Which particle has no charge at all?
neutron : A subatomic particle forming separate of the lens nucleus of an atom. It has no charge. It is adequate in multitude to a proton or it weighs 1 amu . How do you know if a substance is pure? What impact did the Hands Off doctrine have on the correctional system in America?
What is a positively or negatively charged particle?
In simple terms, a particle that has a positive surface charge is known as a positively charged particle. Similarly, any particle that has a negative charge on its surface is known as a negatively charged particle. There are some fundamental particles: neutrons, protons and electrons and these make up all...
Does a charged particle produce electricity?
Moving charged particles create a magnetic force field. Accelerating charged particles produce changing electric and magnetic force fields which propagate as EM waves. EM radiation that has all the electric and magnetic field variations along the same plane is polarized.
What are some examples of charged particles?
They are:
- Electrons – Negatively charged subatomic particles in an atom are known as electrons. ...
- Protons – Positively charged subatomic particles in an atom are known as protons. ...
- Neutrons – Neutrons are neutral subatomic particles that are present in all atomic nuclei except ordinary hydrogen atoms. ...

What does charged particle mean?
On the other hand, if an atom has an unequal number of protons and electrons, then the atom is electrically charged (and in fact, is then referred to as an ion rather than an atom). Any particle, whether an atom, molecule or ion, that contains less electrons than protons is said to be positively charged.
What is an charged particle called?
A charged particle is called an ion. Any atom or group of atoms that bears one or more positive charge is called cation and one or more negative charge is called anion.
What is the charge of matter?
In an atom of matter, an electrical charge occurs whenever the number of protons in the nucleus differs from the number of electrons surrounding that nucleus. If there are more electrons than protons, the atom has a negative charge. If there are fewer electrons than protons, the atom has a positive charge.
What are charged particles in physics?
A charged particle is a particle having an electric charge in physics. It might be an ion, such as a molecule or atom, having an excess or deficiency of electrons in comparison to protons.
Where are charged particles found?
The nucleus contains positively charged particles called protons. The nucleus also contains neutral particles called neutrons. Around the nucleus, there are particles called electrons. The electrons are negatively charged, and they orbit the nucleus at different distances.
How do particles become charged?
An electrical charge is created when electrons are transferred to or removed from an object. Because electrons have a negative charge, when they are added to an object, it becomes negatively charged. When electrons are removed from an object, it becomes positively charged.
Does matter have a charge?
Matter consists of both positively and negatively charged particles. A material which has the same amount of positive and negative charges is electrically neutral. An object gets charged when these charged particles get transferred from one body to another leading to an excess of a certain kind of charged particles.
What is matter made of?
All matter consists of atoms, which, in turn, consist of protons, neutrons and electrons. Both protons and neutrons are located in the nucleus, which is at the center of an atom. Protons are positively charged particles, while neutrons are neutrally charged.
What are the 3 types of charges?
Examples of the types of charges are subatomic particles or the particles of matter: Protons are positively charged. Electrons are negatively charged. Neutrons have zero charge.
Which particles are charged in an atom?
There are three subatomic particles: protons, neutrons and electrons. Two of the subatomic particles have electrical charges: protons have a positive charge while electrons have a negative charge. Neutrons, on the other hand, don't have a charge.
What's a negatively charged particle called?
ElectronsElectrons are a type of subatomic particle with a negative charge.
What are the charged particles present in matter and who discovered them?
Electrons were discovered by Sir John Joseph Thomson in 1897. After many experiments involving cathode rays, J.J. Thomson demonstrated the ratio of mass to electric charge of cathode rays. He confirmed that cathode rays are fundamental particles that are negatively-charged; these cathode rays became known as electrons.
Are electrons charged particles?
Electrons are negatively charged particles of an atom. The negative charge of electrons of an atom balances the positive charge of the protons in the atomic nucleus, hence a normal atom is electrically neutral.
Why anion is a charged particle?
An anion is an ion with negative charge, meaning it has more electrons than protons. Anions are formed when an atom gains one or more electrons: the gain of the negatively-charged electron(s) results in an overall negative charge.
What is a negative particle called?
Electrons are negatively charged subatomic particles found in the outermost regions of atoms.
What are uncharged particles?
The nucleus of an atom is made up of protons and neutrons. Protons are positively charged particles. Neutrons are neutral particles. So, the uncharged particle in the nucleus of an atom is the neutrons.
What are the charged particles in an atom?
These charged particles or subatomic particles in the matter are negatively charged electrons, positively charged protons, and neutrons without any charge.
What is the negative charge of an atom?
Electrons – Negatively charged subatomic particles in an atom are known as electrons. An electron carries a charge of 1.602 × 10 – 19 Coulomb in magnitude. The mass of an electron is 1 1837 times that of a proton.
What are the three subatomic particles that make up an atom?
