How are Boyle and Charles ideal gas laws alike?
The three fundamental gas laws discover the relationship of pressure, temperature, volume and amount of gas. Boyle’s Law tells us that the volume of gas increases as the pressure decreases. Charles’ Law tells us that the volume of gas increases as the temperature increases.
Does gas obey Boyles law?
Gases do not obey gas laws ( Charles’s law, Boyle’s law etc ) at low temperature and high pressure. At low temperature, gas particles have less kinetic energy, and therefore move more slowly and cannot overcome the attraction among them upon collision. The Ideal Gas Law does not account for these interactions.
What is constant k in Boyles law?
Simply put, Boyle's states that for a gas at constant temperature, pressure multiplied by volume is a constant value. The equation for this is PV = k, where k is a constant. The volume of a gas is inversely proportional to its pressure. Boyle's law is a form of the Ideal Gas Law. Likewise, what does K mean in Boyle law? Gas laws.
Is the ideal gas law the same as the combined gas law?
The difference between combined gas law and the ideal gas law is, the combined gas law is a collection of three gas laws whereas ideal gas law is an individual gas law . The combined gas law is formed from Boyle's Law, Charles' Law, and Gay-Lussac's Law.
/apparatus-to-measure-pressure-with-foot-pump-showing-boyle-s-law-the-volume-of-mass-of-gas-at-a-fixed-temperature-will-change-in-relation-to-the-pressure-dor37402-57b5d3563df78cd39c8c0a55.jpg)
What is Boyle's law simple definition?
Definition of Boyle's law : a statement in physics: the volume of a gas at constant temperature varies inversely with the pressure exerted on it.
What is Boyle's law and Charles law explain?
Boyle's Law tells us that the volume of gas increases as the pressure decreases. Charles' Law tells us that the volume of gas increases as the temperature increases. And Avogadro's Law tell us that the volume of gas increases as the amount of gas increases.
What is Boyle's law with example?
As long as the temperature and number of moles of gas remain constant, Boyle's law means doubling the pressure of a gas halves its volume. Here are more examples of Boyle's law in action: When the plunger on a sealed syringe is pushed, the pressure increases and the volume decreases.
What is the formula for Charles Law and Boyle's law?
Boyle's law—named for Robert Boyle—states that, at constant temperature, the pressure P of a gas varies inversely with its volume V, or PV = k, where k is a constant. Charles's law—named for J. -A. -C.
What is the other name of Charles Law?
Charles's law (also known as the law of volumes) is an experimental gas law that describes how gases tend to expand when heated.
Which statement best describes Boyle's law?
The temperature of fixed mass of gas at a constant pressure is inversely proportional to its volume.
Why is Boyle's law important?
Boyle's law is important because it tells us about the behavior of gasses. It explains, with certainty, that the pressure and volume of gas are inversely proportional to one another. So, if you push on gas, its volume becomes smaller and the pressure becomes higher.
Who discovered Boyle's law?
Robert BoyleKnown for his law of gases, Boyle was a 17th-century pioneer of modern chemistry. Every general-chemistry student learns of Robert Boyle (1627–1691) as the person who discovered that the volume of a gas decreases with increasing pressure and vice versa—the famous Boyle's law.
What is Boyle's law class 11?
Boyle's law is a gas law which states that the pressure exerted by a gas (of a given mass, kept at a constant temperature) is inversely proportional to the volume occupied by it.
How is Boyle's law and Charles Law similar?
Answer and Explanation: Boyle's law and Charles' law both speak about the temperature, volume, and pressure of gases though they establish different relationships between these three variables.
What is gas law class 11?
The law states that at a constant volume, the pressure of the gas is directly proportional to the temperature for a given gas.
What is Charles Law graph?
The graph of Charles's law is a volume-temperature graph. And it is as follows: The plot in the volume vs temperature (in K) graph is a straight line passing through the origin. The above graph is a volume vs temperature graph plotted as a constant pressure for a fixed amount of gas.
Which law states that the pressure exerted by a given gas is proportional to its density?
Boyle’s law—that the pressure exerted by a given gas is proportional to its density if the temperature is kept constant as the gas is compressed or expanded—follows immediately from Bernoulli’s assumption that the mean speed of the molecules is determined by temperature alone. Departures from…
What is the name of the first gas law?
See Article History. Alternative Titles: Mariotte’s law, first gas law. Boyle ’s law, also called Mariotte’s law , a relation concerning the compression and expansion of a gas at constant temperature. This empirical relation, formulated by the physicist Robert Boyle in 1662, states that the pressure ...
What is the relationship between pressure and volume?
This empiricalrelation, formulated by the physicist Robert Boylein 1662, states that the pressure(p) of a given quantity of gas varies inversely with its volume (v) at constant temperature; i.e., in equation form, pv= k, a constant. The relationship was also discovered by the French physicist Edme Mariotte(1676).
Who discovered the relationship between volume and pressure?
