
What does certificate authority stand for?
What Does Certificate Authority (CA) Mean? A certificate authority (CA) is a trusted entity that manages and issues security certificates and public keys that are used for secure communication in a public network.
How do I create my own certificate authority (CA)?
Using the Procedure
- Create Certificate Authority Certificate. Makecert will ask you for a Certificate Authority password. ...
- Run MMC.EXE
- Install the new Certificate Authority Certificate. ...
- Create the Signing Certificate. ...
- Install the Signing Certificate. ...
- Create a BAT File named SIGNCODE.BAT. ...
- Example of How to Sign a Program. ...
What is the abbreviation for certificate authority?
In cryptography, a certificate authority or certification authority ( CA) is an entity that issues digital certificates. A digital certificate certifies the ownership of a public key by the named subject of the certificate.
Do I need a certificate of authority for my business?
States that require a Certificate of Authority have different criteria to determine whether a business needs one. In California, for example, companies that “ transact intrastate business " need a Certificate of Authority. Physical presence, such as a having a warehouse or sales representative in the state, would fall into this category.
What is certification authority example?
Examples include Comodo, GeoTrust, and Symantec. Becoming a Certificate Authority (CA) simply means that you (or your customers) are in charge of the issuing process of cryptographic pairs of private keys and public certificates.
How do I find my certificate authority?
Go to Start -> Run -> Write adsiedit. msc and press on Enter button. Under Certification Authorities, you'll find your Enterprise Root Certificate Authority server.
What does certificate authority mean?
A certificate authority (CA) is a trusted entity that issues Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) certificates. These digital certificates are data files used to cryptographically link an entity with a public key. Web browsers use them to authenticate content sent from web servers, ensuring trust in content delivered online.
What is a certification authority name any two?
A certificate authority (CA), also sometimes referred to as a certification authority, is a company or organization that acts to validate the identities of entities (such as websites, email addresses, companies, or individual persons) and bind them to cryptographic keys through the issuance of electronic documents ...
Why do I need a certificate authority?
A certificate authority, also known as a certification authority, is a trusted organization that verifies websites (and other entities) so that you know who you're communicating with online. Their objective is to make the internet a more secure place for organizations and users alike.
How do I create a certificate authority?
Create your own Certificate AuthorityStep 1 : Create the private key. As the first step you should create the private key for the CA. ... Step 2: Generate the root certificate. ... Step 3 : Generate the CSR. ... Step 4: Generate the Certificate using the CSR. ... Step 5: Testing the generated certificate. ... 3. —
What are the types of certificate authority?
There are generally two types of CAs – a root CA and a subordinate CA. A root CA is tasked with creating the certificates that are used by other CAs. As such, it is the root-of-trust for the entire PKI and its security and integrity are therefore critically important.
How many certificate authorities are there?
There are over 100 different certificate authorities around the world that validate businesses and sites across the globe. Notably, imposters may still attempt to take advantage of certificates, so web users should still be familiar with site trust indicators, including site seals, to know if a website is secure.
What is local certificate authority?
A Certificate Authority (CA) is a trusted central administrative entity that can issue digital certificates to users and servers.
Is GoDaddy a certificate authority?
GoDaddy is an SSL certificate authority that sells web hosting, domain names, SSL certificates, and other web services. GoDaddy was established in 1997, and is headquartered in Scottsdale, Arizona, USA.
Who is the best certificate authority?
Top 6 Best SSL Certificate Authority List & SSL Certificate BrandsDigiCert SSL.Comodo SSL.RapidSSL.Thawte SSL.Sectigo SSL.GeoTrust SSL.
Is DigiCert a certificate authority?
As a certificate authority (CA) and trusted third party, DigiCert provides the public key infrastructure (PKI) and validation required for issuing digital certificates or TLS/SSL certificates.
What server is the certificate authority?
Microsoft Certificate Authority (CA) is part of the Windows Server operating system. A certification authority (CA) is responsible for attesting to the identity of users, computers, and organizations. The CA authenticates an entity and vouches for that identity by issuing a digitally signed certificate.
How do I know if my certificate authority is working?
On the Windows Certificate Authority server, open the Certification Authority console (Start > Run > certsrv. msc ) and verify that the certificates are in the Issued Certificates folder.
