
What does an analytical chemist do?
Analytical Chemists perform qualitative and quantitative analysis. They use their data to assess the chemical properties of materials and food. The primary job responsibility of an Analytical Chemist is to perform analytical chemistry testing on materials and chemicals. The purpose of the testing depends on the industry and the product.
What is analytical method in chemistry?
What is Analytical Chemistry | Applications, Methods
- Definition of Analytical Chemistry. Analytical chemistry is the study of the composition of matter. ...
- History. Analytical chemistry has been important since the early days of chemistry, providing methods for determining.
- Methods Used In Analytical Chemistry. ...
- Applications of Analytical Chemistry. ...
- Scope of Analytical Chemistry. ...
What is an analytical chemistry?
Analytical chemistry is the science of obtaining, processing, and communicating information about the composition and structure of matter. In other words, it is the art and science of determining what matter is and how much of it exists. It is one of the most popular fields of work for ACS chemists.
What is the example of chemical reaction?
Some examples of simple synthesis reactions include:
- hydrogen + oxygen ---> water
- iron + oxygen ---> rust
- potassium and chlorine gas ---> chloride
- lime + carbon dioxide ---> calcium carbonate (used to strengthen masonry)
- water + carbon dioxide + light ---> glucose and oxygen (photosynthesis)
- sodium + chloride ---> sodium chloride (table salt)

How small is a sample for FTIR?
Very small samples, as little as 20 microns in diameter, can be used as a sample for FTIR analysis. Example: Manufacturers can use FTIR analysis to identify particles, residues, films, and fibers. FTIR can also help identify and, in some cases, quantify potentially harmful chemicals and contaminants on products such as electronics, toys, ...
What is FTIR analysis?
To determine the composition of unknown materials, FTIR analysis measures the infrared wavelengths absorbed by a sample. This chemical analysis method is often the first step in the materials analysis process because it is simple to perform and can illuminate so much information about the sample. Very small samples, as little as 20 microns in diameter, can be used as a sample for FTIR analysis.
How does TGA work?
Materials analysts use TGA to determine qualitative and quantitative differences in materials, such as polymers, by heating them in a controlled environment and plotting the volatilization temperatures of the sample’s components. If an inorganic filler is used in a polymer, TGA helps determine the quantity within.
What is Innovatech Labs?
Innovatech Labs conducts each of the chemical analysis methods listed above for a great variety industries. Contact us if you are having a manufacturing issue, and we will help you find a way to solve it.
Why is AES important?
Example: AES is especially helpful for evaluating the chemical treatments of metals used in medical devices and microelectronics. Chemical analysis methods can solve many problems for manufacturers, from contamination issues and reverse engineering to ensuring the cleanliness of a product and the corrosion resistance of a metal.
What is a DSC?
DSC is another type of thermal analysis method; DSC measures quantitative heat flow of samples undergoing phase transitions, say from a solid to a liquid. During testing, DSC measures the temperature at moments of transition and compares the rate of change to that of known reference materials. Manufacturers can use this information to analyze their materials and products for quality control, studying purity and composition variations, and the degree of crystallinity or oxidation.
What is TGA in polymer?
If an inorganic filler is used in a polymer, TGA helps determine the quantity within. Example: This chemical analysis method can help manufacturers understand how their products will react to extreme weather conditions. TGA defines the thermal limits of products.
What are the Similarities Between Qualitative Analysis and Quantitative Analysis in Chemistry?
Chemical analysis can be categorized as either qualitative or quantitative. Chemical analyses both qualitatively and quantitatively reveal details about sample components. The quantitative and qualitative methods are often applied in conjunction with each other. The main analytical method in chemistry for quantifying and qualitatively determining the chemical composition of a sample is Qualitative and Quantitative Chemical Analysis.
What is the method of separation used in chemistry?
Ans: Separations such as precipitation, extraction, and distillation, as well as qualitative analysis by colour, odour, or melting point, are used in traditional methods (also known as wet chemistry methods). The materials are separated using chromatography or electrophoresis techniques.
How to determine the identity of an analyte?
The identity of the analyte can be determined by studying chemical reactions and their components. The added reagents are selected to react selectively with one or a single class of chemical compounds to produce a distinct reaction product. In certain cases, the reaction product is a precipitate, a gas, or a coloured substance.
How are potentials measured in an electrochemical cell?
The potential (volts) and/or current (amps) in an electrochemical cell containing the analyte are measured using electroanalytical methods. These techniques are classified based on which aspects of the cell are regulated and which are calculated. Potentiometry (measuring the difference in electrode potentials), coulometry (measuring the transferred charge over time), amperometry (measuring the cell's current over time), and voltammetry (measuring the cell's current while actively altering the cell's potential) are the four major groups.
What is titrimetric analysis?
