What chemical is used to make soap?
Types of Soaps
- Hard Soap. : Hard soap is made using sodium hydroxide (NaOH) or lye. ...
- Soft Soap. : Soft soap is made using potassium hydroxide (KOH) rather than sodium hydroxide. ...
- Lithium Soap. : Moving down the periodic table in the alkali metals group, it should be obvious soap may be made using lithium hydroxide (LiOH) as easily as NaOH or ...
What chemicals make up soap?
Step 1: Setting the Stage
- Hot plate
- Thermometer
- 6M Solution of Sodium Hydroxide (NaOH)
- ph Strips
- Stir Rod
- 1000 ml beaker
- Scale (grams)
- Shorting
- Computer
- Ingredient (Look up soapcalc.com and go through list of ingredients and pick one.)
What are the chemical equations in soap making?
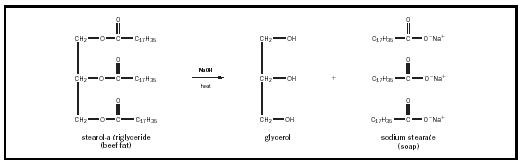
The chemical equation for soap is a fat, such as stearol, plus a strong base, such as sodium hydroxide or potassium hydroxide. This produces glycerol and crude soap, which consists of sodium or potassium salts of fatty acids. The reaction that occurs in making soap is called saponification.
What is the molecular formula of soap?
Soaps are denoted by the general formula RCOO-Na+, where R is any long chain alkyl group consisting 12 to 18 carbon atoms. Some common examples of fatty acids that are used in soaps are stearic acid having chemical formula C17H35COOH, palmitic acid having chemical formula C15H31COOH. Click to read full answer.

What are the components of SOAP?
SOAP specification can be broadly defined to be consisting of the following three conceptual components: protocol concepts, encapsulation concepts and network concepts.
What does SOAP stand for?
SOAP originally stood for "Simple Object Access Protocol " but version 1.2 of the standard dropped this acronym.
Why is XML used in SOAP?
XML Information Set was chosen as the standard message format because of its widespread use by major corporations and open source development efforts. Typically, XML Information Set is serialized as XML. A wide variety of freely available tools significantly eases the transition to a SOAP-based implementation. The somewhat lengthy syntax of XML can be both a benefit and a drawback. While it promotes readability for humans, facilitates error detection, and avoids interoperability problems such as byte-order ( endianness ), it can slow processing speed and can be cumbersome. For example, CORBA, GIOP, ICE, and DCOM use much shorter, binary message formats. On the other hand, hardware appliances are available to accelerate processing of XML messages. Binary XML is also being explored as a means for streamlining the throughput requirements of XML. XML messages by their self-documenting nature usually have more 'overhead' (e.g., headers, nested tags, delimiters) than actual data in contrast to earlier protocols where the overhead was usually a relatively small percentage of the overall message.
What is SOAP in computer?
SOAP (formerly an acronym for Simple Object Access Protocol) is a messaging protocol specification for exchanging structured information in the implementation of web services in computer networks. It uses XML Information Set for its message format, and relies on application layer protocols, most often Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP), ...
What is a SOAP machine?
These are physical/logical machines with processing units which are used to transmit/forward, receive and process SOAP messages. These are analogous to nodes in a network.
What is SOAP in web development?
SOAP allows developers to invoke processes running on disparate operating systems (such as Windows, macOS, and Linux) to authenticate, authorize, and communicate using Extensible Markup Language (XML). Since Web protocols like HTTP are installed and running on all operating systems, SOAP allows clients to invoke web services and receive responses independent of language and platforms.
What is SOAP independence?
independence (SOAP allows for any programming model) As an example of what SOAP procedures can do, an application can send a SOAP request to a server that has web services enabled—such as a real-estate price database—with the parameters for a search.
What are the ingredients in soap?
Liquid soaps have slightly different ingredients because their liquid state must be maintained at room temperature, and too many bubbles must be prevented from forming. Here are some of the common ingredients of liquid soaps: 1 Sodium benzoate and benzoic acid 2 Sodium laureth sulfate 3 Methylisothiazolinone and methylchloroisothiazolinone 4 Cocamidopropyl betaine 5 Fragrance, either from essential oils of flowers or from synthetic sources 6 pH adjusters
What are soaps made of?
In either case, the basic ingredients and the process are the same: soaps are made from an alkaline substance, namely lye (also known as sodium hydroxide), oil, and a choice of fragrance. However, the specific types of ingredients vary from soap to soap.
Why are soaps classified as salts?
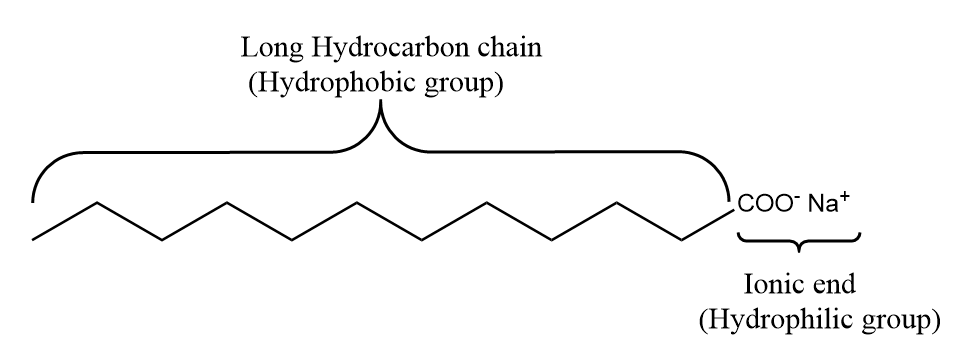
Soaps are chemically classified as salts of fatty acids because of the presence of an ionic, or polar head, and a nonpolar glyceride tail.
