The term "blueshift" refers to the shift in wavelengths of light toward the blue end of the spectrum as an object moves toward us in space. Astronomers use blueshift to understand motions of galaxies toward each other and toward our region of space.
Full Answer
What is a blue shift in the spectrum?
Key Takeaways. The term "blueshift" refers to the shift in wavelengths of light toward the blue end of the spectrum as an object moves toward us in space. Astronomers use blueshift to understand motions of galaxies toward each other and toward our region of space.
What is redshift and blueshift in astronomy?
That relies on two phenomena — redshift and blueshift. As objects move away from us, their light gets shifted into longer wavelengths or the red end of the spectrum — that’s redshift. Blueshift is the opposite, when light is shifted to shorter wavelengths on the blue side of the spectrum as an object comes towards us.
What is the difference between redshift and Blue Shift?
As objects move away from us, their light gets shifted into longer wavelengths or the red end of the spectrum — that’s redshift. Blueshift is the opposite, when light is shifted to shorter wavelengths on the blue side of the spectrum as an object comes towards us.
What does it mean when a galaxy is blue shifted?
Blue Shift Contrary to the spectra of most other galaxies that show a distinct red shift, the spectrum of M90 is blue-shifted, which means that the galaxy is approaching us.
What is the blue shift?
So basically what is a Blue Shift? It is that shortening of the wavelength and increasing in frequency, which means the object is moving toward the observer. It is named blue not because it was the favorite color of the one who discovered it, but because in the optical spectrum (or the rainbow), the blue end has the shorter wavelength. The longer wavelength, the Red Shift then is the increase in wavelength and decrease in frequency, where the object is traveling away from the observer.
What happens to the pitch of sound as it moves away?
The pitch of the sound of an object gets higher as it approaches an observer and lower as it moves away. In a shorter distance, the sound frequency increases and wavelength decreases. In longer distances, the sound frequency decreases and wavelength increases. Aside from sound waves, this also happens with light and water waves. The Doppler Effect must be first understood to define what a Blue Shift is.
How does redshift help astronomers?
Redshift helps astronomers compare the distances of faraway objects. In 2011, scientists announced they had seen the farthest object ever seen — a gamma-ray burst called GRB 090429B, which emanated from an exploding star. At the time, scientists estimated the explosion took place 13.14 billion years ago. By comparison, the Big Bang took place 13.8 billion years ago.
What is the redshift of light?
Redshift is defined as the change in the wavelength of the light divided by the wavelength that the light would have if the source was not moving — called the rest wavelength:
Why do gravitational waves have redshifts?
Because gravitational waves carry a signal that shows their redshifted mass, extracting the redshift from that requires some calculation and estimation, according to a 2014 article in the peer-reviewed journal Physical Review X. Editor's note: This article was updated on Aug. 7, 2019 to reflect a correction.
What is redshift in radio waves?
The terms redshift and blueshift apply to any part of the electromagnetic spectrum, including radio waves, infrared, ultraviolet, X-rays and gamma rays. So, if radio waves are shifted into the ultraviolet part of the spectrum, they are said to be blueshifted, or shifted toward the higher frequencies. Gamma rays shifted to radio waves would mean ...
Why are galaxies moving away from Earth?
The galaxies are moving away from Earth because the fabric of space itself is expanding. While galaxies themselves are on the move — the Andromeda Galaxy and the Milky Way, for example, are on a collision course — there is an overall phenomenon of redshift happening as the universe gets bigger. The terms redshift and blueshift apply to any part ...
What is the spectrum of visible light?
The concept is key to charting the universe's expansion. Visible light is a spectrum of colors, ...
How many types of redshifts are there?
Three types of redshift. At least three types of redshift occur in the universe — from the universe's expansion, from the movement of galaxies relative to each other and from "gravitational redshift," which happens when light is shifted due to the massive amount of matter inside of a galaxy. This latter redshift is the subtlest ...
What causes blue shift?
blue shift Motion-induced changed in the observed wavelength from a source that is moving toward us. Relative approaching motion between the object and the observer causes the wavelength to appear shorter (and hence bluer) than if there were no motion at all.
What does it mean when the spectrum is red shifted?
Astronomer s describe the spectrum as being either red shifted or ~ ed. This just means that the light has been shifted due to, respectively, relative motion away from you or motion towards you. The degree of the shift depends upon the speed of the motion. You can determine the speed using this formula - ...
How to determine radial velocity of a star?
