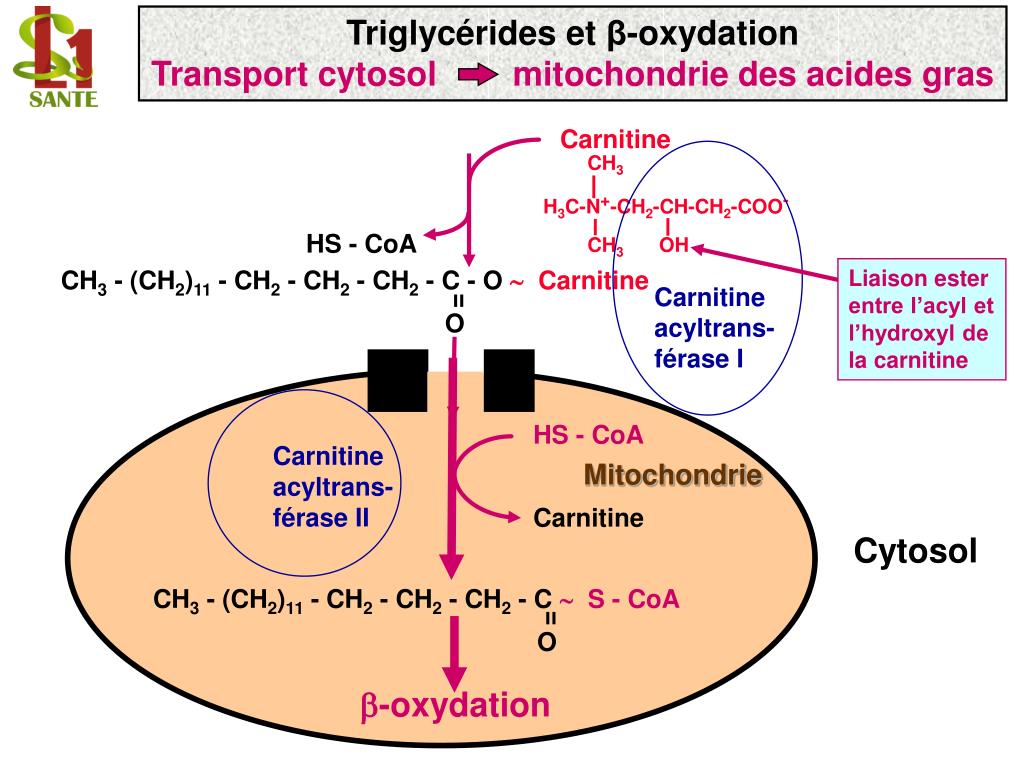
The carnitine cycle: The enzymes affecting the transport of carnitine into the cell, and the carnitine cycle whereby carnitine mediates the entry into the mitochondria of long-chain fatty acyl CoAs as acylcarnitines. Source publication Disorders of the carnitine cycle and detection by newborn screening Article Full-text available Dec 2008
See more

What is the function of carnitine?
Carnitine plays a critical role in energy production. It transports long-chain fatty acids into the mitochondria so they can be oxidized ("burned") to produce energy. It also transports the toxic compounds generated out of this cellular organelle to prevent their accumulation.
What is carnitine Acylcarnitine cycle?
The carnitine-acylcarnitine translocase (CACT) is one of the components of the carnitine cycle. The carnitine cycle is necessary to shuttle long-chain fatty acids from the cytosol into the intramitochondrial space where mitochondrial beta-oxidation of fatty acids takes place.
What is the point of the carnitine shuttle?
Carnitine acyltransferases reversibly transfer an acyl group from an acyl-CoA to carnitine for long-chain substrates. The carnitine shuttle system facilitates the transport of longchain fatty acids from the cytosol into the mitochondrial matrix, where FAO takes place.
What are the symptoms of carnitine deficiency?
What are the symptoms of carnitine deficiency?Decreased or floppy muscle tone or muscle weakness.Tiredness (fatigue)Irritability.Delayed movement (motor) development.Poor feeding in a baby.Symptoms of low blood sugar (hypoglycemia) if the liver is affected.More items...
What does a high carnitine levels mean?
What does this mean? High levels of free carnitine can indicate that your child has carnitine palmitoyl transferase type I (CPT-I) deficiency. A positive result does not mean your baby has CPT-I deficiency, but more testing is needed to know for sure.
What causes carnitine disease?
