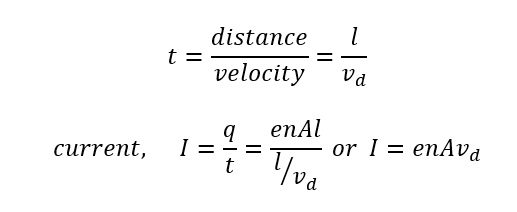
How do you calculate drift velocity?
How do you calculate drift?
- Find the distance to your destination in nautical miles.
- Divide this distance by your average speed in knots.
- Multiply this time by the average speed (drift) of the current.
- From your destination, plot the set of the current.
What are the factors on which drift velocity depends?
It depends upon the following factors:
- Mass of the object
- The acceleration due to gravity
- Surface area
- 5K views
What does drift velocity mean?
The drift velocity refers to the average velocity obtained by a particle, such as an electron, as a result of an electric field’s action. Because the movement or motion of the particle is believed to be in a plane, the axial drift velocity can be used to describe the motion.
What is DIRFT velocity?
In physics, the drift velocity refers to the average velocity reached by electrons and other kinds of charged particles in a given material because of an electric field. Generally, electrons in conductors tend to randomly propagate at the Fermi velocity.

What is meant by velocity?
Velocity is the rate at which bodies change their position relative to a frame of reference (rate change of position). Velocity can be described as...
What is meant by drift velocity?
It is the average velocity acquired by a charged particle (like an electron or proton) in the body due to an electric field. Usually, an electron i...
What is meant by electron mobility?
Electron mobility is generally stated as drift velocity per unit electric field.
What is the formula to find the drift velocity?
The formula is, I = nAvQ Here, I – the current flowing through the conductor n – the number of electrons A – the area of the cross-section of...
What are the characteristics of drift velocity?
Drift velocity is directly proportional to current. When an electric field is exerted over a conductor, the electrons jump towards the high potent...
What is a drift velocity in physics?
Drift velocity in physics is the motion of charged particles in a material acted upon by an electric field. Charged particles experience a net velo...
How do you calculate drift velocity?
The drift velocity can be calculated using the current, the density of charge carriers, the cross-sectional area of the wire, and the charge of an...
Why is it called drift velocity?
The velocity of charged particles in an electric field is called drift velocity because it is a small net flow in one direction. This drift is prop...
What is meant by drift velocity?
Drift velocity is the average velocity of charged particles due to an electric field. Charged particles propagate randomly unless acted upon by an...
Drift velocity
The name is drift velocity because the electron drifts in the opposite direction of the electric field at low velocity and at high thermal velocities between two collisions. The drift velocity refers to the average velocity obtained by a particle, such as an electron, as a result of an electric field’s action.
Relaxation time (τ)
The time interval between two successive collisions of electrons with the positive ions in the metallic lattice is defined as relaxation time.
Mobility (μ)
Electron mobility is defined as “drift velocity per unit electric field.
Relation between Current Density and Drift velocity
The current density is defined as ” The whole current supplying throughout a cross-sectional conductor unit within a unit of time.
Sample problems
Drift velocity is defined as “The Average velocity with which the free electrons get drifted towards the positive end of the conductor under the influence of an external electric field.”
What is drift velocity?
In physics a drift velocity is the average velocity attained by charged particles, such as electrons, in a material due to an electric field. In general, an electron in a conductor will propagate randomly at the Fermi velocity, resulting in an average velocity of zero.
How fast do electrons flow in a switch?
By comparison, the Fermi flow velocity of these electrons (which, at room temperature, can be thought of as their approximate velocity in the absence of electric current) is around 1570 km/s.
How many atoms are in 1 m3 of copper?
In one mole of any element there are 6.022 × 1023 atoms (the Avogadro number ). Therefore, in 1 m3 of copper there are about 8.5 × 1028 atoms ( 6.022 × 1023 × 140 685.5 mol/m3 ).
When a potential difference is applied across a conductor, what happens?
When a potential difference is applied across a conductor, free electrons gain velocity in the direction opposite to the electric field between successive collisions (and lose velocity when traveling in the direction of the field), thus acquiring a velocity component in that direction in addition to its random thermal velocity. ...
Is drift velocity proportional to current?
Drift velocity is proportional to current. In a resistive material it is also proportional to the magnitude of an external electric field. Thus Ohm's law can be explained in terms of drift velocity. The law's most elementary expression is:
Is current density vector?
But the current density and drift velocity, j and u, are in fact vectors, so this relationship is often written as:
What is the Drift Velocity of an Electron?
Electrons will be the primary focus of this lesson, however, ions and positively charged holes are also charged carriers.
What is the term for how quickly an electron can move through metal in the presence of an electric field?
Electron mobility describes how quickly an electron can move through metal in the presence of an electric field. The mobility is dependent on the drift velocity and the magnitude of the electric field. The equation for electron mobility is
How does electricity appear instantaneous when a switch is flipped?
As soon as a switch is flipped, electrons are added to a circuit. These electrons interact with electrons already in the circuit through electromagnetic fields. The closer two electrons are, the stronger they repel each other. This effect propagates through the wires in a circuit much more rapidly than the actual electrons. The velocity with which these effects propagate is close to the speed of light. This is why electricity appears instantaneous when flipping a switch.
Why is the velocity of charged particles in an electric field called drift velocity?
The velocity of charged particles in an electric field is called drift velocity because it is a small net flow in one direction. This drift is proportional to the current in the material and the magnitude of the electric field.
How do electrons move in a material?
