Who were the bourgeois in France before the French Revolution?
The majority were peasants who lived in near poverty, but around two million were the middle classes: the bourgeoisie. These had doubled in number between the years of Louis XIV (r. 1643–1715) and XVI (r. 1754–1792) and owned around a quarter of French land.
Did Robespierre support the French Revolution?
Robespierre was an outspoken member of the National Assembly and a supporter of the Declaration of the Rights of Man and of the Citizen. Soon, the French Revolution had begun. As the Revolution progressed, Robespierre joined the Jacobins Club where he found many like-minded people.
How to use "bourgeoisie" in a sentence?
Use “bourgeois” in a sentence | “bourgeois” sentence examples
- He had a petit bourgeois mentality.
- It’s a bit bourgeois, isn’t it, joining a golf club?
- They’ve become very bourgeois since they got married.
- The princess was ostracised for marrying a rich bourgeois.
- He described the film as ‘middle-class, bourgeois horseshit’.
- The princess was ostracized for marrying a rich bourgeois.
Who were the extremist leaders of French Revolution?
Who were the extremist leaders of the French Revolution? The Puritan government – initially governed by the Long Parliament from 1640 to 1648, followed by the Rump Parliament from 1648 to 1653, and later led by Cromwell [21] as Lord Protector from 1653 to 1658 – ushered in a very restrictive era called the “Puritan Revolution” (or ...

What does bourgeoisie mean in the French Revolution?
What does bourgeoisie mean? The term bourgeoisie refers to the social order that is dominated by the so-called middle class. In social and political theory, the notion of the bourgeoisie was largely a construct of Karl Marx and of those influenced by him.
What is the bourgeoisie in France?
In English, the word "bourgeoisie", as a term referring to French history, refers to a social class oriented to economic materialism and hedonism, and to upholding the political and economic interests of the capitalist ruling-class.
Who were the bourgeoisie in the French Revolution?
The bourgeoisie—merchants, manufacturers, professionals—had gained financial power but were excluded from political power. Those who were socially beneath them had very few rights, and most were also increasingly impoverished. The monarchy was no longer viewed as divinely ordained.
What did the bourgeoisie want in the French Revolution?
The bourgeois had to demand a voice in commercial politics, taxation and foreign policy. It had to oppose upper-class privilege and impose political forms within which its social and economic interests could be uninterruptedly pursued.
What is an example of bourgeoisie?
The bourgeoisie is defined as the middle class, typically used with reference to feelings of materialism when describing the middle class. An example of the bourgeoisie is the middle class who like to buy big houses and cars. A class of citizens who were wealthier members of the Third Estate.
Are the bourgeoisie the middle class?
From a Marxist standpoint, middle class initially referred to the 'bourgeoisie,' as distinct from nobility. With the development of capitalist societies and further inclusion of the bourgeoisie into the ruling class, middle class has been more closely identified by Marxist scholars with the term 'petite bourgeoisie. '
Who were the bourgeoisie quizlet?
Who was the Bourgeoisie? The middle class which included bankers, merchants and manufacturers, lawyers, doctors, journalists, and professors.
What is proletariat and bourgeoisie?
The bourgeoisie are the people who control the means of production in a capitalist society; the proletariat are the members of the working class. Both terms were very important in Karl Marx's writing.
What estate was the bourgeoisie?
The Third EstateThe Third Estate was made up of everyone else, from peasant farmers to the bourgeoisie – the wealthy business class.
Which class had the main role in French Revolution?
The French Revolution. The French Revolution was the most important event in modern history. It destroyed the old order of society and government and brought about modern changes in the world. It swept away the last remnants of feudalism and made the middle class the dominant class of modern society.
Which class started the French revolution?
Historians disagree about what caused the French Revolution, but one theory is that people in the Third Estate, especially the bourgeoisie, were tired of the Ancien Régime and wanted a more equal society. France was in bad economic shape due to massive debt and food shortages.
Did the bourgeoisie pay taxes?
First Group-Bourgeoisie or middle class: this group was bankers, factory owners, merchants, and professionals. Well educated and believed in the Enlightenment ideals. This group paid high taxes and lacked privileges. Some thought they deserved more status and political power.
What are the 3 social classes in France?
Ancien Régime The old French society before the French revolution was divided on the basis of three 'estates' and they were as follows: Clergy. Nobility. Common people.
Where did bourgeoisie live in France?
The word bourgeoisie came about to refer to those living in market towns, which used to be called “le bourg” or “burgeis” (walled city) in old French. For instance, if you walk around Paris, you will see “Faubourg” marked on several street signs, meaning the edge of the city.
What were the three major classes in France?
French society was divided into three classes known as Estates with the First Estate being the clergy, the Second Estate being the nobility and the Third Estate, which included the rest of the society consisting of peasants and the middle class merchants and professionals.