Causes. Mutations in the SLC22A5 gene cause primary carnitine deficiency. This gene provides instructions for making a protein called OCTN2 that transports carnitine into cells. Cells need carnitine to bring certain types of fats (fatty acids) into mitochondria , which are the energy-producing centers within cells.
Can I take carnitine with protein?
One of the best times to take L-carnitine is post-workout, but you can take it with any other high-carb, high-protein meal throughout the day. If you want to stack carnitine with other fat-burning ingredients between meals, consider using the acetyl L-carnitine form.
What activates the carnitine shuttle?
Carnitine shuttle activation occurs due to a need for fatty acid oxidation which is required for energy production. During vigorous muscle contraction or during fasting, ATP concentration decreases and AMP concentration increases leading to the activation of AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK).
How does the body make carnitine?
Mitochondria exist inside every cell in the body. They produce the energy that cells need to function. The body creates carnitine from the amino acids lysine and methionine.
Who should not take carnitine?
Acetyl-L-carnitine is not known to be safe for children or for women who are pregnant or breastfeeding. You should also avoid this supplement if you have hypothyroidism (low thyroid levels) or a history of seizures.
Does carnitine burn fat?
L-carnitine is best known as a fat burner — but the overall research is mixed. It is unlikely to cause significant weight loss. However, studies support its use for health, brain function and disease prevention. Supplements may also benefit those with lower levels, such as older adults, vegans and vegetarians.
Does carnitine increase testosterone?
L-carnitine can work in a number of ways to encourage optimal testosterone levels: It appears to directly stimulate production of testosterone: A recent study showed that serum levels of carnitine were independently associated with free testosterone concentrations in men.
What does carnitine-Acylcarnitine Translocase do?
Carnitine-acylcarnitine translocase (CACT) is a critical component of the carnitine shuttle, which facilitates the transfer of long-chain fatty acylcarnitines across the inner mitochondrial membrane. CACT deficiency causes a defect in mitochondrial long-chain fatty acid β-oxidation, with variable clinical severity.
What is the function of carnitine-Acylcarnitine Translocase?
This gene provides instructions for making a protein called carnitine-acylcarnitine translocase (CACT). This protein is essential for fatty acid oxidation, a multistep process that breaks down (metabolizes) fats and converts them into energy.
What does carnitine acyltransferase II do?
This gene provides instructions for making an enzyme called carnitine palmitoyltransferase 2. This enzyme is essential for fatty acid oxidation, which is the multistep process that breaks down (metabolizes) fats and converts them into energy.
What is the role of carnitine in fatty acid synthesis?
The main function of carnitine is the transfer of long-chain fatty acids to mitochondria for subsequent β-oxidation [1]. Carnitine also binds acyl residues deriving from the intermediary metabolism of amino acids and help in their elimination functioning as a scavenger [2].
What is the second reaction of acyl-coa?
In the second reaction, acyl-CoA is transiently attached to the hydroxyl group of carnitine to form fatty acyl–carnitine. This transesterification is catalyzed by an enzyme found in the outer membrane of the mitochondria known as carnitine acyltransferase 1 (also called carnitine palmitoyltransferase 1, CPT1).
What is the role of carnitine in the body?
In support of energy metabolism, carnitine transports long-chain fatty acids into mitochondria to be oxidized for energy production, and also participates in removing products of metabolism from cells. Given its key metabolic roles, carnitine is concentrated in tissues like skeletal and cardiac muscle that metabolize fatty acids as an energy source. Healthy individuals, including strict vegetarians, synthesize enough L-carnitine in vivo to not require supplementation.
What is the role of the carnitine shuttle in muscle contraction?
During vigorous muscle contraction or during fasting, ATP concentration decreases and AMP concentration increases leading to the activation of AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK). AMPK phosphorylates acetyl-CoA carboxylase, which normally catalyzes malonyl-CoA synthesis. This phosphorylation inhibits acetyl-CoA carboxylase, which in turn lowers the concentration of malonyl-CoA. Lower levels of malonyl-CoA disinhibits carnitine acyltransferase 1, allowing fatty acid import to the mitochondria, ultimately replenishing the supply of ATP.
How do humans synthesize carnitine?