The titrimetric analysis is another name for volumetric analysis. From a buret, the reagent (the titrant) is progressively or stepwise applied to the analyte. The secret to good titrimetric analysis is to consider the titration's equivalence point (the point at which the quantities of the two reacting species are equivalent), which is usually visible as a colour transition.
What is the reaction between bromine and carbon tetrachloride?
The reaction between bromine in a carbon tetrachloride solution and organic compounds containing carbon-carbon double bonds is an example of a chemical reaction that can be used to classify organic functional groups. Owing to the addition of bromine through the double bonds, the distinctive red-brown colour of bromine vanishes, indicating the existence of a carbon-carbon double bond.
How is a precipitate formed?
A precipitate is formed when an excess of added reagent reacts with the analyte. The filtrate is measured after it has been washed, dried, and weighed. The concentration or quantity of the assayed material in the analyte is calculated using its mass.
What is chemical analysis of salts?
Chemical analysis for salts is usually restricted to chlorides, sulfates, carbonates, and sulfides. The latter two are analyzed qualitatively, and chlorides and sulfates are analyzed quantitatively. Quantitative analysis of chlorides and sulfates is undertaken by gravimetric, volumetric, or colorimetric (semiquantitative) analysis. The gravimetric and volumetric analysis of sulfates is detailed in BS 1881. For corrosion purposes, only the water-soluble sulfates are of concern, rather than total sulfates.
Why is chemical analysis important?
Chemical analysis of biomarkers generates information of great importance to environmental forensic investigations in terms of determining the source of spilled oil, differentiating and correlating oils, and monitoring the degradation process and weathering state of oils under a wide variety of conditions.
What is gamma ray spectroscopy?
Gamma ray spectroscopy is the technique by which the intensities of various gamma energies emanating from a radioactive source are measured. (See Chapter 30.) It can be used for qualitative identification of the components of radionuclide mixtures and for quantitative determination of their relative abundance. Such a situation arises in neutron activation analysis. This is a technique of chemical analysis for extremely minute traces down to ppb (parts per 109) of chemical elements in a sample. It employs a beam of neutrons for activation of isotopes that can then be identified, with counters, by the radioactive characteristics of the new nuclear species. This technique has been applied for the trace analysis of many elements in a variety of materials, from coal ash to catalysts, halides in phosphors, and trace impurities in many metals.
What is ESCA analysis?
An ESCA analysis of a surface will provide both qualitative and quantitative information on all elements and compounds (except H and He) present at >0.1 atomic%. However, ESCA will probe only the top 50–60 Å of the surface. From elemental chemical shifts (see in what follows), one can determine molecular environment, including oxidation state and bonding. For organic systems, such features as aromatic vs unsaturated structures can be determined from a combination of principal peaks and shake-up (π to π*) satellites. By using angle dependent ESCA (photoelectrons with varying escape depths), the chemistry of the surface to subsurface layer can be studied in both inorganic and organic systems. If one wants to study the surface of bulk chemistry, an elemental depth profile for several layers of the sample can be achieved using ion etching (often known as sputtering (a destructive process)). The overall advantage in using ESCA (using both core level and valence band spectra) is in the fingerprinting of materials and identifying of bonding orbitals that permits the physics and chemistry of the samples to be studied.
What is neutron activation?
Neutron activation is also used as a way to measure level in vessels with very thick walls or high temperature in which normal sensors cannot be placed . The neutron backscatter detector is mounted outside the vessel and measures the gamma radiation “reflected” from the process inside the vessel.
What is an analytical chemist?
Thus, the analytical chemist has become more than just a chemist measuring the chemical composition of a substance; he is now a problem solver with two more steps in the analytical process—one at the beginning (definition of the problem) and another at the end (solution to the problem). This means that the analytical chemist may measure things ...
Which class of materials conduct electricity without undergoing any chemical change?
In the first class are the metals and alloys and certain nonmetals, such as graphite, which conduct electricity without undergoing any chemical change. The flow of the current is due to the motion of electrons within the conductor, and the conduction is described as metallic or electronic.
What is differential scanning?
This method measures the quantitative heat flow of samples that are going through a transition. For example, if a sample is going from solid to liquid, you use differential scanning to measure the temperature during the moments of transition. Then these temperatures are compared to the rate of change to known reference materials.
What is gas chromatography used for?
It is used to identify unknown materials by comparing the mass spectrum of the sample to a reference library of spectra. This analysis is also used to determine the concentration of the components that are being studied within the sample.
What is the purpose of a materials analyst?
This is used by materials analysts to determine the quantitative and qualitative differences in materials. Analysts heat up the materials in a controlled environment and plot the temperatures of the samples.
How to determine if a strand breaks phosphate end group?
