Is a CD a worthwhile investment?
One instance in which a CD would be a worthwhile investment is saving for a home down payment. If you have the money already saved up and just want it to earn a little interest until you’re ready to buy the home in a few years, a CD would be a good place to park the money.
Are CD worth investing in?
The other thing that makes CDs worth it from a risk standpoint is that they are insured by the Federal Deposit Insurance Corp. So, even if the bank fails, you won’t lose what you invested. No matter what kind of CD climate you’re in, CDs are still worth it as a savings product.
Why to invest in a CD?
The benefits of CDs
- Superior safety. While there are a few uninsured CDs in the market, most CDs offered by banks and credit unions are insured against losses.
- Better returns than savings accounts. Compared to putting your extra cash in a savings account, buying CDs can boost your returns without additional risks.
- Help you stick to saving. ...
What is an example of a CD investment?
With a CD ladder, you divide your initial investment into equal parts and invest each portion in a CD that matures every year. For example, say Leo has $10,000. To build a CD ladder, he invests $2,000 each in a 1-year, 2-year, 3-year, 4-year and 5-year CD.

What is a CD investment and how does it work?
A certificate of deposit, more commonly known as a CD, is a special type of savings account. You deposit your money into the account and agree not to make any withdrawals for a certain period of time. At the end of that time, you get your money plus whatever was earned in interest back.
Can you lose money on a CD?
Can you lose money in a brokered CD? Market interest rates frequently fluctuate, which means that the market value of a CD fluctuates, too. If a CD is sold on the secondary market at a lower value than its face value, it will have lost money. But there are no losses if the CD is kept until maturity.
Are CDs safe investments?
CDs are one of the safest ways to store money and earn a set rate of interest, which can help you better plan your finances. CDs opened at FDIC-insured banks or credit unions backed by the NCUA are guaranteed by the federal government.
What is investing in a CD?
A CD is a type of federally insured savings account in which you invest funds for a specified period of time in exchange for predetermined monthly interest payments. Accessing funds invested in a CD prior to the maturity date, even when allowed, often results in an early withdrawal penalty.
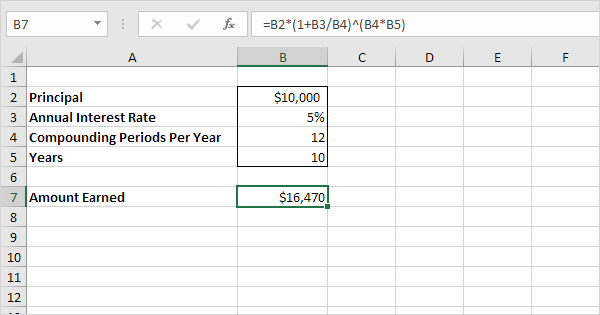
How much does a 10000 CD make in a year?
Here's an example. If you invested $10,000 in a five-year CD at 0.50% APY, which is close to the national average rate, you would have earned about $253 in interest at the end of five years.
Are CDs a good investment in 2022?
Though the Federal Reserve is poised to raise rates three times in 2022, McBride's forecast calls for just two hikes, with the national average for one-year CDs rising to 0.35 percent and the average for five-year CDs climbing to 0.56 percent.
How much will my CD earn in a year?
This depends on the CD rate. A one-year CD with a rate of 1% APY earns $100, while a CD with a rate of 0.10% APY earns $10. To compare current rates, see the best one-year CD rates this month.
What are the disadvantages of CDs?
The cons of CDsLess flexibility. With a savings account, the money is easily accessible in case of a financial emergency or a change in spending priorities. ... Inflation. The other disadvantage is that CD interest rates can sometimes struggle to keep up with inflation.
Do CDs pay interest monthly?
Generally, CDs compound daily or monthly. The more often the CD compounds, the faster your savings will grow. The answer varies by account, but most CDs credit interest monthly.
Can I open a CD with $100?