The relationship was also discovered by the French physicist Edme Mariotte (1676). Boyle's law, showing the relationship between volume and pressure when mass and temperature are held constant. The law can be derived from the kinetic theory of gases assuming a perfect (ideal) gas ( see perfect gas ).
Who first described the elastic properties of gas?
The first is Boyle’s law, which refers to the elastic properties of the gas; it was described by the Anglo-Irish scientist Robert Boyle in 1662 in his famous “ . . . Experiments . . . Touching the Spring of the Air . . . .” It states…
Do real gases obey Boyle's law?
Real gases obey Boyle’s law at sufficiently low pressures, although the product pv generally decreases slightly at higher pressures, where the gas begins to depart from ideal behaviour. Demonstration of Boyle's law showing that for a given mass, at constant temperature, the pressure times the volume is a constant.
Who developed Boyle's law?
Daniel Bernoulli (in 1737–1738) derived Boyle's law by applying Newton's laws of motion at the molecular level. It remained ignored until around 1845, when John Waterston published a paper building the main precepts of kinetic theory; this was rejected by the Royal Society of England. Later works of James Prescott Joule, Rudolf Clausius and in particular Ludwig Boltzmann firmly established the kinetic theory of gases and brought attention to both the theories of Bernoulli and Waterston.
What are the laws of gas?
Other gas laws : 1 Dalton's law – Gas law describing pressure contributions of component gases in a mixture 2 Charles's law – Relationship between volume and temperature of a gas at constant pressure
What is the relationship between kinetic theory and ideal gases?
Boyle's law states that at constant temperature the volume of a given mass of a dry gas is inversely proportional to its pressure. Most gases behave like ideal gases at moderate pressures and temperatures.
How was the law of motion derived?
Boyle (and Mariotte) derived the law solely by experiment. The law can also be derived theoretically based on the presumed existence of atoms and molecules and assumptions about motion and perfectly elastic collisions (see kinetic theory of gases ). These assumptions were met with enormous resistance in the positivist scientific community at the time, however, as they were seen as purely theoretical constructs for which there was not the slightest observational evidence.
What is the law of inverse relationship?
Or Boyle's law is a gas law, stating that the pressure and volume of a gas have an inverse relationship.
What happens to the pressure of gas as volume increases?
This equation shows that, as volume increases, the pressure of the gas decreases in proportion. Similarly, as volume decreases, the pressure of the gas increases. The law was named after chemist and physicist Robert Boyle, who published the original law in 1662.
What is the law of pressure and volume?
The equation states that the product of pressure and volume is a constant for a given mass of confined gas and this holds as long as the temperature is constant. For comparing the same substance under two different sets of conditions, the law can be usefully expressed as:
Density & Pressure Relation with Boyles Law
Boyle’s experiments show that gases are very compressible when carried out in a quantitative manner. This is due to the fact that as a gas’s mass is reduced, the same number of molecules occupy a smaller space.
Conclusion
Despite the fact that Boyle’s law describes the behavior of an ideal gas, it may be applied to real gases at regular temperatures and pressures. Gases begin to depart from any version of the ideal gas law as temperature and pressure rise.
Why is the gas law called the Boyle-Mariotte law?
The gas law is sometimes called Mariotte's law or the Boyle-Mariotte law because French physicist Edme Mariotte independently discovered the same law in 1679.
How does Boyle's law work?
Boyle's law may be applied to explain how people breathe and exhale air. When the diaphragm expands and contracts, lung volume increases and decreases, changing the air pressure inside of them. The pressure difference between the interior of the lungs and the external air produces either inhalation or exhalation.
Who wrote the law of pressure?
Updated August 05, 2019. Boyle's law states that the pressure of an ideal gas increases as its container volume decreases. Chemist and physicist Robert Boyle published the law in 1662.
What is Boyle’s gas law formula?
This empirical relation, formulated by the physicist Robert Boyle in 1662, states that the pressure (p) of a given quantity of gas varies inversely with its volume (v) at constant temperature; i.e., in equation form, pv = k, a constant. The relationship was also discovered by the French physicist Edme Mariotte (1676).
How does Boyle’s law affect everyday life?
If you decrease its pressure, its volume increases. You can observe a real-life application of Boyle’s Law when you fill your bike tires with air. When you pump air into a tire, the gas molecules inside the tire get compressed and packed closer together.
What are the three gas laws?
The gas laws consist of three primary laws: Charles’ Law, Boyle’s Law and Avogadro’s Law (all of which will later combine into the General Gas Equation and Ideal Gas Law).
What is the difference between Charles Law and Boyle’s law?
Charles Law is a direct relationship between temperature and volume. … The differences are that Boyle’s Law is a direct relationship while Charles Law is an inverse relationship. Both laws involve volume but one involves pressure and the other temperature.17 мая 2018 г.
Does Boyle’s law have to be in ATM?
