
FATTY ACIDS (C8 - C18 AND C18 UNSATURATED) It is widely used as a lubricant and as an additive in industrial preparations. It is used in the manufacture of metallic stearates, pharmaceuticals, soaps, cosmetics, and food packaging. It is also used as a softener, accelerator activator and dispersing agent in rubbers.
What are the names of fatty acids?
essential fatty acids were originally designated as Vitamin F, until it was realized that they must be classified with the fats.3 There are two fatty acids designated as essential fatty acids: linoleic acid and alpha-linolenic acid. This does not mean that the other 15 or so fatty acids found in the omega 3, 6 and 9 groups aren’t
What are essential fatty acids examples?
What are essential fatty acids examples?
- gamma-linolenic acid or GLA (18:3n-6)
- dihomo-gamma-linolenic acid or DGLA (20:3n-6)
- arachidonic acid or AA (20:4n-6)
What are the benefits of fatty acids?
These benefits address:
- Triglycerides: Omega-3s can cause a major reduction in triglycerides, usually in the range of 15–30% ( 25, 26, 27 ).
- Blood pressure: Omega-3s can reduce blood pressure levels in people with high blood pressure ( 25, 28 ).
- “Good” HDL cholesterol: Omega-3s can raise “good” HDL cholesterol levels ( 29, 30, 31 ).
What is cis trans fatty acid?
Unsaturated fats come in a ‘cis’ form and a ‘trans’ form, according to the arrangement of the carbon chains across one or more double bonds. Trans fats are unsaturated fats with trans double bonds instead of cis bonds. The type of bond affects the shape of the fatty acid chain.
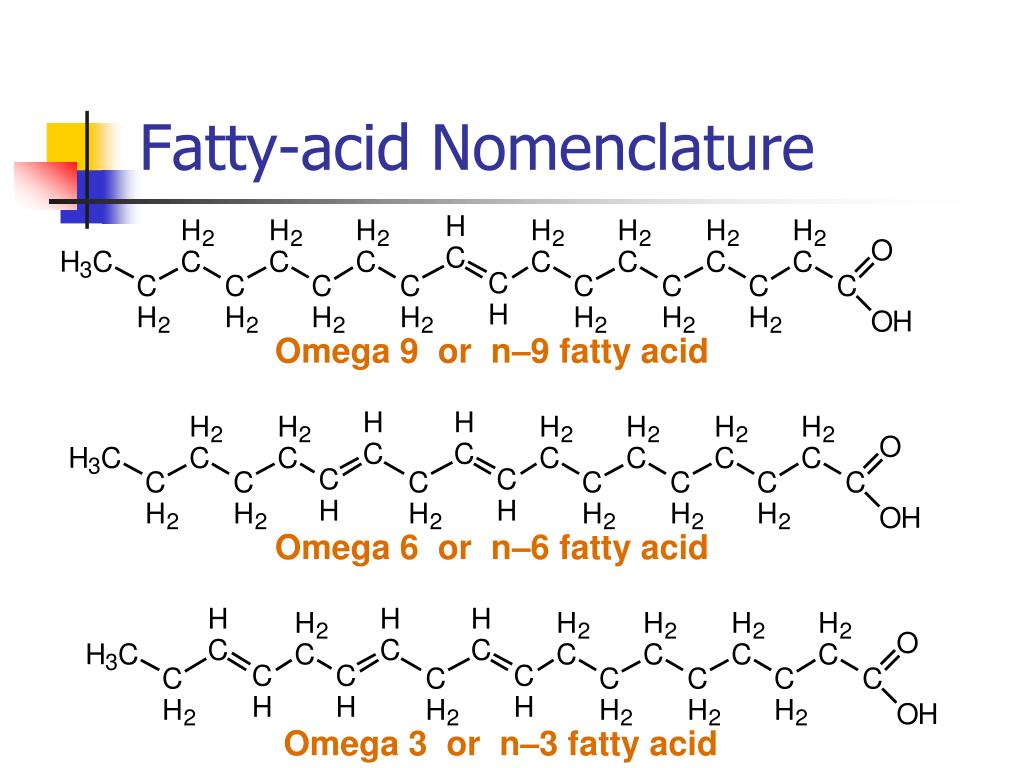
What is C18 2 fatty acid?
Linoleic acidNamesPreferred IUPAC name (9Z,12Z)-Octadeca-9,12-dienoic acidOther names cis,cis-9,12-Octadecadienoic acid C18:2 (Lipid numbers)IdentifiersCAS Number60-33-333 more rows
Is stearic acid a C18?
