
Is caesium a metal or nonmetal?
Caesium (IUPAC spelling) (also spelled cesium in American English) is a chemical element with the symbol Cs and atomic number 55. It is a soft, silvery-golden alkali metal with a melting point of 28.5 °C (83.3 °F), which makes it one of only five elemental metals that are liquid at or near room temperature.
What is the chemical symbol for caesium?
The chemical symbol for Caesium is Cs. Caesium is a soft, silvery-gold alkali metal with a melting point of 28.5 °C, which makes it one of only five elemental metals that are liquid at or near room temperature. Caesium has physical and chemical properties similar to those of rubidium and potassium.
Is caesium a solid liquid or gas?
Caesium is a soft, silvery-gold alkali metal with a melting point of 28.5 °C, which makes it one of only five elemental metals that are liquid at or near room temperature. Caesium has physical and chemical properties similar to those of rubidium and potassium.
What is caesium used for?
It is a ready marker of the movement of soil and sediment from those times. Caesium is a relatively rare element, estimated to average 3 parts per million in the Earth's crust. It is the 45th most abundant element and the 36th among the metals.
See more

What kind of metal is cesium?
alkali metalcesium (Cs), also spelled caesium, chemical element of Group 1 (also called Group Ia) of the periodic table, the alkali metal group, and the first element to be discovered spectroscopically (1860), by German scientists Robert Bunsen and Gustav Kirchhoff, who named it for the unique blue lines of its spectrum (Latin ...
Is cesium a pure metal?
Gallium, francium, rubidium, mercury, and cesium are the only pure metals that are liquid at room temperature. Cesium reacts to cold water and ice in an explosive manner.
Does cesium contain metal?
Caesium (IUPAC spelling) (or cesium in American English) is a chemical element with the symbol Cs and atomic number 55. It is a soft, silvery-golden alkali metal with a melting point of 28.5 °C (83.3 °F), which makes it one of only five elemental metals that are liquid at or near room temperature.
Is cesium found pure in nature?
What is Cesium? Cesium is a soft, silvery-golden alkali metal that is liquid just above room temperature. It is rare on Earth and is usually found in minerals that contain other alkali metals. Like all alkali metals, it is very reactive, and so does not exist in nature in its pure form.
How do you make cesium?
Cesium can be isolated by electrolysis of the fused cyanide, by vacuum distillation upon reduction of the chloride by calcium or sodium metal, and by other methods. High purity cesium salts are available for about $100/pound.
Is cesium more expensive than gold?
Per gram, cesium is more expensive than gold, and when it solidifies, it forms delicate crystal structures that even look like gold.
What are the minerals of cesium?
The only economically important source mineral for cesium is pollucite [Cs2Al2Si4O12] which is found in very few places in the world in certain zoned pegmatites and is associated with the more commercially important lithium minerals lepidolite and petalite.
What happens if you touch cesium?
When contact with radioactive cesium occurs, which is highly unlikely, a person can experience cell damage due to radiation of the cesium particles. Due to this, effects such as nausea, vomiting, diarrhoea and bleeding may occur. When the exposure lasts a long time people may even lose consciousness.
What happens if you eat cesium?
HIGHLIGHTS: Exposure to stable or radioactive cesium occurs from ingesting contaminated food or drinking water or breathing contaminated air. High levels of radioactive cesium in or near your body can cause nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, bleeding, coma, and even death.
Where do we get cesium?
Caesium is found in the minerals pollucite and lepidolite. Pollucite is found in great quantities at Bernic Lake,Manitoba, Canada and in the USA, and from this source the element can be prepared. However, most commercialproduction is as a by-product of lithium production.
Does cesium glow in the dark?
In the context of the Goiânia accident, CsCl is described as showing a blue glow in the dark. Still, there is little explanation to be found in terms of the glow's origin.
Which is the softest metal in the world?
CesiumCesium is considered the softest metal, Lead is also considered among the softest metals.
