
What is an example of chemical differentiation in chemistry?
Chemical differentiation. For instance, although the rare element uranium is very dense as a pure element, it is chemically more compatible as a trace element in the Earth's light, silicate -rich crust [citation needed] than in the dense metallic core.
What drives the process of cell differentiation?
The process of cell differentiation is driven by genetics, and their interaction with the environment. All organisms begin from a single cell. This single cell carries the DNA coding for all the proteins the adult organism will use. However, if this cell expressed all of these proteins at once it would not be functional.
How do cells differentiate into different types of cells?
In the other cell, chemical triggers activate the process of cell differentiation, and the cell will start to express the DNA of a specific cell type. Stem cells which can differentiate into entire organisms are known as embryonic stem cells and are said to be totipotent.
What is the role of transcription factors in cell differentiation?
One of the keys to the cell differentiation process is transcription factors. These hormones and chemicals direct the activities surrounding DNA, determining what gets transcribed and what is ignored.
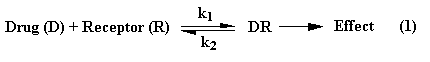
What is Earth differentiation?
The differentiation, or organization, of the Earth into layers is perhaps the most significant event in its history. It led to the formation of a core, a crust, and eventually continents. The light elements were driven from the interior to form an ocean and atmosphere. These four blocks are the same size.
What causes planetary differentiation?
The process of planetary differentiation is mediated by partial melting with heat from radioactive isotope decay and planetary accretion. Planetary differentiation has occurred on planets, dwarf planets, the asteroid 4 Vesta, and natural satellites (such as the Moon).
What does it mean when an asteroid goes through differentiation?
Differentiated asteroids are inferred to be objects, or fragments of objects, that were once heated to the point of partial melting and geochemical segregation of materials. Vesta is a classic example of a largely intact differentiated body.
How did Earth's composition become so differentiated?
Once the melting temperature of iron was reached within the earth, the initially random mixture of dust particles and gases began to unmix and differentiate according to the density of the various materials involved.
What happens when a planet goes through differentiation?
Planetary differentiation is the separation of different constituents of planetary materials resulting in the formation of distinct compositional layers. Denser material tends to sink into the center and less dense material rises toward the surface.
What evidence do we have that Earth differentiated?
What evidence do we have that Earth differentiated? The curved paths of seismic waves indicate that the interior density of Earth is greater than can be explained by compression alone. Why are Phobos and Deimos not spherical? Their gravity fields are too weak to pull their material into a spherical shape.
What is the difference between differentiated and undifferentiated meteorites?
Another important characterization of the meteorites is as differentiated or undifferentiated meteorites. The differentiated meteorites, including the irons and stony-irons, appear to be fragments of larger bodies for which separation according to density took place while they were in the molten state after formation.
Is Mars differentiated?
Like Earth, the interior of Mars has undergone a process known as differentiation. This is where a planet, due to its physical or chemical compositions, forms into layers, with denser materials concentrated at the center and less dense materials closer to the surface.
What is the definition of planetary differentiation quizlet?
Planetary differentiation. The process by which individual planets form their internal structure due to gravity and accretion and temperature.
What happens during the process of differentiation astronomy?
When planets begin to melt, the materials in them begin to separate from one another. The heaviest materials, such as metallic iron, sink to form cores. Low-density magmas rise, forming crusts. This process is called differentiation.
What does the term differentiated mean when applied to a planet would you expect to find that planets are usually differentiated Why?
Definition. Planetary differentiation is the separation of different constituents of planetary materials resulting in the formation of distinct compositional layers. Denser material tends to sink into the center and less dense material rises toward the surface.
How does core formation lead to an increase in heat in a differentiating planet?
- Iron being pulled to the core to build up (due to differentiation), and when they hit the core they stop transforming the kinetic energy into heat because when atoms collide, deformation occurs and there is an increase in heat.
Abstract
The formation, storage and chemical differentiation of magma in the Earth’s crust is of fundamental importance in igneous geology and volcanology.
Main
Magma reservoirs occur at several depths within the crust and typically grow incrementally through the intrusion of dykes or sills 1, 11, 13, 16, 17. High melt fractions must sometimes be present in these reservoirs to produce eruptible, low-crystallinity magmas 1, 7, 8, 9, 13.
Methods
To understand processes within crustal mush reservoirs, a quantitative model is required that includes three key features. First, the model must include the addition of hot magma or heat to initially solid crust, in order to create and grow the reservoir 22, 23, 31, 32, 33, 34.
Data availability
No original data are reported that were not created using the software code (MUSHREACT). Data can be recreated using the code.
Acknowledgements
M.D.J. and J.B. acknowledge funding from NERC Grant NE/P017452/1 “From arc magmas to ores (FAMOS): A mineral systems approach”. This paper is FAMOS contribution F05. M.D.J.
Additional information
Publisher’s note: Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Extended data figures and tables
a, Static melt fraction versus temperature for the modelled basalt and crust, extracted from the binary phase diagram for the chosen initial bulk compositions. Also shown are experimental equilibrium melting/crystallization data for metagreywackes and basalt over the pressure range 12, 73, 74 400–900 MPa. Triangles denote data from ref.