Generally, CD minimums begin at around $1,000, but they will vary depending on the type of CD you choose. Some banks offer a variety of CDs with different terms and returns to meet the needs of their customers.
How do you put money on a CD?
Unless you already have one, you'll need to create a new account with the issuing bank or credit union to open a certificate of deposit. You may have to share personal information such as your name, address, contact info and tax identification number (such as a Social Security number). Fund the CD.
How long does a CD account last?
three months to five yearsCD terms typically range from three months to five years. The trick is to find a CD with the right maturity date for you. If your term's too short, you might miss out on a higher rate available for a longer term. If your term's too long, you may need the money prematurely and pay an early withdrawal penalty to get it.
What is the biggest negative of putting your money in a CD?
For a 1-year CD, you might lose two or three months' worth of interest for cashing out a CD before it matures. And to be clear, you generally can't take a withdrawal from a CD. If you have $5,000 in a CD but only need $500, you'll generally have to cash out your CD in its entirety to get that money.
What is the disadvantage of a CD account?
Limited Liquidity: The owner of a CD cannot access their money as easily as a traditional savings account. To withdrawal money from a CD before the end of the term requires that a penalty has to be paid. This penalty can be in the form of lost interest or a principal penalty.
How long can you leave money in a CD?
CD terms typically range from three months to five years. The trick is to find a CD with the right maturity date for you. If your term's too short, you might miss out on a higher rate available for a longer term. If your term's too long, you may need the money prematurely and pay an early withdrawal penalty to get it.
How much do you lose if you cash in a CD early?
Penalties at Major BanksBankEarly Withdrawal Penalty, 1-Year CDU.S. BankGreater of one-half of the interest earned or 1% of the amount withdrawn, plus a $25 feeWells Fargo3 months' interestMarcus by Goldman Sachs90 days' simple interestSallie Mae Bank90 days' simple interest9 more rows•Mar 25, 2022
What is a CD?
What Is a Certificate of Deposit (CD)? A certificate of deposit (CD) is a product offered by banks and credit unions that provides an interest rate premium in exchange for the customer agreeing to leave a lump-sum deposit untouched for a predetermined period of time.
What Is a Certificate of Deposit (CD)?
A certificate of deposit (CD) is a product offered by banks and credit unions that provides an interest rate premium in exchange for the customer agreeing to leave a lump-sum deposit untouched for a predetermined period of time . Almost all consumer financial institutions offer CDs, although it’s up to each bank which terms it wants to offer, how much higher the rate will be compared to the bank’s savings and money market products, and what penalties it applies for early withdrawal.
What Are the Advantages and Disadvantages of a Certificate of Deposit?
On the other hand, certificates of deposit generally promise a very modest rate of return, particularly in recent years when the federal funds rate is at historically low levels. 1 If the interest rate offered is below the current inflation rate, then investors in certificates of deposit will actually lose money on their investment, when measured on an inflation-adjusted basis. For this reason, yield-conscious investors might prefer investments that are riskier but offer higher potential returns.
How Are CD Rates Determined?
Anyone who’s been following interest rates or business news, in general, knows that the Federal Reserve Board’s rate-setting actions loom large in terms of what savers can earn on their deposits. 1 That’s because the Fed’s decisions can directly affect a bank’s costs. Here’s how it works.
Are CDs Safe?
Certificates of deposit are one of the safest savings or investment instruments available, for two reasons. First, their rate is fixed and guaranteed, so there is no risk that your CD’s return will be reduced or even fluctuate. What you signed up for is what you’ll get—it’s in your deposit agreement with the bank or credit union.
When Is Opening a CD a Good Idea?
Certificates of deposit are useful in a few different situations. Perhaps you have cash you don’t need now, but will want within the next few years —maybe for a special vacation or to buy a new home, car, or boat. For near-term uses like that, the stock market generally isn’t considered a suitable investment, as you could lose money over that period of time.
Where Can I Get a CD?