History and Discovery
Caesium is considered the first element who was discovered spectroscopically in 1860 by Robert Bunsen and Gustav Kirchhoff. They also derived its name from Latin caesius ‘’sky-blue’’ due to the formation of unique blue lines in the emission spectrum. [1]
Occurrence
Caesium occurs in minute quantity in earth crust in the form of minerals like pollucite (zeolite mineral Caesium ore). It is mostly present with rubidium in nature and other alkali metals. The abundance of Caesium on the earth crust is about 3 part per million and it is the 50 th most common element in the earth crust [2].
Physical Characteristics
Caesium is a silvery-gold metallic element. It is an extremely soft metal. Caesium is one of four elements who exist in liquid form at or near room temperature. In periodic table it belongs to alkaline elements. Its physical properties are similar with rubidium and potassium. In the presence of mineral oil it loses its metallic luster.
Chemical Characteristics
Caesium is very reactive and pyrophoric (ignites spontaneously in air). It reacts with water vigorously and explosively, even at low temperatures. Caesium resembles rubidium in its chemical characteristics [3]. Caesium can be handled only under an inert gas, such as argon. It is exit in +1 oxidation state.
Significance and Uses
Caesium is used in vacuum tubes as a “getter” to clean the traces of oxygen and other gases when sealed.
Health Hazards
Due to its high reactivity, Caesium is considered as a hazardous metal. People who work in nuclear power station may be exposed to Caesium, otherwise there is no health risk associated with Caesium. People can experience cell damage due to its radiation effects and may suffer from nausea, vomiting, diarrhea and bleeding.
Isotopes of Caesium
It has thirty-nine known isotopes, having atomic masses ranging from 112 to 151. The only stable isotope of Caesium is 133 Cs. Cs-135 has very long half-life of about 2.3 million years.
Uses and properties
The symbol reflects the use of the element in highly accurate atomic clocks.
History
Caesium was almost discovered by Carl Plattner in 1846 when he investigated the mineral pollucite (caesium aluminium silicate). He could only account for 93% of the elements it contained, but then ran out of material to analyse. (It was later realised that he mistook the caesium for sodium and potassium.)
Podcasts
You're listening to Chemistry in its element brought to you by Chemistry World, the magazine of the Royal Society of Chemistry.
Video
Learn Chemistry: Your single route to hundreds of free-to-access chemistry teaching resources.
Cesium
S.C. Gad, T. Pham, in Encyclopedia of Toxicology (Third Edition), 2014
Environmental Geochemistry
M.D. Siegel, C.R. Bryan, in Treatise on Geochemistry (Second Edition), 2014
Time and Frequency
Michael A. Lombardi, in Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology (Third Edition), 2003
Meteorites and Cosmochemical Processes
A.M. Davis, K.D. McKeegan, in Treatise on Geochemistry (Second Edition), 2014
Short-Lived Waste Radionuclides
Michael I. Ojovan, ... Stepan N. Kalmykov, in An Introduction to Nuclear Waste Immobilisation (Third Edition), 2019
Geochemical Behavior of Trace Elements in the Upper and Lower Silesian Basin Coal-Fire Gob Piles of Poland
Glenn B. Stracher, Łukasz Kruszewski, in Coal and Peat Fires: A Global Perspective, 2019
Seabirds As Indicators Of Ocean Pollution
Radionuclides (e.g. cesium) are released from weapon testing and use and from industrial accidents, such as those associated with power-generating facilities. As is the case with many other pollutants, specific radionuclides are taken up in specific tissues. These chemicals are monitored in shellfish with concerns for human consumption.
What is Caesium
Caesium is a chemical element with atomic number 55 which means there are 55 protons and 55 electrons in the atomic structure. The chemical symbol for Caesium is Cs.
Atomic Number of Caesium
Caesium is a chemical element with atomic number 55 which means there are 55 protons and 55 electrons in the atomic structure. The chemical symbol for Caesium is Cs.
Caesium – Crystal Structure
A possible crystal structure of Caesium is body-centered cubic structure.
Physical Properties
It is a soft, silvery-golden alkali metal. It is very ductile, a pale metal which darkens in the presence of trace amounts of oxygen. In the presence of mineral oil (which is used to keep it, during transport), it loses metallic lustre and takes on duller, grey appearance.
