
What causes Boerhaave's syndrome?
Pathophysiologically, Boerhaave’s syndrome occurs due to a sudden rise in intraluminal oesophageal pressure during vomiting, in the presence of a closed glottis. However there are several other reasons which can cause rupture of esophageal wall.
What is esophageal rupture and Boerhaave syndrome?
Esophageal rupture is a rupture of the esophageal wall. Iatrogenic causes account for approximately 56% of esophageal perforations, usually due to medical instrumentation such as an endoscopy or paraesophageal surgery. In contrast, the term Boerhaave syndrome is reserved for the 10% of esophageal perforations which occur due to vomiting.
What are the mortality rates for Boerhaave syndrome?
Boerhaave syndrome is one of the most lethal gastrointestinal tract disorders, with mortality rates up to 40%. Symptoms may vary, and diagnosis can be challenging. Also, several factors, including difficulty assessing the esophagus and the unusual blood supply of the organ, contribute to the conditi …
How is Boerhaave syndrome differentiated from Mallory-Weiss syndrome?
Boerhaave syndrome, a transmural perforation of the esophagus, should be distinguished from Mallory-Weiss syndrome, a nontransmural esophageal tear that is also associated with vomiting. Because it is often associated with emesis, Boerhaave syndrome usually is not truly spontaneous.

What causes Boerhaave syndrome?
Boerhaave's syndrome — also called effort rupture of your esophagus — is a perforation (hole or split) of your esophagus caused by forceful vomiting or excessive straining. Healthcare professionals call this a “spontaneous rupture,” to distinguish it from an “iatrogenic rupture,” which is caused by a direct injury.
How is Boerhaave syndrome diagnosed?
Symptoms consist of vomiting, lower thoracic pain, and subcutaneous emphysema. A provider should suspect Boerhaave's syndrome when a patient presents with retrosternal chest pain with or without subcutaneous emphysema when associated with heavy alcohol intake and severe or repeated vomiting.
How is Boerhaave syndrome treated?
Antibiotics: Imipenem/cilastatin or ticarcillin/clavulanate offer good broad-spectrum coverage. Nasogastric suction should be applied. Keep the patient nil per os (NPO). Adequate drainage with tube thoracostomy or formal thoracotomy is vital.
Is Boerhaave syndrome rare?
Spontaneous oesophageal rupture due to an abrupt rise in intraluminal pressure caused by vomiting is also known as Boerhaave's syndrome. It is a rare but potentially life-threatening condition.
How is Mallory Weiss different from boerhaave?
1:4317:51Mallory-Weiss syndrome vs Boerhaave Syndrome - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipSo mallory-weiss usually secondary to an increase in intra-abdominal. Pressure. With Boerhaave theMoreSo mallory-weiss usually secondary to an increase in intra-abdominal. Pressure. With Boerhaave the perforation is a result of an increase in intra. Esophageal pressure with negative intrathoracic
Is an esophageal tear painful?
Pain is the first symptom of esophageal perforation. You'll usually feel pain in the area where the hole is located. You may also feel chest pain and have trouble swallowing.
Can the esophagus heal on its own?
Esophagitis can usually heal without intervention, but to aid in the recovery, eaters can adopt what's known as an esophageal, or soft food, diet. The goal of this kind of diet is to make eating less painful and to keep food from lingering in the esophagus and causing irritation.
What would cause an esophagus to explode?
Causes include endoscopic procedures, surgery, blunt injuries, fall from the height, inflammatory process and spontaneously due to severe vomiting [3–7]. Spontaneous oesophageal ruptures rarely happen due to swallowing of food material.
Is Mallory Weiss tear painful?
Individuals with Mallory-Weiss syndrome may also experience severe, painless internal gastrointestinal bleeding (hemorrhaging) due to the tears in the mucous membranes. In most cases (80-90%) however, such bleeding ceases spontaneously.
How is Mallory Weiss tear diagnosed?
What tests are used to diagnose Mallory Weiss tears? Healthcare providers typically use upper endoscopy to diagnose Mallory Weiss tears and rule out other disorders of your esophagus. During the endoscopy, your provider guides a long, thin, flexible probe (endoscope) down your throat.
What are the symptoms of a perforated esophagus?