Virtually every bank and credit union offers at least one certificate of deposit, and most have a wide array of terms on offer. So not only is your local brick-and-mortar bank an outlet, but so is every bank or credit union in your community, as well as every bank that accepts customers nationwide via the internet.
What Type of Investment Is a CD?
CDs are relatively safe investments when it comes to the risk of losing money in your account. At a federally insured bank or credit union, your CDs are protected up to $250,000. 2 They are best for situations when you cannot accept the risk of losing your money. For example, you might have plans to buy a new home in two or three years, and you’re building up a down payment. You won’t need to spend the money in the immediate future, so locking it up for a higher interest rate could make sense.
What is CD in savings?
Updated October 01, 2020. Certificates of deposit (CDs) are investments that help you grow your money safely, and using them can be as simple or as complicated as you want. If your needs are basic, it’s easy to put money into a CD and start earning more than you can earn in a savings account.
Why do CDs pay more?
Longer-term CDs usually pay more than shorter-term CDs because your commitment is greater, but there are exceptions . Some CDs also adjust the interest rate you earn over time. If you pull your funds out of a CD before it matures (before the specified amount of time passes), you’ll have to pay an early withdrawal penalty .
How to renew a CD?
When your CD matures, you should receive a notice explaining your options. In most cases, you can: 1 Let the CD renew (into another CD with the same length of time) 2 Buy a different CD (switching from a six-month to a one-year CD, for example) 3 Move the funds into a checking or savings account 4 Withdraw the funds
How long can you leave a CD in a bank account?
For example, a six-month CD is meant to be left alone for six months. CDs are available in various terms ranging from six months to five years (or longer). ...
What to do when CD matures?
When your CD matures, you should receive a notice explaining your options. In most cases, you can: Let the CD renew (into another CD with the same length of time) Buy a different CD (switching from a six-month to a one-year CD, for example) Move the funds into a checking or savings account. Withdraw the funds.
Do you need to spend CDs in the future?
You won’t need to spend the money in the immediate future, so locking it up for a higher interest rate could make sense. For longer-term goals, like a retirement that is more than 20 years away, CDs might or might not be the right investment.
How to invest in CDs?
The simplest approach to investing in CDs is to buy one and hold it until it matures. There are several risks and limitations with this strategy. The first is that interest rates may fall over time, so when the CD reaches maturity and the proceeds are ready to be reinvested into another CD, the next investment will offer a lower interest rate. Alternatively, if interest rates rise, you can lose out on a higher rate if your CD hasn’t yet reached maturity.
What is a CD account?
Key Takeaways. A CD is a type of federally insured savings account in which you invest funds for a specified period of time in exchange for predetermined monthly interest payments. Accessing funds invested in a CD prior to the maturity date, even when allowed, often results in an early withdrawal penalty.
What is laddered CD?
One option is known as a CD ladder. To construct a laddered portfolio, equal sums of money are invested into multiple CDs, each with a different maturity date. For example, a $100,000 investment could be spread out over 10 years as follows:
Why do CDs have higher interest rates?
CDs typically offer higher interest rates than traditional savings accounts as compensation for reduced flexibility in withdrawal options. Longer maturity dates tend to pay higher rates of interest than shorter maturities, so investors with long time horizons have an even greater incentive to choose a CD instead of a savings account.
What is zero coupon CD?
Zero-coupon CD: Zero-coupon CDs are purchased at a discount to their face value. Rather than make periodic interest payments, they return the amount of the original investment and all interest due in a single lump-sum payment at maturity.
How often do you need to keep CDs?
Whereas traditional savings accounts enable depositors to access their money whenever they want it (albeit only six times a month ), CDs generally require investors to keep their money invested for a specific period of time in exchange for predetermined monthly interest payments.
Why are CDs safe?
