What is caput succedaneum in labour?
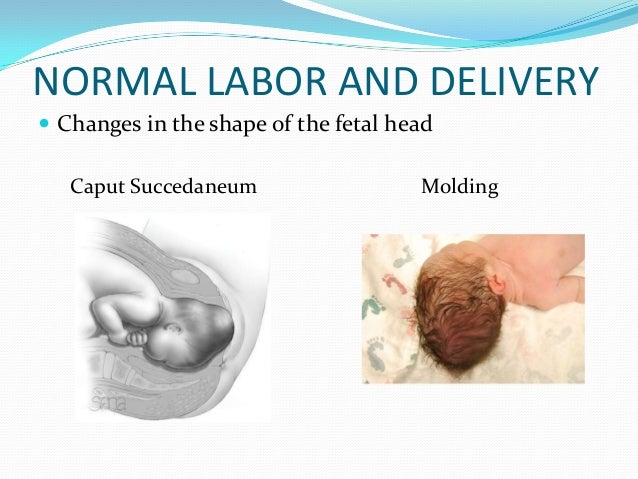
Caput succedaneum is a diffuse swelling of the scalp caused by the pressure of the scalp against the dilating cervix during labour. It may extend over the midline (as opposed to cephalhaematoma) and is associated with moulding of the head. Caput can make it difficult to define the position of the fetal head.
What is caput in fetal anatomy?
It may extend over the midline (as opposed to cephalhaematoma) and is associated with moulding of the head. Caput can make it difficult to define the position of the fetal head.
What are the symptoms of Caput succedaneum during labor?
Prolonged pressure from the dilated cervix or vaginal walls on the baby’s head causes swelling, puffiness, and bruising. These are hallmark symptoms of caput succedaneum. A long, difficult labor with a lot of pushing can cause this condition.
What are caput Medu´SAE?
caput medu´sae the dilated cutaneous veins around the umbilicus, seen mainly in the newborn and in patients suffering from cirrhosis of the liver. caput succeda´neum localized edema, congestion, and petechiae on the fetal and newborn scalp (presenting part), crossing the suture lines.

What does caput mean in Labour?
Images from Radswiki Caput succedaneum is a diffuse swelling of the scalp caused by the pressure of the scalp against the dilating cervix during labour. It may extend over the midline (as opposed to cephalhaematoma) and is associated with moulding of the head.
What causes baby caput?
Caput succedaneum is swelling (edema) that affects a newborn's scalp. It most commonly occurs from pressure on the head as the baby moves through the birth canal during a prolonged or difficult vaginal delivery.
Is caput normal?
Caput succedaneum is a very common and usually benign neonatal condition resulting from normal pressure and compression on the baby's head as it passes through the birth canal. Caput succedaneum itself is harmless as the swelling is limited to the scalp and is not a symptom of a deeper injury to the skull or brain.
What is fetal caput?
Caput succedaneum is a medical term that refers to swelling around an infant's skull. This medical condition typically forms after a difficult delivery. Caput succedaneum is usually not life-threatening and clears up within a few days.
What does caput feel like?
It is most often brought on by pressure from the uterus or vaginal wall during a head-first (vertex) delivery. Swelling and bruising usually occur on the top of the scalp where the head first enters the cervix during birth. This area is called a caput succedaneum and feels like a soft, spongy mass.
What is the difference between caput succedaneum and?
Caput succedaneum is similar to cephalohematoma as both involve unusual bumps or swelling on the newborn's head. However, the main difference is that lumps caused by bleeding under the scalp is cephalohematoma, whereas lumps caused by scalp swelling due to pressure is known as caput succedaneum.
How long does caput take to resolve?
Caput succedaneum typically resolves without the need for intervention within a couple of days following delivery. When there are no additional injuries or risks factors, a case of cephalohematoma typically resolves without the need for intervention within 2 to 6 weeks following delivery.
How does caput succedaneum go away?
Caput succedaneum will clear up on its own within a few days. Any efforts to drain the fluid from the scalp can lead to other issues such as infection.
What is caput and Moulding?
Caput succedaneum is defined as a diffuse swelling of the fetal scalp caused by the pressure of the scalp against the dilating cervix during labor. Caput is often associated with molding and may extend across the midline (as opposed to cephalohematoma, which does not cross the suture lines).
Can caput cause cerebral palsy?
If left untreated, a baby could develop Kernicterus and suffer from permanent brain damage, hearing loss, athetoid cerebral palsy, and vision problems.
Will caput succedaneum go away?
Caput succedaneum is a condition where your baby's scalp swells shortly after they're born. This is a type of edema, or fluid collection, just underneath the skin. Caput succedaneum can look alarming. However, it is usually not dangerous and it will go away on its own.
Is caput succedaneum blood?
Caput Succedaneum and Cephalohematoma Cephalohematoma is a subperiosteal collection of blood. Edema or hemorrhage of the scalp appears as deep swelling, with or without purpura. The swelling occurs primarily in vertex deliveries, particularly those with prolonged labor, and resolves spontaneously in 7–10 days.
How do you cure caput?