How do I open MMC Certificate Authority?
To access Certificate Manager, click the Start button, type certmgr. msc in the search field, and click the Enter key. If this is a program you use frequently, you can add it to your Start menu.
How many certificate authorities are there?
There are over 100 different certificate authorities around the world that validate businesses and sites across the globe. Notably, imposters may still attempt to take advantage of certificates, so web users should still be familiar with site trust indicators, including site seals, to know if a website is secure.
What is a code signing certificate?
Code signing certificates — Used to sign software releases and validate software from the vendor or developer.
What is an OV certificate?
OV — Organization Validated certificates are authenticated by the CA against business registry databases hosted by governments. CAs may require certain documents and contact personnel to ensure that OV certificates contain legitimate business information. This is the standard type of certificate required on a commercial or public-facing website.
How many TLS certificates does Digicert have?
As one of the largest CAs worldwide, DigiCert has almost two decades of experience delivering trusted solutions to millions of users and devices worldwide, and we currently have over 22 million active TLS certificates. The majority of the Fortune 500 and many Global 2000 companies rely on DigiCert.
What are the different types of TLS certificates?
Three main types of TLS certificates 1 DV — Ownership of Domain Validated certificates is confirmed by having the applicant prove control of the domain. However, DV certificates do not offer identifying organizational information, so they are not recommended for commercial purposes. 2 OV — Organization Validated certificates are authenticated by the CA against business registry databases hosted by governments. CAs may require certain documents and contact personnel to ensure that OV certificates contain legitimate business information. This is the standard type of certificate required on a commercial or public-facing website. 3 EV — Extended Validation certificates offer the highest level of authentication to safeguard brands and protect users. They are used by the world’s leading organizations, including over half of the top 400 ecommerce sites, according to 2019 data from Comscore and Netcraft.
What does it mean when a website says "not secure"?
Additionally, anytime you visit a site that says “ not secure ,” you know that a site has not been validated by a CA or their validation has expired.
How long is a TLS certificate valid?
Keep in mind that all publicly-trusted TLS/SSL certificates are valid for a maximum period of one year (398 days) and you will need to revalidate each year.
Can imposters take advantage of certificates?
Notably, imposters may still attempt to take advantage of certificates, so web users should still be familiar with site trust indicators, including site seals, to know if a website is secure. Additionally, you can check for identifying information about the certificate owner, like organizational name, location and more, ...
What is a CA certificate?
In cryptography, a certificate authority or certification authority ( CA) is an entity that issues digital certificates. A digital certificate certifies the ownership of a public key by the named subject of the certificate. This allows others (relying parties) to rely upon signatures or on assertions made about the private key that corresponds to the certified public key. A CA acts as a trusted third party—trusted both by the subject (owner) of the certificate and by the party relying upon the certificate. The format of these certificates is specified by the X.509 or EMV standard.
Which is the most popular SSL certificate authority?
An updated W3Techs survey shows that IdenTrust, a cross-signer of Let's Encrypt intermediates, has remained as the most popular SSL certificate authority, while Symantec has dropped out of the chart, due to its security services being acquired by DigiCert. Sectigo (formerly Comodo CA) is the third-largest SSL certificate authority with 16.8% of the market: Digicert maintains the GeoTrust, Digicert, Thawte, and RapidSSL brands.
What is domain validation?
The commercial CAs that issue the bulk of certificates for HTTPS servers typically use a technique called " domain validation " to authenticate the recipient of the certificate. The techniques used for domain validation vary between CAs, but in general domain validation techniques are meant to prove that the certificate applicant controls a given domain name, not any information about the applicant's identity.
What is a CA client?
The clients of a CA are server supervisors who call for a certificate that their servers will bestow to users. Commercial CAs charge money to issue certificates, and their customers anticipate the CA's certificate to be contained within the majority of web browsers, so that safe connections to the certified servers work efficiently out-of-the-box. The quantity of internet browsers, other devices and applications which trust a particular certificate authority is referred to as ubiquity. Mozilla, which is a non-profit business, issues several commercial CA certificates with its products. While Mozilla developed their own policy, the CA/Browser Forum developed similar guidelines for CA trust. A single CA certificate may be shared among multiple CAs or their resellers. A root CA certificate may be the base to issue multiple intermediate CA certificates with varying validation requirements.