CDs offer investors a safe place to earn a predictable stream of income. The safety comes from the Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation (FDIC), a government agency that protects depositors against bank failure, which provides up to $250,000 of insurance per depositor in the event of bank failure. 1 (Investors with more than $250,000 should make deposits at multiple banks to make sure all of their assets are protected by the FDIC.) The National Credit Union Administration (NCUA) provides the same level of insurance for CDs purchased through a credit union, which are known as share certificates. 2
What is CD investment?
A CD investment provides guaranteed returns and your money stays federally insured. How much interest you can earn on a CD depends on the rates, which are falling in the current rate environment. See what the best CDs can earn below.
Why should I consider CDs?
Like savings accounts, CDs are federally insured to protect your money, both at online and traditional banks as well as at credit unions. This means they have minimal risk, whereas investing in the stock market — another option to grow your money — is more unpredictable and can lead to losses, especially in the short term. See more about CD safety.
What is savings account?
A savings account is a place where you can store money securely while earning interest.
What is cash management account?
Cash management accounts are typically offered by non-bank financial institutions.
How much money do you need to open a CD?
Some financial institutions also reward you with higher rates in exchange for higher minimum deposits. A CD that requires $5,000 to open an account might earn more than one that requires $1,000.
What happens if you withdraw money from a CD before the term ends?
If you withdraw your money from a CD before the term ends, most banks charge a penalty fee equal to a certain amount of interest — for example, six months’ worth. Learn more about early withdrawal penalties here.
Is a CD safe?
They’re safe. Like savings accounts, CDs are federally insured to protect your money, both at online and traditional banks as well as at credit unions. This means they have minimal risk, whereas investing in the stock market — another option to grow your money — is more unpredictable and can lead to losses, especially in the short term. See more about CD safety.
How can CD investors increase their flexibility?
One way CD investors can increase their flexibility is to create a CD ladder made up of CDs of differing maturities, so portions of your CD savings will be available at regular intervals.
Why are CDs more valuable than savings?
Because CD account holders can’t take their money back at a moment’s notice like savings account holders can, CDs are more valuable to banks than savings deposits. Banks typically pay CD investors a higher yield in exchange for locking up their money for a set amount of time.
Why do CDs have ladders?
Creating a CD ladder of varying maturities on the shorter end of the spectrum allows investors to take advantage of higher rates as their CDs mature.
How long are CDs good for?
You can find CDs with terms ranging from one month to 10 years. This diverse set of options helps investors find a CD that fits their needs.
What are the pros and cons of CDs?
Safety. CDs from federally insured banks and credit unions are backed by the full faith and credit of the U.S. government up to $250,000 per depositor, per insured bank, per ownership category. This essentially amounts to bank-subsidized investment insurance.
Why do CDs have a risk?
CD rates tend to lag rising inflation on the way up and drop more quickly than inflation on the way down. Because of that, investing in CDs carries the danger that your money will lose its purchasing power over time as your interest gains are overtaken by inflation.
How much did the 5-year CD yield in the 1980s?
In the mid-1980s, 5-year CDs boasted yields exceeded 11 percent, but they’ve trended mostly downward ever since.
What is a broker CD?
Brokered CD vs. bank CD. A brokered CD is similar to a bank CD in many ways. Both pay a set interest rate that is generally higher than a regular savings account. Both are debt obligations of an issuing bank and both repay your principal with interest if they’re held to maturity.
Why are CD yields lower than other investments?
Lower yields. Because of the inherent safety and short-term nature of a CD investment, yields on CDs tend to be lower than other higher risk investments. Interest rate fluctuation. Like all fixed income securities, CD valuations and secondary market prices are susceptible to fluctuations in interest rates.
What is callable CD?
The issuer of a callable CD maintains the right to redeem the security on a set date prior to maturity and pay back the CD's owner either par (full) value or a percentage of par value. The call schedule lists the precise call dates of when an issuer may choose to pay back the CDs and the price at which they will do so.
How does Fidelity offer CDs?