No treatment is necessary for this condition, and there should be no long-term effects. The swelling should decrease within several days, and the scalp should appear normal within days or weeks. A large or swollen head is a normal symptom of this condition.
How is caput succedaneum formed?
Caput succedaneum occurs when your baby's head has been squeezed or pulled. This is most common during the labor process. The process of delivery puts a lot of pressure on your baby. Even when dilated for birth, the cervix and vaginal canal still squeeze your baby.
Can caput cause cerebral palsy?
If left untreated, a baby could develop Kernicterus and suffer from permanent brain damage, hearing loss, athetoid cerebral palsy, and vision problems.
When does caput succedaneum occur?
A caput succedaneum may be detected by prenatal ultrasound, even before labor or delivery begins. It has been found as early as 31 weeks of pregnancy. Very often, this is due to an early rupture of the membranes or too little amniotic fluid. It is less likely that a caput will form if the membranes stay intact.
What is the condition where a baby's scalp swells shortly after birth?
Caput succedaneum is a condition where your baby’s scalp swells shortly after they’re born. This is a type of edema, or fluid collection, just underneath the skin.
Why is my baby's skull rounded?
Your baby’s skull is delicate, but it’s also resilient. The bones are just starting to fuse. This is why their skull will typically shift back to a rounded shape on its own without any other effects.
Why does my baby have a bump on his head?
Caput succedaneum isn’t the only condition that can cause your baby to have a bump on their head. Cephalohematoma occurs when body fluids collect between the periosteum and the skull bones, instead of the periosteum and the skin. It can also lead to a bump, but it’s a more serious health hazard. Unlike caput succedaneum, it involves significant bruising and may not resolve on its own.
Can a baby have a caput succedaneum?
Similarly, if the baby is in an amniotic sac with too little fluid, they can be bruised by their mother’s pelvic bones while still in the womb. This can cause caput succedaneum before your baby is born.
What is a caput?
Caput. Caput succedaneum is a diffuse swelling of the scalp caused by the pressure of the scalp against the dilating cervix during labour. It may extend over the midline (as opposed to cephalhaematoma) and is associated with moulding of the head. Caput can make it difficult to define the position of the fetal head.
Is caput a first line instrument?
It is graded subjectively from 0 (none) to +3 (marked). The vacuum cup may not maintain its suction if there is marked caput – forceps should be considered as a first-line instrument.
What is the symptom of caput succedaneum?
The main symptom of caput succedaneum is puffiness under the skin of the scalp. The skin is swollen and soft. Pressing on it may result in a dimple in the flesh. The swelling may be on one side or may extend over the midline of the scalp. The effects are usually most apparent on the part of the skull that was the first to come down the birth canal.
How long does it take for a caput succedaneum to clear?
Caput succedaneum will clear up on its own within a few days. Any efforts to drain the fluid from the scalp can lead to other issues such as infection.
Where are the effects of birth canals most apparent?
The effects are usually most apparent on the part of the skull that was the first to come down the birth canal.
Does a baby's head fuse?
This should go away over time. The bones of your baby’s head aren’t fused and can move considerably without damage.
What is a caput succedaneum?
Home / Birth Injuries / Caput Succedaneum. Quick Answer. Caput succedaneum is a medical term that refers to swelling around an infant’s skull. This medical condition typically forms after a difficult delivery. Caput succedaneum is usually not life-threatening and clears up within a few days.
How to tell if a baby has caput succedaneum?
Symptoms of caput succedaneum include soft, swollen spots on the top of the infant’s scalp that are 1-2 centimeters deep. This softness might appear on one side of the infant’s head or across the scalp. The swollen area usually appears on the portion of the head that first emerged from the birth canal.
Why is it important to compare caput succedaneum with cephalohematoma?
This is important because cephalohematomas are more likely to cause complications like blood clotting and anemia.
How long does it take for caput succedaneum to go down?
While the swelling often goes down within a couple of days, there may be a risk of more serious health problems. Most notably, babies born with caput succedaneum are at risk of newborn jaundice, or a buildup of a pigment (bilirubin) that can cause brain injuries.
What happens if a baby is born with caput succedaneum?
If your baby was born with caput succedaneum and you are concerned for their health, speak to your doctor today. It’s likely that the condition will quickly heal — but if it doesn’t, your child may be suffering from a more serious birth injury.
Where does the pressure come from during a vaginal delivery?
However, this can make the infant’s head the primary pressure point during the birth. Pressure commonly comes from the mother’s vaginal wall, cervix, and/or uterus. While any baby may develop caput succedaneum during delivery, ...
What are some examples of mistakes made by doctors during the birthing process?
For example, sometimes doctors rush through the birthing process or make mistakes when using delivery tools such as vacuum extractors or forceps.
What is the definition of caput?
2. The upper, anterior, or larger extremity, expanded or rounded, of any body, organ, or other anatomic structure. 3. The rounded extremity of a bone. 4. That end of a muscle that is attached to the less movable part of the skeleton. Synonym (s): caput [TA] [A.S. heāfod] Farlex Partner Medical Dictionary © Farlex 2012.