Humans synthesize carnitine from the substrate TML (6- N -trimethyllysine), which is in turn derived from the methylation of the amino acid lysine. TML is then hydroxylated into hydroxytrimethyllysine (HTML) by trimethyllysine dioxygenase (TMLD), requiring the presence of ascorbic acid and iron. HTML is then cleaved by HTML aldolase (a pyridoxal phosphate requiring enzyme), yielding 4-trimethylaminobutyraldehyde (TMABA) and glycine. TMABA is then dehydrogenated into gamma-butyrobetaine in an NAD + -dependent reaction, catalyzed by TMABA dehydrogenase. Gamma-butyrobetaine is then hydroxylated by gamma butyrobetaine hydroxylase (a zinc binding enzyme) into l -carnitine, requiring iron in the form of Fe 2+.
How much carnitine does a person produce in a day?
As an example of normal synthesis, a 70 kilograms (150 lb) person would produce 11–34 mg of carnitine per day. Adults eating mixed diets of red meat and other animal products ingest some 60–180 mg of carnitine per day, while vegans consume about 10–12 mg per day.
How does the liver make triglycerides?
The liver starts actively making triglycerides from excess glucose when it is supplied with glucose that cannot be oxidized or stored as glycogen. This increases the concentration of malonyl-CoA, the first intermediate in fatty acid synthesis, leading to the inhibition of carnitine acyltransferase 1, thereby preventing fatty acid entry into the mitochondrial matrix for β oxidation. This inhibition prevents fatty acid breakdown while synthesis occurs.
Where does fatty acyl-carnitine enter the matrix?
The fatty acyl–carnitine ester formed then diffuses across the intermembrane space and enters the matrix by facilitated diffusion through carnitine-acylcarnitine translocase (CACT) located on inner mitochondrial membrane. This antiporter return one molecule of carnitine from the matrix to the intermembrane space for every one molecule of fatty acyl–carnitine that moves into the matrix.
What is the role of carnitine in the cell?
Carnitine plays an essential role in the transfer of long-chain fatty acids across the inner mitochondrial membrane. This transfer requires enzymes and transporters that accumulate carnitine within the cell (OCTN2 carnitine transporter), conjugate it with long chain fatty acids (carnitine palmitoyl ….
What is the role of carnitine in the mitochondrial cycle?
Carnitine plays an essential role in the transfer of long-chain fatty acids across the inner mitochondrial membrane. This transfer requires enzymes and transporters that accumulate carnitine within the cell (OCTN2 carnitine transporter), conjugate it with long chain fatty acids ...
Can CACT deficiency cause cardiac arrest?
These patients can have elevated levels of plasma carnitine. CACT deficiency presents in most cases in the neonatal period with hypoglycemia, hyperammonemia, and cardiomyopathy with arrhythmia leading to cardiac arrest. Plasma carnitine levels are extremely low.
What are the different types of carnitine?
Here are several other types of carnitine: 1 D-carnitine: This inactive form may cause a carnitine deficiency in your body by inhibiting the absorption of other, more useful forms ( 7#N#Trusted Source#N#, 8#N#Trusted Source#N#). 2 Acetyl-L-carnitine: Often called ALCAR, this is possibly the most effective form for your brain. Studies suggest that it may benefit people with neurodegenerative diseases ( 9#N#Trusted Source#N#). 3 Propionyl-L-carnitine: This form is well-suited for circulatory issues, such as peripheral vascular disease and high blood pressure. It may boost production of nitric oxide, which improves blood flow ( 10#N#Trusted Source#N#, 11#N#Trusted Source#N#). 4 L-carnitine L-tartrate: This is commonly added to sports supplements due to its rapid absorption rate. It may aid muscle soreness and recovery in exercise ( 12#N#Trusted Source#N#, 13#N#Trusted Source#N#, 14#N#Trusted Source#N#).
What is the role of L-carnitine in the body?
L-carnitine is a nutrient and dietary supplement. It plays a crucial role in the production of energy by transporting fatty acids into your cells’ mitochondria ( 1. Trusted Source.
How long does it take for L-carnitine to appear?
L-carnitine’s benefits may be indirect and take weeks or months to appear. This differs from supplements like caffeine or creatine, which can directly enhance sports performance. L-carnitine may benefit: Recovery: May improve exercise recovery ( 46.
How much L-carnitine is needed for exercise?
L-carnitine L-tartrate: This form is most effective for exercise performance. Doses vary from 1,000–4,000 mg per day.
What is the mitochondria?
Trusted Source. ). The mitochondria act as engines within your cells, burning these fats to create usable energy. Your body can produce L-carnitine out of the amino acids lysine and methionine. For your body to produce it in sufficient amounts, you also need plenty of vitamin C ( 4. Trusted Source. ).
How much L-carnitine is absorbed?