Fidelity offers brokered CD s through two main venues—as new issue offerings and from the secondary market. Investors typically will see 50–100 new issue offerings and as many as 2,000 secondary offerings at any point in time. New issue offerings are typically sold at par and investors do not pay a trading fee to purchase them. 4 Purchases (and sales) of secondary CDs incur a trading fee of $1 per CD (1 CD = $1,000 par value). 5
How long are CDs good for?
Brokered CDs come in a wide range of maturities—as little as 3 months and as long as 20 years. This allows you to choose between high degrees of liquidity, meaning you have the opportunity to reinvest your funds frequently, and stability, meaning you can lock in favorable interest rates for long periods of time.
What is a CD ladder?
Model CD Ladders provide an easy way to invest in multiple Certificates of Deposit (CDs) at a time, blending longer-term CDs with shorter-term CDs. By selecting one of the three models shown below you can easily filter our new issue CD inventory using a set of objective screening criteria to model your own CD Ladder (requires login).
How long does a step up CD pay interest?
Generally, a step-up CD pays a below-market interest rate for an initial defined period (often one year). After the expiration of that initial period, the coupon rate generally increases, and the CD will pay this interest rate until the next step, at which time it changes again, and so on through the maturity date.
What are the pros and cons of investing in CDs?
Cons to investing in CDs. 1. You lose access to money in a CD. You can think of CDs as locked storage boxes for some of your money. Once you put a lump sum into a CD for a fixed time, you can’t add or remove any of it until the day the term ends, known as its maturity date.
How much deposit insurance does a CD have?
Like other bank accounts, CDs have federal deposit insurance up to $250,000 (or $500,000 in a joint account for two people). There’s no risk of losing money in a CD, except if you withdraw early. 2. CDs have fixed rates and predictable returns. Once you open a CD, you lock in a rate.
Why do you need a CD?
A more strategic approach to investing in CDs is to split one investment into several parts and invest in multiple CDs of different term lengths at once. When each CD ends, reinvest that sum in a new CD for a longer term. This is called a CD ladder (see more on how CD ladders work).
What happens when you open a CD?
Once you open a CD, you lock in a rate. This lets you know exactly how much money you’ll earn over your CD term, whether that’s months or years. In contrast, banks and credit unions can change rates on regular savings accounts at will. 3. CDs provide a variety of terms that can offer structure to savings goals.
What is savings account?
A savings account is a place where you can store money securely while earning interest.
What is the best CD rate for 2020?
In January 2020, the best CD rates were higher than 2% annual percentage yield for one-year and five-year terms, while in January 2021, you’d be hard-pressed to find 1% APY for any term, according to a NerdWallet analysis of over 20 financial institutions with some of the most competitive high-yield CDs.
What is cash management account?
Cash management accounts are typically offered by non-bank financial institutions.
What is a CD in investing?
CDs have been a staple of modern investing since the 1960s, and have existed in some form for centuries. Yet many people still have basic questions about them, like, “What does CD stand for?” “What is a bank CD?” and, “How do bank CDs work?”
What is CD in savings?
A CD is a way to put away money beyond what you’ve accumulated in your savings account, without taking on much more market risk. Think of it like buying a baseball card for your favorite player, knowing its value will go up when he retires in a year or two.
Why do banks value CDs?
Banks value CDs because they can count on your money staying put for a certain period of time, allowing them to lend to others. But don’t worry, CD accounts are generally insured by the FDIC (more on that later).
What is the upside of CDs?
Weighing those upsides and downsides will help determine whether they’re right for you and your money. The big upside of CDs is predictability. Because of the fixed rate and specific term, you’ll know exactly how much money you’ll have when you reach the end of your investment.
How does an IRA CD work?
An IRA CD works just like a bank CD, but with the added tax benefits of an IRA. Everything else—the fixed term, the fixed rate and the early withdrawal penalties—are typically similar. 3 And what is a Roth IRA CD? The same thing, basically, only with the tax benefits of a Roth IRA rather than a traditional IRA. 4
What are the drawbacks of CDs?
