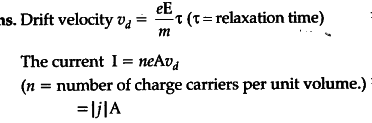
The drift velocity is the average velocity of the charge carriers in the drift current. The drift velocity, and resulting current, is characterized by the mobility; for details, see electron mobility (for solids) or electrical mobility (for a more general discussion).
How do you find the drift velocity of charge carriers?
The formula for evaluating the drift velocity of charge carriers in a material of constant cross-sectional area is given by: u = j n q , {displaystyle u={j over nq},}. where u is the drift velocity of electrons, j is the current density flowing through the material, n is the charge-carrier number density, and q is the charge on the charge-carrier.
What is the relation between drift velocity and electric current mobility?
Relation between Drift Velocity and Electric Current Mobility is always a positive quantity and depends on the nature of the charge carrier, the drift velocity of an electron is very small usually in terms of 10 -3 ms -1. Hence, at this velocity it will take approx. 17 mins for electrons to pass through a conductor of 1 meter.
What is drift velocity of electron?
Drift velocity is the average velocity attained by charged particles in a material due to an electric field. The drift velocity of an electron for a unit electric field is called mobility of the electron. Visit to know more.
What is the unit of drift velocity?
The net velocity at which these electrons drift is known as drift velocity. The average velocity attained by charged particles, (eg. electrons) in a material due to an electric field. The SI unit of drift velocity is m/s. It is also measured in m 2 / (V.s).
What is meant by velocity?
Velocity is the rate at which bodies change their position relative to a frame of reference (rate change of position). Velocity can be described as...
What is meant by drift velocity?
It is the average velocity acquired by a charged particle (like an electron or proton) in the body due to an electric field. Usually, an electron i...
What is meant by electron mobility?
Electron mobility is generally stated as drift velocity per unit electric field.
What is the formula to find the drift velocity?
The formula is, I = nAvQ Here, I – the current flowing through the conductor n – the number of electrons A – the area of the cross-section of...
What are the characteristics of drift velocity?
Drift velocity is directly proportional to current. When an electric field is exerted over a conductor, the electrons jump towards the high potent...
1. Give Some Common Theory on how Drift Velocity and Electric Current are Related.
Let’s take a conducting wire having length L and of uniform cross-section area A, which contains the electric field—assuming that the wire contains...
2. What is Mobility in Physics?
In a solid-state, mobility in physics is a measure of the ease with which a particular type of charged particle passes through a solid under the in...
3. Does Drift Velocity Depend on Diameter?
Drift velocity does not depend on the cross-sectional area or the diameter of any conductor. For the same p.d. Here, with V across the conductor, a...
Drift velocity
The name is drift velocity because the electron drifts in the opposite direction of the electric field at low velocity and at high thermal velocities between two collisions. The drift velocity refers to the average velocity obtained by a particle, such as an electron, as a result of an electric field’s action.
Relaxation time (τ)
The time interval between two successive collisions of electrons with the positive ions in the metallic lattice is defined as relaxation time.
Mobility (μ)
Electron mobility is defined as “drift velocity per unit electric field.
Relation between Current Density and Drift velocity
The current density is defined as ” The whole current supplying throughout a cross-sectional conductor unit within a unit of time.
Sample problems
Drift velocity is defined as “The Average velocity with which the free electrons get drifted towards the positive end of the conductor under the influence of an external electric field.”
What happens to the charge carriers in motion when they are positive?
If the charge carriers in motion are positive instead of negative, then the field force acting on the carriers would be following the electric field direction and movement, or the drift velocity of the particle will be from left to right.
How to understand drift velocity?
The concept of drift velocity can be understood by studying the random motion of free electrons moving around the conductor. These free electrons keep on moving in the conductor in a disorganized way with random velocities. But when the conductor is subjected to an electric field, some kind of electrical force is applied to the randomly moving electrons and in the direction of the field. The field forces the electrons to switch towards high potential while maintaining the randomness of the motion. Scientifically we can express that the electrons will drift towards higher potentials by maintaining the random motions.