Manifestations of esophageal perforation include:Air bubbles under the skin.Difficulty swallowing.Fever and chills.Low blood pressure and rapid heart rate.Pain at the perforation site (in the neck, chest, or abdomen)Rapid or labored breathing.Vomiting.
Can the esophagus heal on its own?
Esophagitis can usually heal without intervention, but to aid in the recovery, eaters can adopt what's known as an esophageal, or soft food, diet. The goal of this kind of diet is to make eating less painful and to keep food from lingering in the esophagus and causing irritation.
How do you get a Mallory Weiss tear?
A Mallory-Weiss tear is most often caused from violent coughing or vomiting. Less common causes are a hiatal hernia, or childbirth, which can increase pressure in your abdomen.
What is Boerhaave Syndrome?
This is a syndrome that is also referred to as “Spontaneous esophageal rupture”. It is a very rare – only accounting for sixteen (16) % of all ruptures that are traumatic to the esophagus. This is a very serious condition.
Symptoms
Individuals with the hole in the mid portion or lower portion of the esophagus can have the following symptoms:
Causes
A hole or tear in the esophagus can let contents of the esophagus pass into the mediastinum which is the surrounding area in the chest. This frequently causes infection of the mediastinum referred to as mediastinitis.
Treatment
Management that is ideal involves combining a conservative as well as a surgical approach.
Surgery
The majority of physicians believe that surgical intervention is the standard of care particularly in cases where the diagnosis is made within the first 24 hours.
Why does Boerhaave's syndrome occur?
Pathophysiologically, Boerhaave’s syndrome occurs due to a sudden rise in intraluminal oesophageal pressure during vomiting, in the presence of a closed glottis. However there are several other reasons which can cause rupture of esophageal wall. Vomiting is the most frequent cause of Boerhaave’s syndrome, but it is certainly not the only cause and this has led to some debate as to the name of the syndrome.
What is the best treatment for Boerhaave's syndrome?
Foundation of therapy for Boerhaave’s syndrome includes the following: 1 Intravenous volume resuscitation 2 Administration of broad-spectrum antibiotics 3 Prompt surgical intervention
Who first described spontaneous rupture of the esophagus?
Answer. In 1724, Hermann Boerhaave, a Dutch physician and professor of clinical medicine, first described spontaneous rupture of the esophagus, which typically occurs after forceful emesis. Boerhaave syndrome, a transmural perforation of the esophagus, should be distinguished from Mallory-Weiss syndrome, a nontransmural esophageal tear ...
Is Boerhaave syndrome spontaneous?
Because it is often associated with e mesis, Boerhaave syndrome usually is not truly spontaneous. However, the term is useful for distinguishing it from iatrogenic perforation, which accounts for 85-90% of cases of esophageal rupture.
What is Boerhaave's syndrome?
Boerhaave’s syndrome is described as a rupture of the oesophagus due to a raised intra-oesophageal pressure,secondary to vomiting against a closed cricopharyngeal sphincter. To put it in simpler words, the patient attempts to vomit out forcibly, the contents of the stomach enter into the oesophagus.
How long does Boerhaave's syndrome last?
Without treatment, survival of Boerhaave’s syndrome is in days.
What is the name of the condition where the esophagus is swollen and the food pipe
Boerhaave syndrome is a condition characterized by chest or epigastric pain following repeated bouts of severe vomiting, often with blood. Due to the trauma inflicted on the esophagus (food pipe) by the severe retching and vomiting, the muscular wall of the food pipe ruptures or tears.
What causes a sudden esophageal rupture?
Spontaneous esophageal rupture is caused by a sudden increase in intra-esophageal pressure, leading to a complete transmural tear through the esophagus. The complications will depend on the location of the rupture, as the esophagus abuts different areas of the body.
How long did Boerhaave survive?
Unfortunately, he survived for only 24 hours after the incident. Today, Boerhaave’s syndrome accounts for approximately 15% of all cases of esophageal rupture. Although the actual incidence of esophageal perforation worldwide is unclear, some studies estimate an incidence of approximately 3.1 per 1,000,000 per year.
What is the medical term for spontaneous esophageal rupture?
Management relies on rapid recognition and intervention, as lack of therapeutic interventions can be fatal.Boerhaave’s syndrome is also known as spontaneous esophageal rupture or effort rupture of the esophagus.
What is the difference between A and B?