The main drawback of CDs is the lack of flexibility. Unlike a savings account, you can’t withdraw the money whenever you want—at least not without paying a penalty. Most banks charge you some of your accrued interest, and maybe even part of your original investment, if you decide to withdraw early.
What is the disadvantage of CD interest rates?
The other disadvantage is that CD interest rates can sometimes struggle to keep up with inflation. 2 When inflation rises, the value of your dollar goes down. So if you invest $1,000 in a 1-year CD with a 1.5% interest rate, and inflation rises 1.9% in that same year, your money will be less valuable at the end of the year.
What is a CD?
A certificate of deposit (CD) is a low-risk savings tool that can boost the amount you earn in interest while keeping your money invested in a relatively safe way. Like savings accounts, CDs are considered low risk because they are FDIC-insured up to $250,000. However, CDs generally allow your savings to grow at a faster rate than they would in ...
What happens if you withdraw money before the CD term ends?
If you need to access your funds before the CD’s term ends, you are subject to an early withdrawal penalty, which can significantly reduce the interest you earned on the CD.
How to build a CD ladder?
With a CD ladder, you divide your initial investment into equal parts and invest each portion in a CD that matures every year. For example, say Leo has $10,000. To build a CD ladder, he invests $2,000 each in a 1-year, 2-year, 3-year, 4-year and 5-year CD. As each CD matures, he reinvests the money at the current interest rate or uses the cash for another purpose. If Leo reinvests his money, he might choose a new 5-year CD, which would ensure he has one CD maturing each year as long as he continues laddering.
What happens when a CD matures?
When the term is up (or when the CD matures), you get back the money you deposited (the principal) plus any interest that has accrued.
Do CDs have a minimum balance?
CDs come in varying terms and may require different minimum balances. The rate you earn typically varies by the term and how much money is in the account. In general, the longer the term and the more money you deposit, the higher the rate you are offered. (A longer term does not necessarily require a larger minimum balance.)
Can interest rates change on CDs?
Overall interest rates may change during your CD’s term. If rates rise, you miss out on earning those higher rates, since your money is committed for the CD’s term. However, if rates go down, you benefit: You still earn the higher rate that was offered when you opened the CD. CD laddering, buying multiple CDs of varying term lengths, ...
Is CD laddering good for saving?
But if you’re saving for something five years down the line, a CD with a longer term and higher rate may be more beneficial. Also, consider the economic environment. If it seems that interest rates may rise, or if you want to open multiple CDs, CD laddering can be a good option.
/what-is-gdp-definition-of-gross-domestic-product-3306038-final-bff6acefc7f04f17a7c266b06ead1659.png)
Benefits of CDs
Buy One and Hold: Risks and Limitations
- The simplest approach to investing in CDs is to buy one and hold it until it matures. There are several risks and limitationswith this strategy. The first is that interest rates may fall over time, so when the CD reaches maturity and the proceeds are ready to be reinvested into another CD, the next investment will offer a lower interest rate. Alternatively, if interest rates rise, you can lose o…
Portfolio Construction
- Early withdrawal penalties can present both short-term and long-term challenges with regard to an investor’s ability to address unplanned spending needs and financial developments that require an adjustment to long-term plans. Fortunately, there are investment strategies available to help address these challenges.
Variations
- Traditional CDs are purchased and then held to maturity to avoid early withdrawal penalties. Because this model doesn’t fit every investor’s needs, there are a wide variety of innovative alternatives ranging from simple to sophisticated. Some of the more notable variations include: Bear CD:Designed for sophisticated investors, bear CDs increase the rate of interest that they pa…
CDs Are Safe…But Pay Attention
- CDs are typically viewed as a “set it and forget” investment, meaning that there is no ongoing monitoring required. Investors simply hand over their money, sit back, and collect interest, safe in the knowledge that the FDIC or NCUA (in most cases) is providing protection against losses. While that is generally true, this is where a bit of complacen...