What is the current generated by the movement of the electrons in the conductor?
Since the movement of the electron is known as the drift velocity, the current that is generated due to the drift movement of the electrons in the electrically charged conductor is known as the drift current . Every current flowing through a conductor is known as drift current.
What is drift velocity?
Drift is the slow movement of an object toward something. The average-velocity attained by the charged particles in a material due to the influence of the electric field is known as the drift velocity. Drift velocity is directly proportional to current. It is also directly proportional to the magnitude of the external electric field in ...
What is the measure of the ease with which a particular type of charged particle passes through a solid under the influence?
In a solid-state, mobility in physics is a measure of the ease with which a particular type of charged particle passes through a solid under the influence of an electric field. Such particles are drawn by electric fields and periodically interact with solid molecules. The combination of electric field and collision causes the particles to move at an average speed is known as drift speed. The charge carrier in most metals is a negatively charged electron.
How fast do electrons move in a metal?
Generally, the electrons move at very high speeds of around a million m/s along a wire, but the electron drift or move very slowly in the direction of the current.
How do electrons drift?
Scientifically we can express that the electrons will drift towards higher potentials by maintaining the random motions. Further, it has been observed that each electron has its velocity while they move towards the higher potential point of the conductor. This net velocity is known as the drift velocity of electrons.
What is drift velocity?
In physics a drift velocity is the average velocity attained by charged particles, such as electrons, in a material due to an electric field. In general, an electron in a conductor will propagate randomly at the Fermi velocity, resulting in an average velocity of zero.
How fast do electrons flow in a switch?
By comparison, the Fermi flow velocity of these electrons (which, at room temperature, can be thought of as their approximate velocity in the absence of electric current) is around 1570 km/s.
How many atoms are in 1 m3 of copper?
In one mole of any element there are 6.022 × 1023 atoms (the Avogadro number ). Therefore, in 1 m3 of copper there are about 8.5 × 1028 atoms ( 6.022 × 1023 × 140 685.5 mol/m3 ).
When a potential difference is applied across a conductor, what happens?
When a potential difference is applied across a conductor, free electrons gain velocity in the direction opposite to the electric field between successive collisions (and lose velocity when traveling in the direction of the field), thus acquiring a velocity component in that direction in addition to its random thermal velocity. ...
Is drift velocity proportional to current?
Drift velocity is proportional to current. In a resistive material it is also proportional to the magnitude of an external electric field. Thus Ohm's law can be explained in terms of drift velocity. The law's most elementary expression is:
Is current density vector?
But the current density and drift velocity, j and u, are in fact vectors, so this relationship is often written as:
What is Drift Velocity?
Drift velocity definition is, subatomic particles like electrons shift in random ways continually. Once electrons are subjected to an electric field then they shift randomly, however they drift slowly in one way within the direction of the applied electric field. The net velocity at which point electrons will drift is called also called drift velocity. To understand this concept first we have to know about drift. So, drift is the movement of an object slowly in the direction of something. The SI unit of drift velocity is m/s or m2/ (V.s).
How to understand drift velocity?
The drift velocity concept can be understood by observing the random movement of electrons around the conductor. These electrons keep on traveling in the conductor in a random way through random velocities. Sometimes, a conductor may be subjected to an electric field & consequently some type of electrical energy is used on the randomly moving electrons except in the field direction.
How is the electron movement around a conductor explained?
In a conductor, the movement of the electrons will be continuous within a random manner using random velocities. Once the conductor is in the electric field then some force is applied toward the moving electrons within the field’s direction.
How is the average velocity obtained in an electric field?
Under the electric field impact, the average velocity can be obtained through the electrons because of the electron’s drift.
How fast does an electron move in 0.1 amps?