As its ester, stearic acid is one of the most common saturated fatty acids found in nature following palmitic acid. The triglyceride derived from three molecules of stearic acid is called stearin....Stearic acid.NamesOther names Stearic acid C18:0 (Lipid numbers)IdentifiersCAS Number57-11-43D model (JSmol)Interactive image52 more rows
What is C22 fatty acid?
Docosahexaenoic acid (C22:6 omega 3) and linoleic acid are anti-aggregatory, and alter arachidonic acid metabolism in human platelets. Prostaglandins Leukot Med.
What is C6 fatty acid?
Hexanoic acid is a C6, straight-chain saturated fatty acid. It has a role as a human metabolite and a plant metabolite. It is a straight-chain saturated fatty acid and a medium-chain fatty acid. It is a conjugate acid of a hexanoate.
What type of fat is stearic acid?
saturated fatty acidStearic acid is a long-chain saturated fatty acid.
Is stearic acid an omega 3 fatty acid?
Stearic acid, C18:0, saturated. Oleic acid, C18:1, omega-9. Linolic acid, C18:2, omega-6.
What is a C20 fatty acid?
Eicosenoic acid C20:1, a monounsaturated fatty acid that exists in three different forms: 9-eicosenoic acid (gadoleic acid), an omega-11 fatty acid common in fish oils, 11-eicosenoic acid (gondoic acid), an omega-9 fatty acid characteristic of jojoba oil, and 13-eicosenoic acid (paullinic acid), an omega-7 fatty acid.
What is CH3 CH2 4CH CHCH2CH CH CH2 7COOH?
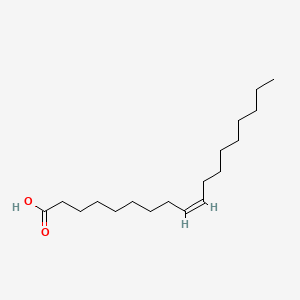
oleic acid CH3(CH2)7CH=CH(CH2)7COOH 16 linoleic acid CH3(CH2)4CH=CHCH2CH=CH(CH2)7COOH -5 linolenic acid CH3CH2CH=CHCH2CH=CHCH2CH=CH(CH2)7COOH -11 m.p. Double bonds. are cis. Fatty acids always contain an even number of carbons and are invariably straight chain rather than branched.
What does hexanoic acid smell like?
Caproic acid, also known as hexanoic acid, is the carboxylic acid derived from hexane with the chemical formula CH 3(CH 2) 4COOH. It is a colorless oily liquid with an odor that is fatty, cheesy, waxy, and like that of goats or other barnyard animals.
What does C18 0 mean?
C18:0 means that the carbon chain of the fatty acid consists of 18 carbon atoms and there are no (zero) double bonds in it, whereas C18:1 describes an 18-carbon chain with one double bond in it.
What is C8 MCT oil?
Brain Octane C8 MCT Oil is, it turns out, a refined coconut oil made by the brand Bulletproof. The oil consists of 100 per cent octanoic acid, a fatty acid with 8 carbon atoms that's also known as caprylic acid or C8 and falls into the category of medium-chain triglycerides or MCTs.
What is the simplest 18 carbon fatty acid?
Terms in this set (32)Stearic acid and Oleic acid. is the simplest 18-carbon saturated fatty acid., an 18-carbon monounsaturated fatty acid. oleic acid.Tropical oils. A source of medium-chain saturated fatty acids.Stearic acid. A long-chain saturated fatty acid.Canola oil. ... Lecithin. ... Cholesterol. ... Liver.More items...
What is the caloric content of stearic acid in Cal G?
Stearin has a heat of combustion of -35 663 kJ/mol, so 1 g produces (35 663 kJ/mol) / (891.48 g/mol) x (1 Cal / 4.184 kJ) = 9.57 Cal.
How many acetyl CoA molecules will be produced after complete oxidation of a stearic acid c18 molecule?
For an 18-Carbon saturated fatty acid (stearic acid), it will produce 9 Acety-CoA.
What is the formula for stearic acid?
C18H36O2Stearic acid / FormulaStearic acid ( STEER-ik, stee-ARR-ik) is a saturated fatty acid with an 18-carbon chain. The IUPAC name is octadecanoic acid. It is a waxy solid and its chemical formula is C17H35CO2H. Its name comes from the Greek word στέαρ "stéar", which means tallow.
What is stearic acid in chemistry?
