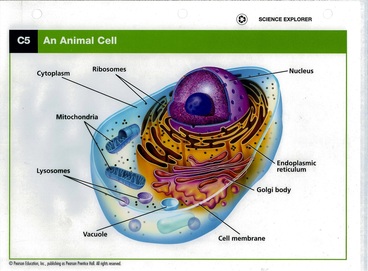
What are the basic components of a cell?
What are the basic components of cells?
- PLASMA MEMBRANE / CELL MEMBRANE. Structure- a bilipid membraneous layer composed of proteins and carbohydrates.
- CYTOPLASM.
- NUCLEUS.
- 1. "
- RIBOSOMES.
- GOLGI BODY / APPARATUS.
- LYSOSOMES.
- MITOCHONDRIA.
What are the major parts of a cell?
Plant Cell Parts
- Cell wall. A plant cell has a rigid cell wall, which is the outermost of the cell. ...
- Cell membrane. This is also called a plasma membrane and is present adjacent to the cell wall. ...
- Cytoplasm. ...
- Mitochondria. ...
- Lysosomes. ...
- Peroxisomes. ...
- Chloroplast. ...
- Amyloplasts. ...
- Golgi apparatus. ...
- Endoplasmic reticulum. ...
What is the main function of a cell?
Six Main Cell Functions
- Provide Structure and Support. Like a classroom is made of bricks, every organism is made of cells. ...
- Facilitate Growth Through Mitosis. In complex organisms, tissues grow by simple multiplication of cells. ...
- Allow Passive and Active Transport. ...
- Produce Energy. ...
- Create Metabolic Reactions. ...
- Aids in Reproduction. ...
What are the three main components to cell theory?
What are the three components of the cell theory quizlet?
- First cell theory. All living things are composed of cells.
- Second cell theory. Cells are the basic unit of structure and function in living things.
- Third cell theory. All cells are produced from other cells.
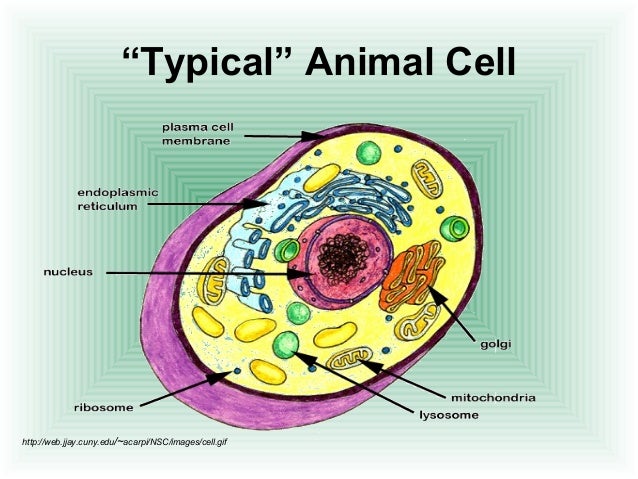
What is the cell parts and their functions?
What's found inside a cellOrganelleFunctionNucleusDNA StorageMitochondrionEnergy productionSmooth Endoplasmic Reticulum (SER)Lipid production; DetoxificationRough Endoplasmic Reticulum (RER)Protein production; in particular for export out of the cell3 more rows
What are the 7 functions of a cell?
The cell wall has the following functions:Protects the cell from physical injury.Gives the cell a sense of organisation.Keeps osmotic bursting at bay.It maintains the shape of the cell.Regulates the flow of information between cells.It regulates the expansion of cells.Provides protection against pathogens.
What are the 13 parts of the cell?
The thirteen parts of an animal cell are vacuoles, cytoplasm, vesicles, centrioles, ribosomes, nuclear membrane, cell membrane, cytoskeleton, mitochondria, endoplasmic reticulum, nucleolus, Golgi apparatus and nucleus.
What is a cell by definition?
(sel) In biology, the smallest unit that can live on its own and that makes up all living organisms and the tissues of the body. A cell has three main parts: the cell membrane, the nucleus, and the cytoplasm. The cell membrane surrounds the cell and controls the substances that go into and out of the cell.
What are the 4 types of cells?
The Four Main Types of CellsEpithelial Cells. These cells are tightly attached to one another. ... Nerve Cells. These cells are specialized for communication. ... Muscle Cells. These cells are specialized for contraction. ... Connective Tissue Cells.
What is importance of cell?