Thus, the electron’s velocity within a specific metal piece showing 0.1 Amps of current is approximately 1×10-5 m/s. Usually, the electrons shift at extremely high speeds like million m/s throughout a wire however, they move extremely slowly within the path of the current. So this is an example of drift current.
What is current density?
The current density can be defined as the whole current supplying throughout a cross-sectional conductor unit within a unit of time. We know the formula of drift velocity.
What is relaxation time?
It can be defined as the time period between the collisions of two electrons.
How fast do electrons travel in a wire?
The drift velocity of electrons in a piece of metal with a current of 0.1 A will be around 1x10 -5 m/s, so imagine how long it takes one electron to travel along a 10 cm long wire! The electrons are actually travelling at speeds of up to a million m/s in the wire but only drift very slowly in the current direction.
Why do charged particles not travel in a straight line through a conductor?
Charged particles do not travel in a straight line through a conductor, because they collide with other particles in the material. We therefore use the average speed the particle travels at along the conductor. This is called the drift velocity.
Which conductor has the most charge carriers?
Good conductors such as metals have the most charge carriers. Semiconductors have about 1 x10 10 times fewer charge carriers than metals. At low voltages insulators have no free electrons so that a current is unable to flow. Current Electricity and Conventional Current Conductors and Insulators.
What is the Drift Velocity of an Electron?
Electrons will be the primary focus of this lesson, however, ions and positively charged holes are also charged carriers.
What is the term for how quickly an electron can move through metal in the presence of an electric field?
Electron mobility describes how quickly an electron can move through metal in the presence of an electric field. The mobility is dependent on the drift velocity and the magnitude of the electric field. The equation for electron mobility is
How does electricity appear instantaneous when a switch is flipped?
As soon as a switch is flipped, electrons are added to a circuit. These electrons interact with electrons already in the circuit through electromagnetic fields. The closer two electrons are, the stronger they repel each other. This effect propagates through the wires in a circuit much more rapidly than the actual electrons. The velocity with which these effects propagate is close to the speed of light. This is why electricity appears instantaneous when flipping a switch.
Why is the velocity of charged particles in an electric field called drift velocity?
The velocity of charged particles in an electric field is called drift velocity because it is a small net flow in one direction. This drift is proportional to the current in the material and the magnitude of the electric field.
How do electrons move in a material?
Without an applied electric field, electrons move around randomly in a material. Focusing on any one electron in a material, it moves in many different directions. This is true for every electron in the material, meaning that there is no overall motion in any particular direction over time. The diagram illustrates this idea. Every electron will follow a path similar to that shown in red.
How to calculate drift velocity?
The drift velocity can be calculated using the current, the density of charge carriers, the cross-sectional area of the wire, and the charge of an electron. It is given by: v_d = frac {I} {nAq}
What is drift velocity?
Drift velocity in physics is the motion of charged particles in a material acted upon by an electric field. Charged particles experience a net velocity in one direction in an electric field, called the drift velocity.

Overview
Experimental measure
The formula for evaluating the drift velocity of charge carriers in a material of constant cross-sectional area is given by:
where u is the drift velocity of electrons, j is the current density flowing through the material, n is the charge-carrier number density, and q is the charge on the charge-carrier.
This can also be written as:
Numerical example
Electricity is most commonly conducted through copper wires. Copper has a density of 8.94 g/cm and an atomic weight of 63.546 g/mol, so there are 140685.5 mol/m . In one mole of any element, there are 6.022×10 atoms (the Avogadro number). Therefore, in 1 m of copper, there are about 8.5×10 atoms (6.022×10 × 140685.5 mol/m ). Copper has one free electron per atom, so n is equal to 8.5×10 electrons per cubic metre.
See also
• Flow velocity
• Electron mobility
• Speed of electricity
• Drift chamber
• Guiding center
External links
• Ohm's Law: Microscopic View at Hyperphysics