Stearic acid, another name for octadecanoic acid CH3(CH2)16COOH, is one of the most common fatty acids. It exists as a glycerol ester in most animal and plant fats (Beare-Rogers, Dieffenbacher, & Holm, 2001). Stearic acid is more abundant in animal fat (up to 30%) than vegetable fat (typically <5%).
When was fatty acid first used?
The concept of fatty acid ( acide gras) was introduced in 1813 by Michel Eugène Chevreul, though he initially used some variant terms: graisse acide and acide huileux ("acid fat" and "oily acid").
Which type of fatty acid has a C-C double bond?
Unsaturated fatty acids have one or more C=C double bonds. The C=C double bonds can give either cis or trans isomers.
How are fatty acids classified?
Fatty acids are classified in many ways: by length, by saturation vs unsaturation, by even vs odd carbon content, and by linear vs branched.
What is the formula for saturated fatty acids?
Saturated fatty acids have no C=C double bonds. They have the same formula CH 3 (CH 2) n COOH, with variations in "n". An important saturated fatty acid is stearic acid (n = 16), which when neutralized with lye is the most common form of soap .
What is a fatty acid?
In chemistry, particularly in biochemistry, a fatty acid is a carboxylic acid with a long aliphatic chain , which is either saturated or unsaturated. Most naturally occurring fatty acids have an unbranched chain of an even number of carbon atoms, from 4 to 28. Fatty acids are a major component of the lipids ...
Which fatty acids are susceptible to degradation by ozone?
Unsaturated fatty acids are susceptible to degradation by ozone. This reaction is practiced in the production of azelaic acid ( (CH 2) 7 (CO 2 H) 2) from oleic acid.
How to find the position of carbon atoms in fatty acids?
The position of the carbon atoms in the backbone of a fatty acid are usually indicated by counting from 1 at the −COOH end. Carbon number x is often abbreviated C- x (or sometimes C x ), with x =1, 2, 3, etc. This is the numbering scheme recommended by the IUPAC .
Overview
Types of fatty acids
Fatty acids are classified in many ways: by length, by saturation vs unsaturation, by even vs odd carbon content, and by linear vs branched.
• Short-chain fatty acids (SCFA) are fatty acids with aliphatic tails of five or fewer carbons (e.g. butyric acid).
• Medium-chain fatty acids (MCFA) are fatty acids with aliphatic tails of 6 to 12 carbons, which can form medium-chain triglycerides.
History
The concept of fatty acid (acide gras) was introduced in 1813 by Michel Eugène Chevreul, though he initially used some variant terms: graisse acide and acide huileux ("acid fat" and "oily acid").
Nomenclature
Most naturally occurring fatty acids have an unbranched chain of carbon atoms, with a carboxyl group (–COOH) at one end, and a methyl group (–CH3) at the other end.
The position of each carbon atom in the backbone of a fatty acid is usually indicated by counting from 1 at the −COOH end. Carbon number x is often abb…
Production
Fatty acids are usually produced industrially by the hydrolysis of triglycerides, with the removal of glycerol (see oleochemicals). Phospholipids represent another source. Some fatty acids are produced synthetically by hydrocarboxylation of alkenes.
Hyper-oxygenated fatty acids are produced by a specific industrial processes for topical skin creams. The process is based on the introduction or saturation of peroxides into fatty acid ester…
Reactions of fatty acids
Fatty acids exhibit reactions like other carboxylic acids, i.e. they undergo esterification and acid-base reactions.
Fatty acids do not show a great variation in their acidities, as indicated by their respective pKa. Nonanoic acid, for example, has a pKa of 4.96, being only slightly weaker than acetic acid (4.76). As the chain length increases, the solubility of the fatty acids in water decreases, so that the lon…
Circulation
Short- and medium-chain fatty acids are absorbed directly into the blood via intestine capillaries and travel through the portal vein just as other absorbed nutrients do. However, long-chain fatty acids are not directly released into the intestinal capillaries. Instead they are absorbed into the fatty walls of the intestine villi and reassemble again into triglycerides. The triglycerides are coated with cholesterol and protein (protein coat) into a compound called a chylomicron.
Analysis
The chemical analysis of fatty acids in lipids typically begins with an interesterification step that breaks down their original esters (triglycerides, waxes, phospholipids etc.) and converts them to methyl esters, which are then separated by gas chromatography. or analyzed by gas chromatography and mid-infrared spectroscopy.
Separation of unsaturated isomers is possible by silver ion complemented thin-layer chromatogr…