How much lye is in soap?
Many recipes for soaps require a 40% lye concentration dissolved in water. The proportion of oil with the lye solution may vary depending on the type of oil. For example, coconut oil can be up to 33% of the lye solution-oil mixture, while only 5% of grapeseed oil is recommended for soapmaking .
What is step 8 in soap making?
Step 8 – Packaging: This step is optional if you’re only making soap for personal use. If you’re intending to sell the soap, however, then you need to package it, not only to make it look presentable but also to ensure that it’s protected. Silicone moulds are popularly used in soapmaking.
Why do you stop cooking soap?
This is because alkalis can deeply penetrate skin tissue, meaning that too much alkali in soap can be very drying or irritating to the skin.
What are some examples of oils used in soap making?
For example, there are many different kinds of oils used in soap production, including tallows from beef or mutton fats, palm oil, coconut oil, olive oil, laurel oil, and canola oil. Even though it’s an ancient practice, the steps taken to make soap haven’t radically changed over the millennia.
What chemical is used to make soap?
If so here is the list of chemicals for making liquid soap: 1. Sodium triphosphate. This compound with symbol or formula of Na 5 P 3 O 10 also widely known as STTP is one of the chemical you should know and use in making liquid soap. This compound is used as cleanliness and thickness agent.
What is the best vitamin for soap?
Most people know that vitamin E is a skin vitamin, it shield skin from damage and at the same time boost the immune system. Vitamin E that used in soap making could be in capsule form or in liquid form as in oil form.
What is the best liquid soap to use for foaming?
7. Sulfonic acid. If you want your liquid soap more natural then sulfonic acid which belongs to organosulfur compound is a right choice to add as cleaning and foaming agent. With general formula of R−S (=O) 2 −OH this chemical will neutralize the basic effect of caustic soda.
How to make liquid shop?
The steps for making liquid shop are : Mixing the Lye-Water Solution and the Oils for the Liquid Soap, after heating the oil up approximately to 160 degrees celcius mix the lye-water compound. At first they might be wanted to separate but keep mixing with your stick blender until they are fully mixed.
How long can you keep liquid soap in a jar?
Sequester, after adding some fragrance and the liquid soap got cooler you can pour it to your jar then let it be for a or two weeks. After one or two you are able to enjoy your homemade liquid soap.
What is the name of the chemical that is used as a foaming agent?
Sodium Lauryl Sulfate. This chemical with formula of C 12 H 25 NaO 4 S is used as foaming agent. Many liquid soap such as shampoo and bath bomb using this chemical because it is inexpensive and very effective as foaming agent. It comes in solid form in the market. You may also read about Common Chemicals Used at Home.
How long to cook soap paste?
Cook, after you find the trace and mixing the soap paste you get to cook the mixture. Regularly check on the mixture in around 5 minutes if you see any separation start steering it until it holds. Diluting, after cooking the mixture up to 3 to 4 hours, you might seen the evolution of the mixture to be vaseline.
Overview
Types
Since they are salts of fatty acids, soaps have the general formula (RCO2 )nM (Where R is an alkyl, M is a metal and n is the charge of the cation). The major classification of soaps is determined by the identity of M . When M is Na (Sodium) or K (Potassium), the soaps are called toilet soaps, used for handwashing. Many metal dications (Mg , Ca , and others) give metallic soap. Wh…
History
It is uncertain as to who were the first to invent soap. The earliest recorded evidence of the production of soap-like materials dates back to around 2800 BC in ancient Babylon. A formula for making soap was written on a Sumerian clay tablet around 2500 BC; the soap was produced by heating a mixture of oil and wood ash, the earliest recorded chemical reaction, and used for washing woolen
Soap-making for hobbyists
A variety of methods are available for hobbyists to make soap. Most soapmakers use processes where the glycerol remains in the product, and the saponification continues for many days after the soap is poured into molds. The glycerol is left during the hot process method, but at the high temperature employed, the reaction is practically completed in the kettle, before the soap i…
See also
• African black soap, popular in West Africa
• Aleppo soap, popular in Syria
• Castile soap, popular in Spain
• Lava (soap), cleaning hands from industrial grease and dirt
Further reading
• Carpenter, William Lant; Leask, Henry (1895). A treatise on the manufacture of soap and candles, lubricants and glycerin. Free ebook at Google Books.
• Donkor, Peter (1986). Small-Scale Soapmaking: A Handbook. Ebook online at SlideShare. ISBN 0-946688-37-0.
• Dunn, Kevin M. (2010). Scientific Soapmaking: The Chemistry of Cold Process. Clavicula Press. ISBN 978-1-935652-09-0.
External links
• Chisholm, Hugh, ed. (1911). "Soap" . Encyclopædia Britannica. Vol. 25 (11th ed.). Cambridge University Press. pp. 296–299.