A is a takotsubo-affected left ventricle, weakened and inflated (ballooned) and B is the normal left ventricle. . Takotsubo cardiomyopathy (degeneration of the heart) is also known as stress cardiomyopathy because it is usually triggered by emotional stress, such as the loss of a loved one, r. Continue Reading.
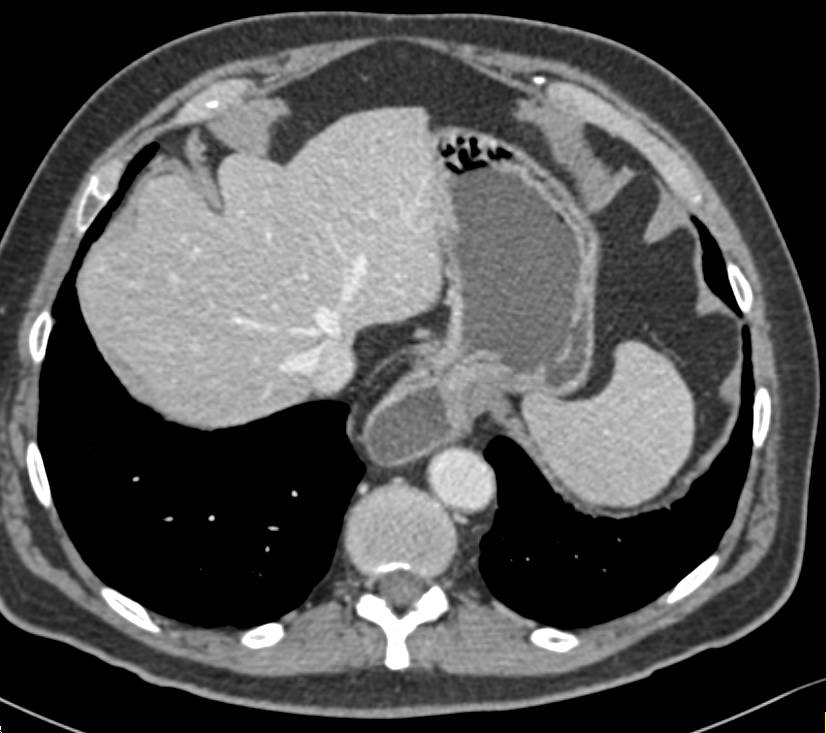
What Is Boerhaave Syndrome?
- This is a syndrome that is also referred to as “Spontaneous esophageal rupture”. It is a very rare – only accounting for sixteen (16) % of all ruptures that are traumatic to the esophagus. This is a very serious condition. This syndrome is categorized by a total rupture thru the entire wall of the esophagus caused by vomiting that is forceful – cau...
Symptoms
- Individuals with the hole in the mid portion or lower portion of the esophagus can have the following symptoms: 1. Swallowing difficulties 2. Difficulty breathing 3. Chest pain Other signs can include: 1. Fever 2. Fast breathing 3. Blood pressure is low 4. Rapid heart rate Individuals with the tear in the top portion of the esophagus might have: 1. Stiffness or pain in the neck 2. Bubble…
Causes
- A hole or tear in the esophagus can let contents of the esophagus pass into the mediastinum which is the surrounding area in the chest. This frequently causes infection of the mediastinum referred to as mediastinitis. Boerhaave syndrome is most often caused by an injury during a medical procedure. But, since more flexible instruments are used now this occurs rarely. The es…
Treatment
- Management that is ideal involves combining a conservative as well as a surgical approach. Mainstays of therapy include: 1. Administering IV broad spectrum antibiotics 2. Administering fluids thru IV 3. Draining any fluid that collects around the lung using a chest tube 4. Surgical intervention that is prompt If very little or no fluid has leaked, placing a stent in the esophagus m…
Surgery
- The majority of physicians believe that surgical intervention is the standard of care particularly in cases where the diagnosis is made within the first 24 hours. Repair of the rupture that is direct with acceptable drainage of the pleural and mediastinum cavity offers the best rates of survival. The favored surgical method is a left thoracotomy, although laparotomy might be needed if the r…
Complications
- Possible complications consist of: 1. Destruction of the esophagus that is lasting 2. Formation of abscess around and in the esophagus 3. Infection around or in the lungs This condition may progress to shock and even death if not treated. For individuals with a diagnosis that is early – 24 hours or less, the prognosis is good. Survival rate is approximately 90% when surgery occurs wit…