Without an applied electric field, electrons move around randomly in a material. Focusing on any one electron in a material, it moves in many different directions. This is true for every electron in the material, meaning that there is no overall motion in any particular direction over time. The diagram illustrates this idea. Every electron will follow a path similar to that shown in red.
How to calculate drift velocity?
The drift velocity can be calculated using the current, the density of charge carriers, the cross-sectional area of the wire, and the charge of an electron. It is given by: v_d = frac {I} {nAq}
What is drift velocity?
Drift velocity in physics is the motion of charged particles in a material acted upon by an electric field. Charged particles experience a net velocity in one direction in an electric field, called the drift velocity.
What happens to electrons when they collide?
In a conductor, electrons move randomly as gas molecules. During this motion, they collide with each other. The relaxation time of the electron is the time required by the electron to return to its initial equilibrium value after the collision.
How long does it take an electron to pass through a conductor?
The drift velocity of an electron is very small usually in terms of 10 -1 m/s. Thus, with this amount of velocity, it will take an electron usually 17 mins to pass through a conductor of length one meter. That means if we switch on an electric bulb it should turn on after 17 mins.
What direction do electrons move?
The electron will move in the direction of the applied electric field. Here electron does not give up its randomness of motion but shifts towards higher potential with their random motion.
Why can't we turn on the electric bulb?
This is because the speed of the electric current does not depend on the drift velocity of the electron. Electric current moves with a speed of light. It is not established with the drift velocity of the electrons in the material.
What is the term for the time for which electrons can move freely between successive collisions with other ions?
Larger the electric field time, more the time needed by electrons to come to initial equilibrium after the field is removed. Relaxation time is also defined as the time for which the electron can move freely between successive collisions with other ions.
How to find drift velocity of electrons?
When electrons with density n and charge Q causes a current ‘I’ to flow through a conductor of cross-sectional area A, Drift velocity v can be calculated through the formula I = nAvQ.
Why does the average velocity of electrons in a material become zero?
It was observed that when a potential difference is applied to the ends of a material, electrons present in the material acquire a certain amount of velocity which causes a small net flow in one direction.
What causes electrons to drift in the direction shown?
But there is an electric field in the conductor that causes the electrons to drift in the direction shown (opposite to the field, since they are negative). The drift velocity vd v d is the average velocity of the free charges. Drift velocity is quite small, since there are so many free charges.
How to calculate drift velocity?
We can calculate the drift velocity using the equation I = nqAvd I = n q A v d . The current I = 20.0 A I = 20.0 A is given, and q = –1.60 × 10–19C q = – 1.60 × 10 – 19 C is the charge of an electron. We can calculate the area of a cross-section of the wire using the formula A = πr2, A = π r 2, where r r is one-half the given diameter, 2.053 mm. We are given the density of copper, 8.80 × 103 kg/m3, 8.80 × 10 3 kg/m 3, and the periodic table shows that the atomic mass of copper is 63.54 g/mol. We can use these two quantities along with Avogadro’s number, 6.02× 1023 atoms/mol, 6.02 × 10 23 atoms/mol, to determine n, n, the number of free electrons per cubic meter.
How to find the drift velocity of a wire?
All the charges in the shaded volume of this wire move out in a time t t, having a drift velocity of magnitude vd = x/t v d = x / t. See text for further discussion.
Why are conductors of electricity and heat good conductors?
This is because large numbers of free electrons can carry electrical current and can transport thermal energy. The free-electron collisions transfer energy to the atoms of the conductor.
How does an electric field work?
The electric field does work in moving the electrons through a distance, but that work does not increase the kinetic energy (nor speed, therefore) of the electrons . The work is transferred to the conductor’s atoms, possibly increasing temperature. Thus a continuous power input is required to keep a current flowing.
What is the magnitude of drift velocity?
Note that x/Δt x / Δ t is the magnitude of the drift velocity, vd v d, since the charges move an average distance x x in a time Δt Δ t. Rearranging terms gives
What does the minus sign mean in a signal?
The minus sign indicates that the negative charges are moving in the direction opposite to conventional current. The small value for drift velocity (on the order of 10−4 m/s 10 − 4 m/s) confirms that the signal moves on the order of 1012 10 12 times faster (about 108 m/s 10 8 m/s) than the charges that carry it.

Overview
In physics, a drift velocity is the average velocity attained by charged particles, such as electrons, in a material due to an electric field. In general, an electron in a conductor will propagate randomly at the Fermi velocity, resulting in an average velocity of zero. Applying an electric field adds to this random motion a small net flow in one direction; this is the drift.
Drift velocity is proportional to current. In a resistive material, it is also proportional to the magnit…
Experimental measure
The formula for evaluating the drift velocity of charge carriers in a material of constant cross-sectional area is given by:
where u is the drift velocity of electrons, j is the current density flowing through the material, n is the charge-carrier number density, and q is the charge on the charge-carrier.
This can also be written as:
Numerical example
Electricity is most commonly conducted through copper wires. Copper has a density of 8.94 g/cm and an atomic weight of 63.546 g/mol, so there are 140685.5 mol/m . In one mole of any element, there are 6.022×10 atoms (the Avogadro number). Therefore, in 1 m of copper, there are about 8.5×10 atoms (6.022×10 × 140685.5 mol/m ). Copper has one free electron per atom, so n is equal to 8.5×10 electrons per cubic metre.
See also
• Flow velocity
• Electron mobility
• Speed of electricity
• Drift chamber
• Guiding center
External links
• Ohm's Law: Microscopic View at Hyperphysics