Interestingly, food sources of L-carnitine have a greater absorption rate than supplements. According to one study, 57–84% of L-carnitine is absorbed when it’s consumed from food, compared to only 14–18% when taken as a supplement ( 61. Trusted Source.
What is L-carnitine?
L-carnitine is a naturally occurring amino acid derivative that’s often taken as a supplement.
What is L-carnitine?
While it is often categorized as an amino acid, L-carnitine isn't technically an amino. It is considered a "vitamin-like" and "amino-acid-like" compound that is related to the B vitamins. When it was first studied back in the 1950s, L-carnitine was referred to as vitamin BT.
What are the Performance and Physique Applications Of L-Carnitine?
L-carnitine's bona fide role as a fat-burning supplement is well established. During bulking periods, it can help limit fat gains and make a "cleaner" bulk. If you're cutting, it can help transport the fat you have into your cellular furnaces to get burned as energy.
How Should I Stack L-Carnitine?
Quite simply, take it with carbs. Some early studies showed no benefit of carnitine because they failed to adequately raise muscle carnitine levels. This was because the supplement wasn't taken at the right time, when insulin would be spiked and muscle uptake would be adequate.
Should I Cycle L-Carnitine?
At this time, it appears that there is no need to cycle L-carnitine. Taken regularly, it should continue to be effective long term.
How does carnitine work?
How does this work? For one, carnitine reduces oxidative damage in the body's nitric oxide (NO). But it also enhances the activity of a key enzyme involved in your body's NO production. The net result is higher NO blood levels, which not only enhance energy during workouts, but also muscle recovery following workouts.
How much L-carnitine should I take for weight loss?
One strategy I found to work well for both fat loss and performance is to take 2-3 doses of acetyl L-carnitine with other fat-burning ingredients without food between meals, and to take 1 dose of L-carnitine or L-carnitine L-tartrate with a post-workout meal.
Where is acetyl carnitine found?
Acetyl L-carnitine, also known as acetylcarnitine or ALCAR, is another popular supplemental form of carnitine. It can be found throughout the central nervous system , where it plays a role in producing energy and produces the important neurotransmitter acetylcholine.
What Is Carnitine and Why Is It Important?
Carnitine is a specialized amino acid with a variety of duties in the body. It can be found in nearly all the cells of the human body, but unlike many of the other amino acids, carnitine is not found in the protein molecules that form sub-components of the cells.
What is the role of carnitine in the mitochondria?
Carnitine levels often function as the rate-limiting factor in the transport of fatty acids into the mitochondria and subsequent oxidation. Rate-limiting means that everything else can be in place for fatty acids to be oxidized, but if your blood levels of carnitine are too low, that process will not take place.
What happens when carnitine levels are low?
Similarly, low carnitine levels mean there's not enough of this essential amino acid derivative to bind with fatty acids, and the transport of fatty acids into the mitochondria decreases. As a result, fatty acid oxidation drops.
What is the role of carnitine in the body?
The main role of carnitine is to help the body break down fatty acids for energy. Carnitine also transports toxins out of the mitochondria—the cellular powerhouses that produce energy.
Why does fat build up in muscle?
If your body's carnitine content is not sufficient to allow for the transport of fatty acids into the mito chondria, fat can build up in your muscle tissues. This causes a host of metabolic problems, including insulin resistance.
What are the two types of carnitine deficiencies?
So far, experts have identified two types of carnitine deficiencies: primary carnitine deficiency and secondary carnitine deficiency.
Why do people develop secondary carnitine deficiency?
It might arise due to a specific health condition, like chronic, late-stage kidney disease, or because of certain factors that impact carnitine metabolism, like the use of some types of antibiotics .
How long does L-carnitine help with metabolic syndrome?
Early research shows that L-carnitine given intravenously (by IV) daily for 7 days increases weight loss and reduces waist circumference in people with metabolic syndrome.
How long does L-carnitin help with liver disease?
Reduced brain function in people with advanced liver disease (hepatic encephalopathy). Early research shows that taking L-carnitine daily for 60-90 days reduces ammonia levels and improves brain function in people with declining brain function related to severe liver disease.
What is the FDA's recommendation for L-carnitine?
The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has approved L-carnitine for the treatment and prevention of L-carnitine deficiency in people with serious kidney disease who are undergoing hemodialysis. L-carnitine deficiency. The FDA has approved L-carnitine for treating L-carnitine deficiency caused by certain genetic diseases.
How long does it take for L-carnitine to help with muscle soreness?