Who are the bourgeoisie according to Karl Marx?
Bourgeoisie. The bourgeoisie or capitalists are the owners of capital, purchasing and exploiting labour power, using the surplus value from employment of this labour power to accumulate or expand their capital. It is the ownership of capital and its use to exploit labour and expand capital are key here.
What does bourgeoisie mean?
The term bourgeoisie refers to the social order that is dominated by the so-called middle class. In social and political theory, the notion of the...
Where does the term bourgeoisie come from?
The term bourgeoisie originated in medieval France, where it denoted an inhabitant of a walled town. The term gained importance during the 18th cen...
What does Marxist theory state about the bourgeoisie?
In Marxist theory, the bourgeoisie plays a heroic role by revolutionizing the industry and modernizing society. However, it also seeks to monopoliz...
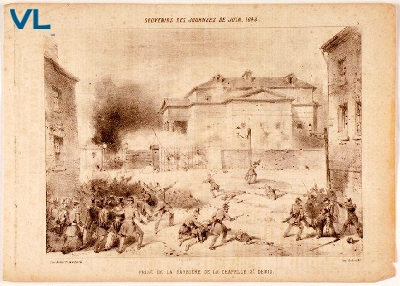
When was the French Revolution?
The French Revolution is the period between the 1789 convocation of the Estates General by Louis XVI and the coup d'état of Bonaparte on 18 Brumaire Year VIII ( November 9–10, 1799).
What did Marx call the Revolution?
Pretty central. I believe Marx called it a bourgeois revolution.
What was the revolutionary period?
The revolutionary period stirred national sentiment, including with regard to language. For the first time, language was associated with nation. Language was a matter of state, for the state had to equip the "united and indivisible Republic" with a national language and raise the people up through education and knowledge of French. The very idea of a "united and indivisible Republic" whose motto was "Fraternité, Liberté, Egalité" (Fraternity, Freedom, Equality) was irreconcilable with linguistic fragmentation and differences between the former provinces of the monarchy. The revolutionary middle classes saw such fragmentation as an obstacle to the spread of their ideas, and declared war on the dialects. Bertrand Barère (1755–1841), a member of the Committee of Public Safety, led the fight for a national language. In a report "on the idioms" (regional dialects) he presented before the Convention on January 27, 1794, Barère stated his position thus:
What was the French government called in 1870?
As a matter of practice, as opposed to legal theory, France between 1815 and 1870 was governed by a political class of what the French called “notables,” which included men of noble birth, wealthy bourgois proprietors and educated professional men. The first cabinet in the post-1870 Third Republic was called “The Republic of the Dukes” because three of its members held that title. Not until President MacMahon was ousted from office c. 1875 did political power move downward to the lower middle class of artisans and small proprietors.
What did the peasants get?
The peasants got the abolition of feudal dues and the ownership of the land they cultivated. This gave them something to lose and made them henceforth a supporter of any established order that didn’t threaten their ownership.
Why is it impossible to teach French in small villages?
Small village schools found it impossible to teach French given the lack of funds and teachers. Even in Paris, public schools were not up to the task, or scarcely so, given the lack of teachers (on account of low salaries, appalling recruitment practices, lack of training, etc.).
Who proposed that there be an elementary school for teaching French in each municipality?
Consequently, a need was felt to impose French via stringent decrees throughout France, something the English language never experienced. Charles-Maurice de Talleyrand (1754–1838), one of the great French politicians of the time, proposed that there be an elementary school for teaching French in each municipality:
Why did the bourgeoisie gain power?
There were many reasons. The bourgeoisie —merchants, manufacturers, professionals—had gained financial power but were excluded from political power. Those who were socially beneath them had very few rights, and most were also increasingly impoverished. The monarchy was no longer viewed as divinely ordained. When the king sought to increase the tax burden on the poor and expand it to classes that had previously been exempt, revolution became all but inevitable.
What was the French Revolution?
The French Revolution was a period of major social upheaval that began in 1787 and ended in 1799. It sought to completely change the relationship between the rulers and those they governed and to redefine the nature of political power. It proceeded in a back-and-forth process between revolutionary and reactionary forces.
What caused the American Revolution?
In North America this backlash caused the American Revolution, which began with the refusal to pay a tax imposed by the king of Great Britain. Monarchs tried to stop this reaction of the aristocracy, and both rulers and the privileged classes sought allies among the nonprivileged bourgeois and the peasants.
Who sent emissaries to the rulers of neighbouring countries seeking their help in restoring his power?
King Louis XVI of France yielded to the idea of a new constitution and to the sovereignty of the people but at the same time sent emissaries to the rulers of neighbouring countries seeking their help in restoring his power.
Did the French Revolution succeed?
In some respects, the French Revolution did not succeed. But the ideas of representational democracy and basic property rights took hold, and it sowed the seeds of the later revolutions of 1830 and 1848 .