It can be determined by chemical as well as by enzymatic analysis that in about half of the strand breaks the altered sugar and the base are lost, which leads to strand breaks carrying phosphate end groups on both sites.
What is the term for the observation of a substance?
Those observations, which dealt with the production of substances, were termed chemical synthesis, and those related to determining what the substances were called chemical analysis. The analysis could be carried out in solution as well as in dry state. The solution methods were termed “wet” methods, and were further divided into volumetric and gravimetric. These methods used sight (visual observation) as detection device. The dry methods also used sight as the detector.
What is the most important step in soil chemical analysis?
The most significant step in soil chemical analysis is collecting the sample. It is important to take the necessary steps to obtain a representative sample; a poor sample can result in incorrect recommendations.
What is the nature of analytes?
The nature of the analytes and their abundances span the full spectrum: from elements to complicated organic molecules and concentrations expressed in percentage to parts per trillion. The most widely used instrumental techniques in current meat and meat product analysis are dealt here with emphasis on traditional ‘chemical’ techniques.
What are the contaminants in canned food?
Besides, food additives, food colorants, and tins of canned food as well as chemical contaminants, such as lead and cadmium and other heavy metals, according to the chemical standard specifications, are also examined.
What is the term for a large body of knowledge that deals with the production of substances?
Those observations, which dealt with the production of substances, were termed chemical synthesis , and those related to determining what the substances were called chemical analysis.
What techniques did the alchemists use to make gold?
The alchemists, in their futile attempts to make gold from base metals introduced the techniques of filtration, decantation, and distillation. Alchemist's zeal, however unsuccessful, leads to a reservoir of observations.
What are the different types of chemical analysis?
Within chemical analysis, there are two main types: quantitative and qualitative. Both of these analyses are often used in partnership with each other, with qualitative analysis used before qualitative – we will explain why below.
Why is chemical analysis important?
This analysis is not only important, but it’s crucial. This analysis increases the safety of everyday life, including the pollution of the air, the food we ingest, and how safe various manufacturing processes and environments are.
To conclude
Chemical analysis is the process of examining chemicals and chemicals present in the environment and/or climate. This is crucial, ensuring these chemicals are safe, and involved in other important processes such as analyzing air pollution.
What is an eval CN0407?
The EVAL-CN0407-SDPZ provides a reference design for real-world application by partitioning the system into a low-leakage mezzanine board and a data acquisition board. The input signal conditioning is implemented with the ADA4530-1 on the mezzanine board. The ADA4530-1 is an electrometer-grade amplifier with ultralow input bias current of 20 fA maximum at 85°C. A guard buffer is integrated on the chip to isolate the input pins from leakage to the printed circuit board (PCB). The default amplifier configuration is in the transimpedance mode with a 10 GΩ glass resistor and a metal shield that prevents leakage current from entering any of the high impedance paths on the board. In addition, the mezzanine board includes unpopulated resistor and capacitor pads to allow prototyping with surface-mount feedback resistors as well as other input configurations.
What is a DAQ system?
The circuit in Figure 1 is a two-channel, bank isolated , wide bandwidth data acquisition (DAQ) system, implemented with a simultaneous sampling architecture using an analog-to-digital converter (ADC) per channel. The system achieves high channel density along with isolation between the bank and the digital backplane, all while delivering exceptional performance. The design also makes efficient use of isolation channels by configuring the ADCs in daisy-chain mode and utilizing an isolator product with a trimmed delay clock feature. Power generation is also simplified using an isolator with an integrated pulse width modulation (PWM) controller and transformer driver to perform dc-to-dc conversion across the isolation barrier. The system also includes many common features of a typical DAQ signal chain, including input circuit protection, programmable gain channels, high accuracy, and high performance.
What is system functional diagram?
The system functional diagram in Figure 1 is a precision analog front end for measurement of current down to the femtoampere range. This industry-leading solution is ideal for chemical analyzers and … Read More..
What is the maximum channel scan rate of the AD7175-2?
It has a maximum channel scan rate of 50 kSPS (20 µs) for fully settled data. The output data rates range from 5 SPS to 250 kSPS.
What is the voltage range of the ADA4530-1?
It has an operating voltage range of 4.5 V to 16 V, enabling it to operate in conventional 5 V and 10 V single supply systems as well as ±2.5 V and ±5 V dual supply systems.
What is the purpose of the conductivity circuit shown in Figure 1?
The circuit shown in Figure 1 is a completely self-contained, microprocessor controlled, highly accurate conductivity measurement system ideal for measuring the ionic content of liquids, water quality analysis, industrial quality control, and chemical analysis.
What is the purpose of electrochemistry?