What is caput medu?
caput medu´saethe dilated cutaneous veins around the umbilicus, seen mainly in the newborn and in patients suffering from cirrhosis of the liver.
What is the ratio of caput to cauda?
In caput, the ratio is 77.3 % and 22.6 % and in cauda is 90.6 % and 9.4 % for OBRa and OBRb, respectively.
What is the head of the human body?
ca·put. , pl. capita ( kap'ŭt, -i-tă) [TA] 1. Head: the superior extremity of the human body, comprising the cranium and face, and containing the brain and organs of sight, hearing, taste, and smell. 2. The superior, anterior, or larger extremity, expanded or rounded, of any body, organ, or other anatomic structure. 3.
What does "head" mean in medical terms?
head. ( hed) 1. [TA] Upper or anterior extremity of animal body, containing brain and organs of sight, hearing, taste, and smell. 2. [TA] Upper, anterior, or larger extremity, expanded or rounded, of any body, organ, or other anatomic structure. 3. Rounded extremity of a bone. Synonym (s): caput.
What is the grade of caput?
However, caput detection should be part of your assessment during each vaginal examination. Like moulding, you grade the degree of caput as 0, +1, +2 or +3. Because of its subjective nature, grading the caput as +1 or +3 simply indicates a ‘small’ and a ‘large’ caput respectively.
When you detect moulding or caput formation in the fetal skull as the baby is moving down the birth canal?
Whenever you detect moulding or caput formation in the fetal skull as the baby is moving down the birth canal, you have to be more careful in evaluating the mother for possible disproportion between her pelvic opening and the size of the baby’s head.
What is the swelling of a baby's skull called?
Some baby’s skulls have a swelling called a caput in the area that was pressed against the cervix during labour and delivery (Figure 4.6); this is common even in a labour that is progressing normally.
Is a caput normal in a newborn?
Figure 4.6 A caput (swelling) of the fetal skull is normal if it develops centrally, but not if it is displaced to one side. A swelling on one side of the newborn’s head is a danger sign and should be referred urgently; blood or other fluid may be building up in the baby’s skull.
What is caput succedaneum?
Caput succedaneum refers to common benign edema that crosses cranial suture lines and midline that appears on an infant’s scalp shortly after birth. This swelling is associated with multiple etiologies related to birth trauma, including strain to the newborn’s head during vertex (head down) and vacuum-assisted delivery. It is important to differentiate caput succedaneum from other, more concerning, etiologies of fetal head trauma that require closer monitoring.[1]
How to diagnose caput succedaneum?
Caput succedaneum can be reliably assessed as early as the first stage of labor with a digital vaginal examination of the mass on the scalp and ultrasound.[5] When evaluating the edema on a newborn's scalp, the clinician needs to note whether the edema crosses the midline (pathognomonic finding for caput succedaneum). Bruising, petechiae, and ecchymosis may be present around the area of swelling as well. When palpating the edematous area, the mass should feel soft, boggy, and fluctuant. Diagnosis of caput succedaneum is most often made on a physical exam alone. Chiefly, it is most important for the clinician should observe the distribution and palpate the swelling. Evaluating and palpating the scalp is an important component of the initial newborn assessment.
What should be documented in the electronic health record for caput succedaneum?
Clinicians involved in the care of newborns should be familiar with the history and physical exam findings of caput succedaneum and be able to differentiate and exclude etiologies of birth-trauma-associated edema. Clinical decision-making and exam findings consistent with a diagnosis of caput succedaneum should be documented in the electronic health record. Parents and caregivers must be educated on the condition. The patient’s primary care provider should be made aware of the finding through the documentation so that they can ensure resolution of the swelling during early well-child checks. [Level 1]
What is the difference between caput succedaneum and cranial suture lines?
The cranial suture lines are collagenous sites for future intramembranous bone growth that lay inferior to the periosteum. The fluid accumulation in caput succedaneumis superior to the cranial sutures leading to an edematous, fluctuant, pitting mass that crosses the cranial sutures lines on an exam. This is an important distinguishing feature from cephalohematoma (birth trauma resulting in edema that does not cross cranial suture lines) and other related injuries. [4]
How long does it take for a caput succedaneum to resolve?
Most cases of caput succedaneum self-resolve within forty-eight hours without complication. The condition is considered benign and has an excellent clinical prognosis with observation.
What are the risk factors for caput succedaneum?
Risk factors for caput succedaneum included a protracted active labor course, operative vaginal delivery, oligohydramnios, primigravida pregnancy, Braxton-Hicks contractions, and premature rupture of membranes. Vacuum-assisted vaginal delivery is the most significant risk factor for developing caput succedaneum and scalp injury, even in comparison to forceps-assisted vaginal delivery. Indications for vacuum-assisted vaginal delivery include but are not limited to a prolonged second stage of labor, nonreassuring fetal heart patterns, and maternal exhaustion. [3]
What is the name of the cs that leave bumps on the head?
Nicholson L. Caput succedaneum and cephalohematoma: the cs that leave bumps on the head. Neonatal Netw. 2007 Sep-Oct;26(5):277-81. [PubMed: 17926657]