There are also two volume variables; they also must have the same unit. … Its pressure changes to 1.93 atm.
Important Things to Consider
The gas law described in this article only applies to ideal gases, which you can read about on our article, The Ideal Gas Law.
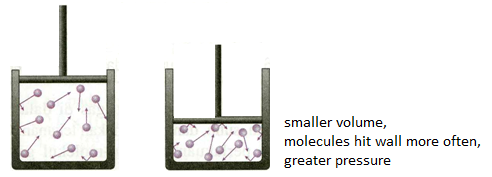
Relationship Between Pressure and Volume
Consider a sample of gas in a 1-liter container. From our article, What is Pressure, we know that the pressure exerted on the container from the gas is the sum of the collisions of the particles, divided by the surface area of the container, .
Change in Pressure and Volume
This proportionality can enable us to solve specific problems relating to the changes in pressure and volume in a closed system.
What is Boyle's law?
Boyle’s law is a gas law that describes the relationship between the pressure and volume of gas for a mass and temperature. This law is the mechanism by which the human respiratory system functions. Boyle’s law is equivalent to PV = K (P is pressure, V is volume, K is a constant), or one may state that pressure is inversely proportional to the volume.
How does Boyle's law affect diving?
As a diver descends in the water, the pressure on the person’s lungs increases, and therefore according to Boyle’s law, the volume of air inside the lungs must decrease. As the diver ascends in the water and the pressure on the thoracic cage decreases, the volume of air increases. It is important to exhale steadily to release the volume of the gas if this does not occur the diver can experience pulmonary barotrauma which is overexpansion and alveolar rupture. The diver may have a pneumothorax (chest pain, dyspnea, unilateral decreased breath sounds) or pneumomediastinum (neck pain, pleuritic chest pain, dyspnea, coughing; there may be subcutaneous emphysema causing a crepitation on palpation). [6]
What organ system is involved in Boyle's law?
The primary organ system involved in the usage of Boyle’s law is the respiratory system. The human body brings air into the lungs by negative pressure. At baseline, the thoracic cavity is in static equilibrium with an intrapleural pressure near -5cmH2O. During inspiration, there is a contraction of inspiratory muscles (diaphragm, external intercostal muscles; additional muscles such as the scalene and sternocleidomastoid can take part under specific circumstances) that increases intrathoracic volume. Due to the combined motion of the lungs and the chest wall, the lungs will begin to expand as the thorax expands during inspiration. According to Boyle’s law, as the volume increases the pressure must decrease, therefore as the intrapleural volume increases, the intrapleural pressure decreases to about -8cm H2O occurs at end inspiration. [1]
What is the law of syringes?
Boyle’s law also applies when using a medical syringe. When the cylinder on the syringe is empty, it is said to be in a neutral state as there is no air in the syringe. As one pulls back on the plunger, the volume in the cylinder increases, therefore by Boyle’s law the pressure decreases. The liquid is thus drawn into the cylinder to balance the pressure within the syringe and outside of the syringe.
Which law leads to errors in the measurement of thoracic gas volume?
The simplified version of Boyle's Law leads to errors in the measurement of thoracic gas volume. [Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1995]
Do lungs follow Boyle's law?
The lungs do not follow Boyle’s law at all volumes. In a resting state with a normal tidal volume, when the alveoli are not collapsed nor are the lungs at maximal capacity, the lungs follow proportional changes of volume and pressure in accordance to Boyle’s law. At low lung volumes, it takes a large pressure change to make small changes in the volume (low compliance of lung tissue). At high volumes within the lung, it takes a more negative pressure to expand the tissue, once again not in compliance with a direct relationship as Boyle’s law dictates. At low and high volumes, the lung has low compliance meaning that the ability of the tissue to expand or its elasticity decreases (compliance = [change in volume]/[change in pressure]). [1]

Overview
Definition
The law itself can be stated as follows:
For a fixed mass of an ideal gas kept at a fixed temperature, pressure and volume are inversely proportional.
Or Boyle's law is a gas law, stating that the pressure and volume of a gas have an inverse relationship. If volume increases, then pressure decreases and vice …
History
This relationship between pressure and volume was first noted by Richard Towneley and Henry Power in the 17th century. Robert Boyle confirmed their discovery through experiments and published the results. According to Robert Gunther and other authorities, it was Boyle's assistant, Robert Hooke, who built the experimental apparatus. Boyle's law is based on experiments with air, whic…
Human breathing system
Boyle's law is often used as part of an explanation on how the breathing system works in the human body. This commonly involves explaining how the lung volume may be increased or decreased and thereby cause a relatively lower or higher air pressure within them (in keeping with Boyle's law). This forms a pressure difference between the air inside the lungs and the environmental air pressure, which in turn precipitates either inhalation or exhalation as air move…
See also
Related phenomena:
• Water thief
• Industrial Revolution
• Steam engine
Other gas laws:
External links
• Media related to Boyle's Law at Wikimedia Commons