The radial velocity of a star away from or towards the observer can be determined by measuring the red shift or ~ of its spectrum. The American astronomer Vesto Slipher made a series of such measurements from 1902 to 1904 and discovered that the radial velocity of α Andromeda e varied period ically.
Does the speed of light change?
The speed of light, c, may never change, but its wavelength can be altered depending on the relative motion of the observer and source - the red and ~. Depending on whether an object is moving toward or away from an observer, it's absorption lines will appear to shift toward the red (away) or blue (toward).
How many galaxies have blueshifts?
There are in all about 100 known galaxies with blueshifts out of the billions of galaxies in the observable universe. Most of these blue-shifted galaxies are in our own local group, and are all bound to each other. Most are also dwarf galaxies which you've probably never heard of, although the Andromeda Galaxy, M31, is in there.
Why are all galaxies redshifted?
Almost all galaxies are redshifted because of the Hubble expansion of the universe. Only a handful of the most nearby galaxies are blue-shifted. You see, in addition to the apparent motion imparted to galaxies due to universal expansion, individual galaxies also have their own intrinsic, what we call "peculiar" motions. This is not because they are peculiar, as in strange, but rather because each galaxy is in motion irrespective of the universe's expansion, and each galaxy has its own unique velocity due to the gravitational attraction of other galaxies in its vicinity.
Who is Dave from Ask the Astronomer?
Dave was the founder of Ask an Astronomer. He got his PhD from Cornell in 2001 and is now an assistant professor in the Department of Physics and Physical Science at Humboldt State University in California. There he runs his own version of Ask the Astronomer. He also helps us out with the odd cosmology question.
Why do astronomers use redshifts?
Astronomers use redshifts to measure how the universe is expanding, and thus to determine the distance to our universe’s most distant (and therefore oldest) objects. What is a redshift?
How do astronomers measure the speed of a star?
By measuring how far away the lines are located from where they’re supposed to be in the spectrum , astronomers can calculate the speed of a star or a galaxy relative to Earth, and even how a galaxy rotates: by measuring a different redshift for one side of the galaxy compared to the other, you can see which side is moving away from you and which side is moving toward you.
What is the name of the galaxy in the inset?
The object in the inset is currently the most distant known galaxy, called GN-z11. Its name is derived from its location in the GOODS-North field of galaxies – captured by the Hubble Space Telescope – and its high cosmological redshift number (GN + z11).
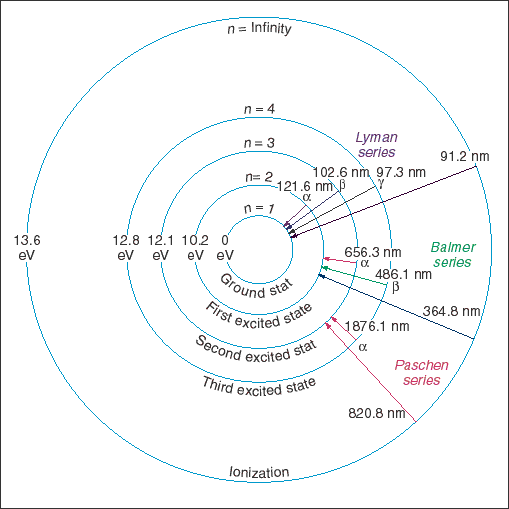
How do hydrogen atoms absorb light?
Image via Wikipedia. The hydrogen atoms are tuned to absorb very specific frequencies of light. When a beam of light consisting of many colors passes through the gas, those frequencies get removed – absorbed – from the beam. The rainbow becomes littered with what astronomers call absorption lines .
What is the absorption line in the rainbow?
The rainbow becomes littered with what astronomers call absorption lines . Replace the hydrogen with helium, and you get a completely different pattern of absorption lines. Every atom and molecule has a distinct absorption fingerprint that allows astronomers to tease out the chemical makeup of distant stars and galaxies.
How do astronomers determine the mass of an invisible companion?
By measuring how far the absorption lines shift , an astronomer can determine the mass of the invisible companion and its distance from the star, and come to the conclusion that a planet is in orbit around the star! As a planet orbits a star, it tugs the star back and forth with tiny movements.
What happens when you shine a flashlight through a prism?
This is the study of spectroscopy. If you shine a flashlight beam through a prism, a rainbow comes out the other side. But if you place a clear container filled with hydrogen gas between the flashlight and the prism, gaps appear in the smooth rainbow of colors, places where the light literally goes missing.