Cells provide structure and function for all living things, from microorganisms to humans. Scientists consider them the smallest form of life. Cells house the biological machinery that makes the proteins, chemicals, and signals responsible for everything that happens inside our bodies.
What is the smallest cell?
Mycoplasma gallicepticumMycoplasma gallicepticum, a parasitic bacterium which lives in the primate bladder, waste disposal organs, genital, and respiratory tracts, is thought to be the smallest known organism capable of independent growth and reproduction. The cell in the work is known as mycoplasma. Its diameter is 0.0001 mm.
What is cell and its types?
Cells are of two types: eukaryotic, which contain a nucleus, and prokaryotic cells, which do not have a nucleus, but a nucleoid region is still present. Prokaryotes are single-celled organisms, while eukaryotes may be either single-celled or multicellular.
What are the 10 functions of cell?
Functions of a CellStructure and Support. You know a house is made of bricks. ... Growth. In complex organisms such as humans, the tissues grow by simple multiplication of cells. ... Transport. ... Energy Production. ... Metabolism. ... Reproduction.
What is cell structure?
A cell consists of three parts: the cell membrane, the nucleus, and, between the two, the cytoplasm. Within the cytoplasm lie intricate arrangements of fine fibers and hundreds or even thousands of miniscule but distinct structures called organelles.
Who discovered cell?
Robert HookeInitially discovered by Robert Hooke in 1665, the cell has a rich and interesting history that has ultimately given way to many of today's scientific advancements.
What are the 2 types of cell?
There are two main types of cells: prokaryotic cells and eukaryotic cells. Prokaryotic cells include bacteria and archaea. Prokaryotes—organisms composed of a prokaryotic cell—are always single-celled (unicellular). Prokaryotic cells don't contain a nucleus.
What are the 10 functions of cell?
Functions of a CellStructure and Support. You know a house is made of bricks. ... Growth. In complex organisms such as humans, the tissues grow by simple multiplication of cells. ... Transport. ... Energy Production. ... Metabolism. ... Reproduction.
What are the four main functions of the cell?
transport process,2. removing waste,3. reproduction,4. produce energy.
What are the five life functions of cells?
The basic processes of life include organization, metabolism, responsiveness, movements, and reproduction.
What are five functions common to all cells?
Cells provide six main functions. They provide structure and support, facilitate growth through mitosis, allow passive and active transport, produce energy, create metabolic reactions and aid in reproduction.
1. What is a Cell?
A cell is defined as the fundamental, structural and functional unit of all living organisms.
2. State the characteristics of cells.
Cells provide the necessary structural support to an organism. The genetic information necessary for reproduction is present within the nucleus. St...
3. Highlight the cell structure and its components.
The cell structure comprises several individual components which perform specific functions essential to carry out life processes. The components...
4. State the types of cells.
Cells are primarily classified into two types, namely Prokaryotic cells Eukaryotic cells
5. Elaborate Cell Theory.
Cell Theory was proposed by Matthias Schleiden, Theodor Schwann, and Rudolf Virchow, who were German scientists. The cell theory states that: All...
6. What is the function of mitochondria in the cells?
Mitochondria are known as the powerhouse of the cells. Their primary function is to produce the energy currency of the cells, ATP. It also regulate...
7. What are the functions of the cell?
The essential functions of the cell include: The cell provides support and structure to the body. It facilitates growth by mitosis. It helps in rep...
8. What is the function of Golgi bodies?
Golgi bodies pack and sort the proteins for secretion. It creates lysosomes and transports lipids around the cells.
9. Who discovered the cell and how?
Robert Hooke discovered cells in 1665. He observed a piece of cork under a compound microscope and noticed minute structures reminiscent of small r...
What is a Cell?
A cell is the structural and fundamental unit of life. The study of cells from its basic structure to the functions of every cell organelle is called Cell Biology. Robert Hooke was the first Biologist who discovered cells.
Why are cells considered the structural and functional unit of life?
Meiosis causes the daughter cells to be genetically different from the parent cells. Thus, we can understand why cells are known as the structural and functional unit of life. This is because they are responsible for providing structure to the organisms and performs several functions necessary for carrying out life’s processes.
How is the cell interior organized?
The cell interior is organised into different individual organelles surrounded by a separate membrane.
Why is the discovery of cells important?
Discovery of cells is one of the remarkable advancements in the field of science. It helps us know that all the organisms are made up of cells, and these cells help in carrying out various life processes. The structure and functions of cells helped us to understand life in a better way.
How big are cells?