Why do we need a trusted certificate?
Trusted certificates can be used to create secure connections to a server via the Internet . A certificate is essential in order to circumvent a malicious party which happens to be on the route to a target server which acts as if it were the target. Such a scenario is commonly referred to as a man-in-the-middle attack.
Why do clients use CA certificates?
The client uses the CA certificate to authenticate the CA signature on the server certificate, as part of the authorizations before launching a secure connection. Usually, client software—for example, browsers—include a set of trusted CA certificates. This makes sense, as many users need to trust their client software.
Do CA certificates expire?
Browsers and other clients of sorts characteristically allow users to add or do away with CA certificates at will. While server certificates regularly last for a relatively short period, CA certificates are further extended, so, for repeatedly visited servers, it is less error-prone importing and trusting the CA issued, rather than confirm a security exemption each time the server's certificate is renewed.
What Does a Certificate Authority Do?
Basically, a public certificate authority is a publicly trusted entity that issues digital certificates to individuals, businesses, and other organizations. These certificates are basically small data files that contain vetted identifying information about the organization. So, CAs are a way to prove yourself to people who don’t know you (or your organization) personally by having a reputable third party vouch for you.
Why Do We Need Certification Authorities?
Why do you need a driver’s license or state ID card? Because it helps you prove that you’re you to third parties who wouldn’t know otherwise. A CA helps you to establish trust with others because they’re trusted for issuing valid, reliable certificates — and that trust is integral to public key infrastructure ( PKI). (We’ll speak more to PKI later.)
Why are third party certification authorities trustworthy?
Third-party certification authorities are inherently trustworthy for two main reasons: Public CAs are autonomous and not controlled by certificate requestors. This is a huge difference between public and private certificate authorities — public CAs are separate from the entities that request certificates.
How long does it take for an extended certificate to be issued?
This type of certificate requires the most verification about your organization and generally takes up to five days to issue.
What does holographic sign mean on a DMV card?
They then print the card with holographic markings that indicate your card is real and isn’t a realistic forgery (think of this like a digital signature). You can then use this documentation to prove your identity.
What does a CA certificate do?
Before issuing a certificate, the certification authority checks out the requesting organization. They look at documents and records from official sources to make sure that the company is legitimate. After that, the CA issues a digital certificate that the organization can use to secure their websites, software, and email communications using encryption and digital signatures .
Why is SSL/TLS certificate important?
By issuing an SSL/TLS certificate for your website, for example, you can then use a secure transport layer security (TLS) protocol to send and receive encrypted data. As a site owner, this helps you to protect the information that travels to and from your servers.
What Is a Certificate Authority (CA)?
A certificate authority, also known as a certification authority, is a trusted organization that verifies websites (and other entities) so that you know who you’re communicating with online. Their objective is to make the internet a more secure place for organizations and users alike. This means that they play a pivotal role in digital security.
How does a certificate authority give credence to individual certificates?
The way that a certificate authority gives credence to those individual certificates is by issuing root certificates that other certificates link back to . This is what we call the chain of trust (we’ll discuss that more in depth shortly).
What is SSL/TLS certificate?
SSL/TLS certificates are based on PKI, and there are a few key parts that need to be in place for the SSL certificate to work: A digital certificate (for example, an SSL/TLS certificate) that proves the website’s identity. A certificate authority that verifies the website and issues the digital certificate.
How many CAs are there?
You may be surprised to know that there are actually a few hundred public CAs that exist globally. They’re often divided by country or region. However, it’s really just the top dozen or so that issue most of the certificates that are in use online.
How long does a certificate last?
(depending on the certificate). These public certificates have a limited lifespan of one year (398 days, more specifically) starting on or before Sept. 1, 2020.
Why are certificate authorities important?
A certificate authority is the Issuer of Certificates, the Signer of (Public) Keys, and the Authenticator of Organizations and Individuals.
Why do developers use certificates?
