of the placebo effect.
Can a blind person see blackness?
We don’t. My blind left eye sees nothing at all. Not even blackness. It has the same visual acuity as my foot, my elbows, my knees… :) So the answer is that a completely blind person does NOT “ see nothing”… instead, they don’t see at all.
Who first described inattentional blindness?
What Is Inattentional Blindness? The term "inattentional blindness" was first coined by psychologists Arien Mack, PhD, and Irvin Rock, PhD, who observed the phenomenon during their perception and attention experiments.
What Is Inattentional Blindness?
The term "inattentional blindness" was first coined by psychologists Arien Mack, PhD, and Irvin Rock, PhD, who observed the phenomenon during their perception and attention experiments.
Do you see when your eyes are open?
It's logical to think that you see whenever your eyes are open. But the reality is that attention plays a major role in visual perception .
Can inattentional blindness be avoided?
Though it is not possible to avoid all instances of inattentional blindness, it's important to remember this very natural occurrence—particularly when you are in a disagreement with someone about the full scope of a situation.
What distinguishes inattentional blindness from the aforementioned phenomena?
What fundamentally distinguishes inattentional blindness from the aforementioned phenomena is the unforeseen character of the optic stimulus which escapes the observer’s attention.
What Is Inattentional Blindness?
Inattentional blindness occurs when one fails to notice a readily visible yet unexpected visual stimulus in one’s sight (Simons & Chabris, 1999). This temporary unawareness is likely to stem from an abundance of visual stimuli meriting one’s notice.
What are the consequences of inattentional blindness?
Consequences of inattentional blindness in the real world may include automobile collisions, aircraft accidents and material threats to the safety of police officers during vehicle stops.
What is the term for the failure to notice something that is completely visible because of a lack of attention?
Inattentional blindness (also called perceptual blindness) is the failure to notice something that is completely visible because of a lack of attention.
What happens if you are blind on the road?
This may result in a failure to notice objects on the road such as stop signs, speed limit indicators or even other cars. Inattentional blindness herein can result in accidents and potentially even death.
When a stimulus’s sensory conspicuity or cognitive conspicuity drastically lessens, inattention?
When a stimulus’s sensory conspicuity or cognitive conspicuity drastically lessens, inattentional blindness is likely to ensue. For instance, when an object is visible yet not visually prominent, it may likely evade notice. On the other hand, even a visually striking object may fail to capture an observer’s attention if it is irrelevant to the observer’s interests.
Why is the stimulus unanticipated?
The stimulus is unanticipated and the failure to recognize it stems from a collapse of attention, and not from any drawbacks of the visual scene or the optic stimulus.