Cells are the fundamental unit of life. They range in size from 0.0001 mm to nearly 150 mm across
Which cell type has a nucleus?
Eukaryotic cells are characterised by a true nucleus.
Which structure controls the exit and entry of molecules into the cell?
Cell membrane. It is a selectively permeable structure that controls the exit and entry of molecules into the cell.
What is a Cell ?
In Biology, there are quite numerous valid definitions of cells and in this article, we define cells as the microscopic units that make up humans and every other living organisms with some having just 1 cell and others having trillions of cells like humans.
Types of Cells
When it comes to types of cells, There exist only two main types of cells ; Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells, with the Prokaryotic cells lacking a true nucleus.
Some Importances and Functions of Cell Parts
Cells provide structure for the body, take in nutrients from food substances and later on convert those nutrients into energy in order to carryout specialised functions. Cells also contain the body's hereditary material and they can also replicate themselves.
Types of Living Things
Based on the study of the cell, it was possible to distinguish between two forms of living beings : unicellular or simple, and multicellular or complex.
Cell Function
Neurons allow the body to be coordinated and its parts to be articulated.
Cell size
The size of the cells can be very varied , depending on the functions they perform and the degree of complexity they possess.
Importance of the cell
The cell is the minimum unit of life endowed with reproductive capacity and autonomy . This means that it is the fundamental, primordial portion of all known life and that without it, it would not have arisen as we know it.
What is the function of a cell?
The cell helps in regulating the movement of water, nutrients, waste matter into and outside the body. It contains the life code, that is, DNA, that coordinates the synthesis of proteins and transfer of genetic information from the parent cell to the daughter cell. It also contains ribosomes, which are very important for protein synthesis.
Why is the cell important?
Each type of cell has a specific function to perform and is present in specific locations in the body of an organism. The cell helps in regulating the movement of water, nutrients, waste matter into and outside the body.
What is the outermost layer of a cell called?
The outermost covering of a cell is called the cell membrane. The cell membrane acts like a traffic policeman that regulates entry and exit of substances, that is, ions and solutes. This helps in regulating the internal cell balance.
What is the basic unit of life?
The basic unit of life is a cell. You will find that there are hundreds and millions of different types of living cells. These cells together make up a multicellular organism or an individual cell makes up a unicellular organism. Each cell is unique and has different functions and features. Cells are differentiated as eukaryotic cells ...
What is the outermost covering of a plant cell?
The outermost covering of a plant cell is called the cell wall. It is made up of cellulose, and it helps provide mechanical support to the cell. It surrounds the cell membrane and helps maintain the pressure within the cell.
Which cell makes up the largest group of organisms?
Prokaryotic cells make up unicellular organisms that form the largest group of organisms. All bacteria have a prokaryotic cell that have simple parts. Eukaryotes on the other hand are an advanced form of cells that make up multicellular organisms and few unicellular organisms have complex parts.
What is the brain of a cell?
The brain of a cell, the cell nucleus, controls all the functions occurring in the cell. It contains the blueprint of life, that is, DNA.
What is the most important part of a plant cell?
The Chloroplast. The chloroplast is one of the most important parts of the plant cell and is crucial to its function. As is commonly known, plants use photosynthesis to harness the power of the sun to create nutrients. The sunlight is used to turn carbon dioxide and water into sugar and oxygen, a waste product.
Where do proteins leave the cell?
The proteins arrive in vesicles from the ER and leave in vesicles from the Golgi as they move between the different parts.
What is the purpose of the vacuole?
They are generally about 80% of the plant cell’s interior space. Their main purpose is to support the cell’s structure by ensuring that it does not collapse.
Why are plants unique among eukaryotic cells?
Plant cells are unique among eukaryotic cells because they are capable of creating their own food. “A dried plant is nothing but a sign to plant ...
Why are cell walls porous?
Besides providing the structure, strength, and rigidity of the cell, the cell walls are also porous and allow the movement of materials into and out of the cell. These channels are regulated to ensure that harmful compounds are kept out.
Why are plant cells so rigid?
Plant cells are very rigid because of their cell wall, a component that does not exist within animal cells. The plant cell wall was inherited from our prokaryotic ancestor and became a highly specialized part of the cell. The rigidity comes from a complex series of cross-linked structures made of cellulose and lignin that reinforce the wall.
What is the membrane of a plant cell?
The plasma membrane, found in all living cells, encloses the plant cell and is surrounded by the cell wall. In plant cells, this membrane adds an additional layer of protection and regulation to the cell wall.