Conclusively, an atom contains three charged subatomic particles: electron, proton, and neutron. Later, by various discoveries, the structure of the atom was defined. An atom consists of a positively charged proton and uncharged neutron at the centre, making it a positively charged nucleus and electrons revolving around the nucleus in their respective orbits like the Solar System. Each electron revolving around the nucleus in the fixed orbit has a discrete amount of energy; this makes an atom more stable. The charge of an electron is – 1.602 × 10 – 19 and that of a proton is almost like an electron numerically but positively charged. Electrons are the lightest subatomic particles, and the maximum mass of an atom is confined to its nucleus, where protons and neutrons are present.
What is the mass of a proton?
The charge of a proton is equal to the charge of an electron in magnitude; but the charge is positive. The mass of a proton is 1.673 × 10 – 27 K g. H + ion or nucleus of a Hydrogen atom is an example of a proton.
What is the structure of an atom?
According to the latest structure of the atom, an atom consists of a positively charged nucleus at the centre that is composed of protons and neutrons and electrons revolving around the nucleus in different orbits . The structure of an atom closely resembles our Solar System, where the Sun at the centre resembles the nucleus, and the planets moving around different orbits resemble electrons. Let’s have a brief discussion on the different ‘Charged Particles in Matter’ and their discoveries.
What are neutrons in chemistry?
Neutrons are subatomic particles that do not have any charge at all , i.e., they are neutral. Along with the discovery of protons, by 1920, scientists knew that most of the mass of the atom was concentrated in a nucleus at the centre of an atom and that this central core of an atom contains protons. James Chadwick, in 1932 announced that the core also contained a new uncharged particle, which he termed as neutron. Thus, with the discovery of the neutron, a complete picture of an atom was clear. The Atomic model consists of three charged subatomic particles, electron, proton, and neutron.
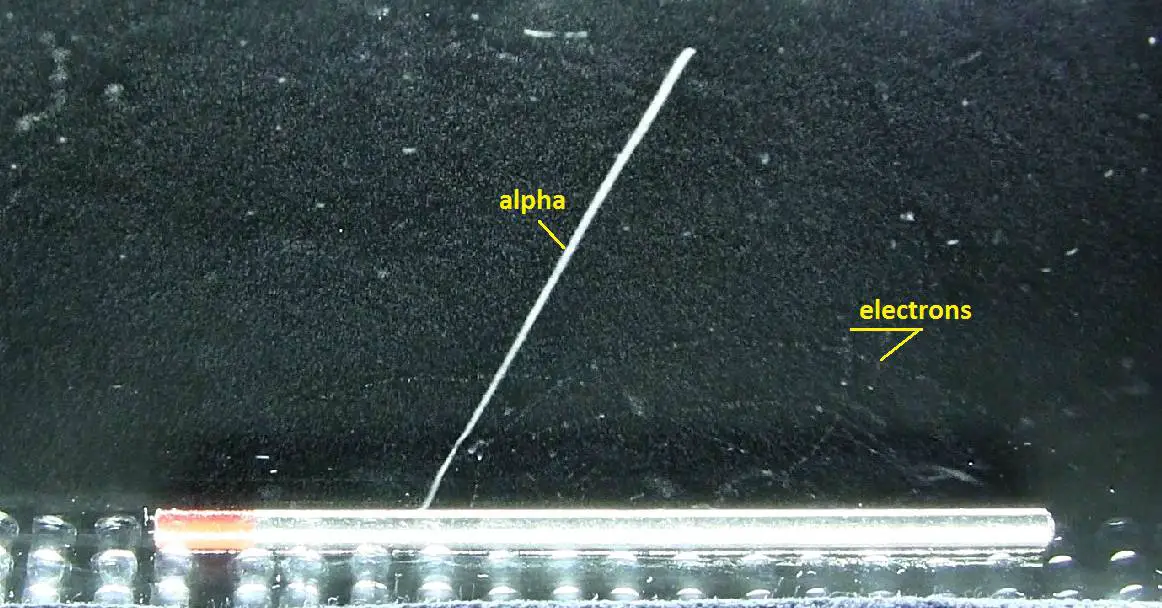
What happens when an incident beam containing high energy electrons falls on the matter?
When an incident beam containing high energy electrons falls on the matter, it can transfer a critical amount of energy to an electron present at the inner shell of an atom. The electron present in the atom gains energy and is ejected by ionizing energy provided by the incident electron to a higher energy level. When this excited electron loses its energy again, it will fall to the lower energy level emitting light energy in the form of scintillations.
What are the particles in matter?
All matter is composed of divisible particles called atoms. The atoms are composed of tiny charged subatomic particles named electrons, protons, and neutrons. Earlier it was postulated by John Dalton that atoms are indivisible particles. However, the contribution of many scientists by the very end of 1800’s or the start ...