Chemical Properties
Caesium metal is highly reactive. It ignites spontaneously in air and reacts explosively with water even at low temperatures. It reacts with ice at temperatures as low as −116 °C. Because of this high reactivity, caesium metal is classified as a hazardous material. It is stored and shipped in dry, saturated hydrocarbons such as mineral oil.
Compounds
Most caesium compounds contain the element as the cation Cs+, which binds ionically to a wide variety of anions. Salts of Cs+ are usually colourless unless the anion itself is coloured. The phosphate, acetate, carbonate, halides, oxide, nitrate, and sulfate salts are water-soluble.
Isotopes
Caesium has 39 known isotopes, ranging in mass number from 112 to 151 but only stable isotope is Caesium-133 with 78 neutrons. Its radioactive Caesium-135 isotope has a very long half-life of about 2.3 million years, the longest of all radioactive isotopes of caesium.
Occurrence
It is a relatively rare element. It is found in few minerals. The only economically important ore for caesium is pollucite Cs (AlSi 2O 6), which is found in a few places around the world in zoned pegmatites, associated with the more commercially important lithium minerals, lepidolite and petalite.
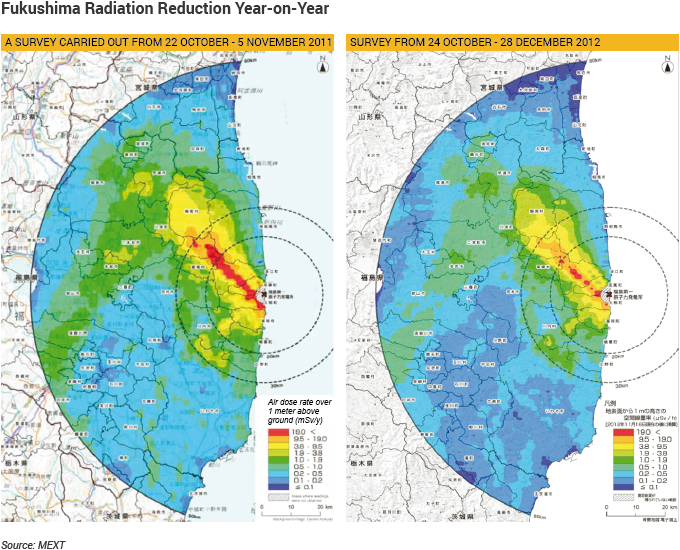
Occurrence
Physical Characteristics
- Caesium is a silvery-gold metallic element. It is an extremely soft metal. Caesium is one of four elements who exist in liquid form at or near room temperature. In periodic table it belongs to alkaline elements. Its physical properties are similar with rubidium and potassium. In the presence of mineral oil it loses its metallic luster. It has the m...
Chemical Characteristics
- Caesium is very reactive and pyrophoric (ignites spontaneously in air). It reacts with water vigorously and explosively, even at low temperatures. Caesium resembles rubidium in its chemical characteristics . Caesium can be handled only under an inert gas, such as argon. It is exit in +1 oxidation state. In compounds it is present as Cs+ and binds ionically with anions. Its salts are u…
Significance and Uses
- Caesium is used in vacuum tubes as a “getter” to clean the traces of oxygen and other gases when sealed.
- Caesium compounds with chlorides are used in photoelectric cells.
- Caesium is used in industries as a catalyst promoter.
- Caesium nitrate is used to make optical glasses.
Health Hazards
- Due to its high reactivity, Caesium is considered as a hazardous metal. People who work in nuclear power station may be exposed to Caesium, otherwise there is no health risk associated with Caesium. People can experience cell damage due to its radiation effects and may suffer from nausea, vomiting, diarrhea and bleeding.
Isotopes of Caesium
- It has thirty-nine known isotopes, having atomic masses ranging from 112 to 151. The only stable isotope of Caesium is 133Cs. Cs-135 has very long half-life of about 2.3 million years.