How do plants develop?
While the plant lifecycle sometimes seems alien and complex, the process of cell differentiation is very similar. While there are different hormones involved, all plants also develop from a single cell. A seed is simply a protective housing for the zygote, which also provides a food supply. It is very similar to an egg in the animal world. The zygote inside undergoes cell division, and becomes a small embryo. Development is halted, as the seed is distributed into the world.
Why do stem cells lose their totipotency?
As the systems continue to form, many of the stem cells lose their totipotency, themselves undergoing cell differentiation. This allows for faster production of specialized cells, which the growing organism needs to sustain its growth and enter the world with success. Through cell differentiation, tissues as different as brain tissue and muscle are formed from the same single cell.
What is the name of the cell that can differentiate into an entire organism?
In this case, one of the cells remains identical to the parent stem cell. In the other cell, chemical triggers activate the process of cell differentiation, and the cell will start to express the DNA of a specific cell type. Stem cells which can differentiate into entire organisms are known as embryonic stem cells and are said to be totipotent.
How does the meristem work?
On the surface, the meristem acts in a similar way. As it divides upward, it creates both inward and outward cells. The inward cells undergo a differentiation similar to that of the roots, creating more vascular tissue. On the outside, the cells undergo cell differentiation into stems and leaves.
How many meristems does an embryo have?
The embryo will begin to form two meristems. A meristem is a unique portion of stem cells, which undergo cell differentiation as they grow outward. One will grow towards the surface, while the other will become the roots. In the roots a layer of cells forms around the meristem, forming the root cap.
What happens if a cell expresses all of the proteins at once?
However, if this cell expressed all of these proteins at once it would not be functional. This cell must divide repeatedly, and the cells must begin the process of cell differentiation as they divide.
What is the original mass of cells that have not undergone differentiation?
The original mass of cells, which have not undergone differentiation, are known as stem cells. Unlike normal cell division, which creates two identical daughter cells, the division of stem cells is asymmetric cell division. In this case, one of the cells remains identical to the parent stem cell. In the other cell, chemical triggers activate ...
What is the name of the material that rises through the crust?
They may take on dome-shaped forms called diapirs when doing so. On Earth, salt domes are salt diapirs in the crust which rise through surrounding rock. Diapirs of molten low-density silicate rocks such as granite are abundant in the Earth's upper crust. The hydrated, low-density serpentinite formed by alteration of mantle material at subduction zones can also rise to the surface as diapirs. Other materials do likewise: a low-temperature, near-surface example is provided by mud volcanos .
What are the compositionally differentiated zones of the Earth?
The main compositionally differentiated zones in the solid Earth are the very dense iron-rich metallic core, the less dense magnesium-silicate -rich mantle and the relatively thin, light crust composed mainly of silicates of aluminium, sodium, calcium and potassium. Even lighter still are the watery liquid hydrosphere and the gaseous, nitrogen-rich atmosphere .
What is the process of separating out different parts of a planetary body?
In planetary science, planetary differentiation is the process of separating out different constituents of a planetary body as a consequence of their physical or chemical behavior, where the body develops into compositionally distinct layers; the denser materials of a planet sink to the center, while less dense materials rise to the surface, generally in a magma ocean. Such a process tends to create a core and mantle. Sometimes a chemically distinct crust forms on top of the mantle. The process of planetary differentiation has occurred on planets, dwarf planets, the asteroid 4 Vesta, and natural satellites (such as the Moon ).
What is the most common element that tends to congregate towards planetary interiors?
This tendency is affected by the relative structural strengths, but such strength is reduced at temperatures where both materials are plastic or molten. Iron , the most common element that is likely to form a very dense molten metal phase, tends to congregate towards planetary interiors. With it, many siderophile elements (i.e. materials that readily alloy with iron ) also travel downward. However, not all heavy elements make this transition as some chalcophilic heavy elements bind into low-density silicate and oxide compounds, which differentiate in the opposite direction.
Why did protoplanets get heated?
Heating due to radioactivity, impacts, and gravitational pressure melted parts of protoplanets as they grew toward being planets. In melted zones, it was possible for denser materials to sink towards the center, while lighter materials rose to the surface. The compositions of some meteorites ( achondrites) show that differentiation also took place in some asteroids (e.g. Vesta ), that are parental bodies for meteoroids. The short-lived radioactive isotope 26 Al was probably the main source of heat.
How much density is the Earth's crust?
On Earth, physical and chemical differentiation processes led to a crustal density of approximately 2700 kg/m 3 compared to the 3400 kg/m 3 density of the compositionally different mantle just below, and the average density of the planet as a whole is 5515 kg/m 3 .
What happens when protoplanets accrete more material?
When protoplanets accrete more material, the energy of impact causes local heating. In addition to this temporary heating, the gravitational force in a sufficiently large body creates pressures and temperatures which are sufficient to melt some of the materials.