What is the stream of negatively charged particles emitted from the cathode?
The streams of negatively charged particles discharged from the cathode end of the discharge tube are called cathode rays.
What is the unit of mass for a neutron?
Gram is not a very appropriate unit for the calculation of such tiny subatomic particles. Therefore, they are alternatively calculated in Dalton or amu (atomic mass unit). A Neutron and a proton have a similar mass that is nearly 1 amu.
What are the positively charged radiations produced from the anode end of the discharge tube called?
The positively charged radiations produced from the anode end of the discharge tube are called canal rays . The rays were named as anode rays or canal rays. A series of experiments led to the discovery of protons. Protons are known as the particles that contribute to the positive charge of the atom.
What was the discovery of subatomic particles?
The discovery of the subatomic particles raised many questions. One of them was how these subatomic particles are arranged in an atom. This led to the proposal of different models of these charged particles. These form the basis of the vast subject of “structure of an atom.”
How is neutron mass measured?
Neutron is represented by the letter “n” and is considered a neutral particle.The mass of a neutron is measured as 1.6 x 10 -24 g.
What is the name of the electrode on a glass tube?
Two electrodes were placed at the two opposite ends of the glass discharge tube which was further connected to high voltage supply (battery). The electrode joined to the negative end was called cathode and the electrode joined to the positive end was called anode.
What is charged particle?
In physics, a charged particle is a particle with an electric charge. It may be an ion, such as a molecule or atom with a surplus or deficit of electrons relative to protons. It can also be an electron or a proton, or another elementary particle, which are all believed to have the same charge (except antimatter ).
Is plasma a gas?
A plasma is a collection of charged particles, atomic nuclei and separated electrons, but can also be a gas containing a significant proportion of charged particles.
What are the particles that stick together?
Protons and neutrons are sticky and stick together into atomic nuclei. This is called the strong nuclear force or the strong interaction. Some matter does not feel the strong force; these particles are called "leptons.". Some matter does, and they are called "quarks" (and combinations of them are called "hadrons").
Which experiment found that electrons have a definite charge?
Starting with the Millikan oil drop experiments the electron was found to have a definite charge and the microcosm of elementary particles made mathematical sense , from nuclear physics to quark physic s with assigned charges and masses and a number of quantum numbers.
Why does the Higgs field have a weak coupling to all of the "matter" particles?
In short, the Higgs explains why everything which is not a proton or a neutron doesn't zip off at the speed of light.
Why do protons and neutrons have a mass so much higher than electrons?
We've secretly also answered why protons and neutrons have a mass so much higher than the electron: the electron is a single particle which does not feel the strong force; the protons and neutrons are made up of three quarks which are bound together by the strong force.
What is the term for the phenomenon where electrons attract and repel protons?
To particle physics, this is all known as "electromagnetism."
What is the standard model of particle physics?
The standard model of particle physics is built on gauge theory, which is a theory of local symmetries. This means that the symmetries act differently at different points in space (and time). For example, if you move everything in the universe 1m in one direction, nothing is changed.
What is the name of the force that attracts matter?
Things fall down. Matter mysteriously attracts other matter through an unscreenable infinite-range force known as "gravity". In those four interactions, and mostly in that third one, we think we can find mostly everything that happens in this world.

Types of Charged Particles in Matter
- The matter is made up of three types of charged, subatomic particles. They are: 1. Electrons– Negatively charged subatomic particles in an atom are known as electrons. An electron carries a charge of \(1.602 \times {10^{ – 19}}\) Coulomb in magnitude. The mass of an electron is \(\frac{1}{{1837}}\) times that of a proton. 2. Protons– Positively cha...
Discovery of Charged Particles in Matter
- According to Dalton’s Atomic Theory, John Dalton assumed atoms as the smallest and indivisible particles of matter. This concept was later proved wrong with the discovery of subatomic particles. Let’s learn about the discoveries of these subatomic particles in detail:
Interaction of Charged Particles
- When charged particles interact, the transfer of energy occurs from the charged particles to the materials through which they travel. For example, when two similar charges interact, they repel each other, on the other hand when two opposite charges interact they attract each other.
Ionization of Electron
- When an incident beam containing high energy electrons falls on the matter, it can transfer a critical amount of energy to an electron present at the inner shell of an atom. The electron present in the atom gains energy and is ejected by ionizing energy provided by the incident electron to a higher energy level. When this excited electron loses its energy again, it will fall to the lower ener…
FAQs on Charged Particles in Matter
- Q.1. What are charged particles called? Ans:A charged particle is called an ion or an atom that consists of an unbalanced number of electrons or protons, making it a negatively charged or positively charged atom. Q.2. What are the 3 charged particles? Ans: An atom contains three types of charged subatomic particles: (i) Negatively charged electron, (ii) Positively charged prot…