Developers and publishers use these types of certificates to digitally sign their code to ensure its integrity. This enables users to tell whether it’s been tampered with since it was signed originally. It also helps you to authenticate yourself or your organization by showing that it was you who actually signed it.
What do certificate authorities do?
Some people use certificate authorities for human verification. After establishing a partnership with a recognized company, these people can do things like sign up for checking accounts or cross borders without burdensome paperwork.
How do certification authorities work?
Connecting with CA companies can reassure visitors that your site is secure and trustworthy. It's relatively easy to get started.
What is cryptographic key?
Cryptographic keys: These pieces of data can encrypt and protect data in transit.
What happens if a website doesn't connect to a certificate authority?
If your website doesn’t connect with a certificate authority, your visitors will get a dialogue box that tells them about the problem. Typically, these warnings tell users that the sites they want to visit just can’t be trusted. Visitors can override these warnings and visit the site anyway. But some won’t take the risk.
Why do people use certification authority?
But most people and organizations use a certification authority to help them prove digital ownership and protect critical assets. We’ll focus on that use case here.
Does Google want to certificate websites?
Anyone who hosts a website should be interested in certification. After all, Google wants encryption on all websites, and the company can penalize those who don’t comply. Without a certificate, Google might devalue your site in search.
What is a Certificate Authority (CA) and What do they do?
A certificate authority (CA) is a company or entity that has been authorized by browsers to issue TLS/SSL and other forms of certificates.
How do Certificate Authorities (CAs) Increase Public Trust on the Internet?
A certificate authority (CA) is a trusted third-party that enables secure communication and transactions to occur online. CAs are also known as PKI Certificate Authorities because they issue digital certificates based on public key infrastructure (PKI).
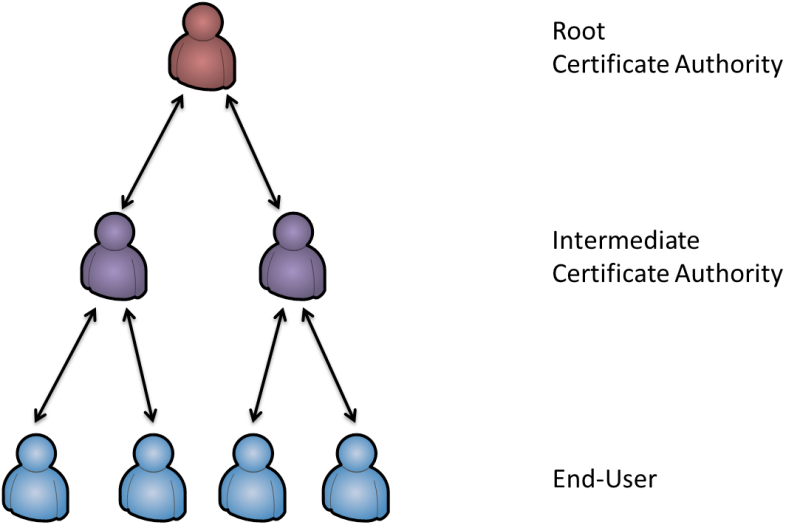
The PKI Certificate Authority Trust Hierarchy
Certificate Authorities are deemed trusted by browsers and devices based on their root certificate.
What is certificate based cryptography?
Certificate-based cryptography uses public-key cryptography to protect and sign data. Over time, attackers could obtain data that was protected with the public key and attempt to derive the private key from it. Given enough time and resources, this private key could be compromised, effectively rendering all protected data unprotected. Also the names that are guaranteed by a certificate may need to be changed over time. Because a certificate is a binding between a name and a public key, when either of these change, the certificate should be renewed.
How many bits is a CA certificate?
When using an RSA certificate for a CA, ensure that the key length is at least 2048 bits. You must not attempt to use an RSA certificate below 1024 bits for the CA. The CA service (certsvc) will not start if an RSA key of less than 1024 bits is installed.
How to protect CA private key?
Many organizations protect CA private keys by using a hardware security module (HSM). If an HSM is not used, the private key is stored on the CA computer. For more information, see Hardware Security Module (HSM) in Microsoft TechNet. Offline CAs should be stored in secure locations and not connected to the network.
What is a subordinate CA?