Muscle soreness caused by exercise. Early research shows that taking L-carnitine helps to reduce muscle soreness and muscle damage in the first four days after exercise. Fatigue. Early research shows that taking L-carnitine daily for 8 days does not reduce fatigue in healthy people.
What is the chemical that converts fat to energy?
Overview. L-carnitine is a chemical similar to an amino acid that is produced in the body. L-carnitine helps the body turn fat into energy. The body can convert L-carnitine to other chemicals called acetyl-L-carnitine and propionyl-L-carnitine.
What is the purpose of the CONDITIONS OF USE AND IMPORTANT INFORMATION?
CONDITIONS OF USE AND IMPORTANT INFORMATION: This information is meant to supplement, not replace advice from your doctor or healthcare provider and is not meant to cover all possible uses, precautions, interactions or adverse effects. This information may not fit your specific health circumstances.
Can you take L-carnitine with D-carnitine?
It can also cause the urine, breath, and sweat to have a "fishy" odor. Avoid using D-carnitine and DL-carnitine. These forms of carnitine might block the effects of L-carnitine and cause symptoms that resemble L-carnitine deficiency.

Overview
Carnitine is a quaternary ammonium compound involved in metabolism in most mammals, plants, and some bacteria. In support of energy metabolism, carnitine transports long-chain fatty acids into mitochondria to be oxidized for energy production, and also participates in removing products of metabolism from cells. Given its key metabolic roles, carnitine is concentrated in tissues like skeletal and cardiac …
Biosynthesis and metabolism
Many eukaryotes have the ability to synthesize carnitine, including humans. Humans synthesize carnitine from the substrate TML (6-N-trimethyllysine), which is in turn derived from the methylation of the amino acid lysine. TML is then hydroxylated into hydroxytrimethyllysine (HTML) by trimethyllysine dioxygenase (TMLD), requiring the presence of ascorbic acid and iron. HTML is then cleave…
Carnitine shuttle system
The free-floating fatty acids, released from adipose tissues to the blood, bind to carrier protein molecule known as serum albumin that carry the fatty acids to the cytoplasm of target cells such as the heart, skeletal muscle, and other tissue cells, where they are used for fuel. But before the target cells can use the fatty acids for ATP production and β oxidation, the fatty acids with chain lengths of 14 or more carbons must be activated and subsequently transported into mitochondri…
Regulation of fatty acid β oxidation
The carnitine-mediated entry process is a rate-limiting factor for fatty acid oxidation and is an important point of regulation.
The liver starts actively making triglycerides from excess glucose when it is supplied with glucose that cannot be oxidized or stored as glycogen. This increases the concentration of malonyl-CoA, the first intermediate in fatty acid synthesis, leading to the inhibition of carnitine acyltransferase 1…
Transcription factors
Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha (PPARα) is a nuclear receptor that functions as a transcription factor. It acts in muscle, adipose tissue, and liver to turn on a set of genes essential for fatty acid oxidation, including the fatty acid transporters carnitine acyltransferases 1 and 2, the fatty acyl–CoA dehydrogenases for short, medium, long, and very long acyl chains, and related enzymes.
Metabolic defects of fatty acid oxidation
More than 20 human genetic defects in fatty acid transport or oxidation have been identified. In case of fatty acid oxidation defects, acyl-carnitines accumulate in mitochondria and are transferred into the cytosol, and then into the blood. Plasma levels of acylcarnitine in newborn infants can be detected in a small blood sample by tandem mass spectrometry.
When β oxidation is defective because of either mutation or deficiency in carnitine, the ω (omega…
Physiological effects
As an example of normal synthesis, a 70 kilograms (150 lb) person would produce 11–34 mg of carnitine per day. Adults eating mixed diets of red meat and other animal products ingest some 60–180 mg of carnitine per day, while vegans consume about 10–12 mg per day. Most (54–86%) carnitine obtained from the diet is absorbed in the small intestine before entering the blood. The total body content of carnitine is about 20 grams (0.71 oz) in a person weighing 70 kilograms (15…
Sources
The form present in the body is l-carnitine, which is also the form present in food. Food sources rich in l-carnitine are animal products, particularly beef and pork. Red meats tend to have higher levels of l-carnitine. Adults eating diverse diets that contain animal products attain about 23-135 mg of carnitine per day. Vegans get noticeably less (about 10–12 mg) since their diets lack these carnitine-rich animal-derived foods. Approximately 54% to 86% of dietary carnitine is absorbed i…