Many important liquid analyses like pH rely on electrochemistry, a branch of chemistry that characterizes the behavior of reduction-oxidation (redox) reaction s by measuring the transfer of electrons from one reactant to another. Electrochemical techniques can be used directly or indirectly to detect several important parameters that affect water quality, including chemical indicators, biological and bacteriological indicators and even some low level contaminants like heavy metals. Many of these indicative measurements are pertinent to determining important quality parameters of the tested analyte.
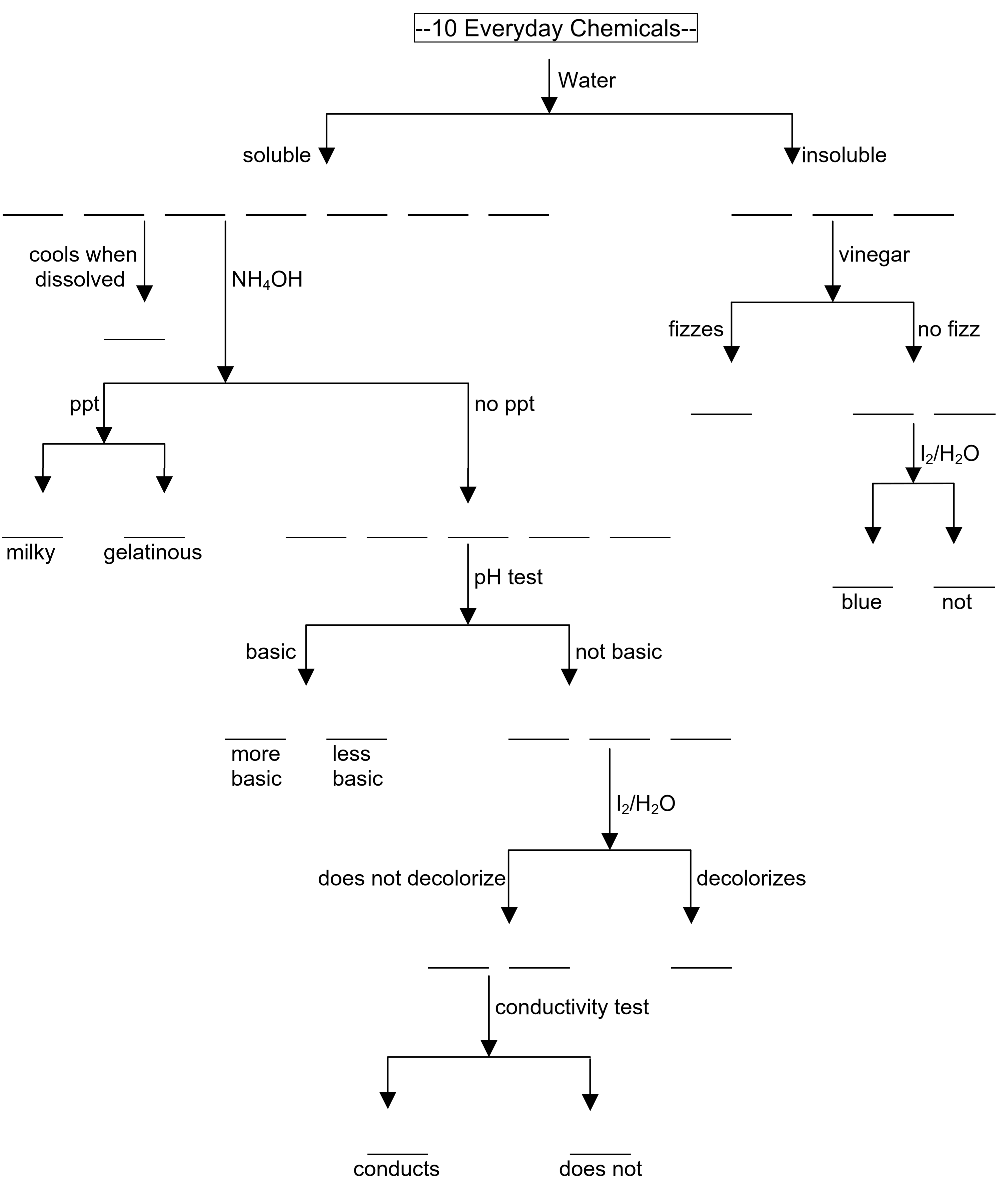
Classification of Analytical Methods
Classical Method
The Classical Method of Analysis For Organic Or Inorganic Analyte
For Quantitative Analysis
Instrumental Methods of Analysis
Classification of Instrumental Methods of Analysis
Electrochemical Analysis
- The potential (volts) and/or current (amps) in an electrochemical cell containing the analyte are measured using electroanalytical methods. These techniques are classified based on which aspects of the cell are regulated and which are calculated. Potentiometry (measuring the difference in electrode potentials), coulometry (measuring the transferred...
Thermal Analysis
Separation
Microscopy