CAs that are not root CAs are considered subordinate. The first subordinate CA in a hierarchy obtains its CA certificate from the root CA. This first subordinate CA can use this key to issue certificates that verify the integrity of another subordinate CA. These higher subordinate CAs are referred to as intermediate CAs. An intermediate CA is subordinate to a root CA, but it serves as a higher certifying authority to one or more subordinate CAs.
How many characters are in a CA name?
If you use non-Latin characters (such as Cyrillic, Arabic, or Chinese characters), your CA name must contain fewer than 64 characters. If you use only non-Latin characters, your CA name can be no more than 37 characters in length.
What is an enterprise CA?
They publish certificates and certificate revocation lists (CRLs) to AD DS. Enterprise CAs use information that is stored in AD DS, including user accounts and security groups, to approve or deny certificate requests. Enterprise CAs use certificate templates. When a certificate is issued, the Enterprise CA uses information in the certificate template to generate a certificate with the appropriate attributes for that certificate type.
Can Enterprise CAs issue certificates?
These features are available only when the CA infrastructure is integrated with Active Directory. Additionally, only Enterprise CAs can issue certificates that enable smart card sign-in, because this process requires that smart card certificates are mapped automatically to the user accounts in Active Directory.
Summary
The following content describes two options to find the name of the Enterprise Root Certificate Authority server.
Option 1
Sign in by using domain administrator to computer that connects to the domain.
Option 2
Sign in by using domain administrator to computer that connects to the domain.
Summary
In cryptography, a certificate authority or certification authority (CA) is an entity that stores, signs, and issues digital certificates. A digital certificate certifies the ownership of a public key by the named subject of the certificate. This allows others (relying parties) to rely upon signatures or on assertions made about the private key that corresponds to the certified public key. A CA acts as a trusted third party—trusted both by the subject (owner) of the certificate and by the party relying …
Overview
Trusted certificates can be used to create secure connections to a server via the Internet. A certificate is essential in order to circumvent a malicious party which happens to be on the route to a target server which acts as if it were the target. Such a scenario is commonly referred to as a man-in-the-middle attack. The client uses the CA certificate to authenticate the CA signature on the server certificate, as part of the authorizations before launching a secure connection. Usuall…
Providers
Worldwide, the certificate authority business is fragmented, with national or regional providers dominating their home market. This is because many uses of digital certificates, such as for legally binding digital signatures, are linked to local law, regulations, and accreditation schemes for certificate authorities.
However, the market for globally trusted TLS/SSL server certificates is largely held by a small nu…
Validation standards
The commercial CAs that issue the bulk of certificates for HTTPS servers typically use a technique called "domain validation" to authenticate the recipient of the certificate. The techniques used for domain validation vary between CAs, but in general domain validation techniques are meant to prove that the certificate applicant controls a given domain name, not any information about the applicant's identity.
Validation weaknesses
Domain validation suffers from certain structural security limitations. In particular, it is always vulnerable to attacks that allow an adversary to observe the domain validation probes that CAs send. These can include attacks against the DNS, TCP, or BGP protocols (which lack the cryptographic protections of TLS/SSL), or the compromise of routers. Such attacks are possible either on the network near a CA, or near the victim domain itself.
Issuing a certificate
A CA issues digital certificates that contain a public key and the identity of the owner. The matching private key is not made available publicly, but kept secret by the end user who generated the key pair. The certificate is also a confirmation or validation by the CA that the public key contained in the certificate belongs to the person, organization, server or other entity noted in t…
Industry organizations
• Certificate Authority Security Council (CASC) – In February 2013, the CASC was founded as an industry advocacy organization dedicated to addressing industry issues and educating the public on internet security. The founding members are the seven largest Certificate Authorities.
• Common Computing Security Standards Forum (CCSF) – In 2009 the CCSF was founded to promote industry standards that protect end users. Comodo Group CEO Melih Abdulhayoğlu is co…
CA compromise
If the CA can be subverted, then the security of the entire system is lost, potentially subverting all the entities that trust the compromised CA.
For example, suppose an attacker, Eve, manages to get a CA to issue to her a certificate that claims to represent Alice. That is, the certificate would publicly state that it represents Alice, and might include other information about Alice. Some of the information about Alice, such as her e…