As nouns the difference between chemotaxis and phototaxis is that chemotaxis is (biology|biochemistry) the movement of a cell or an organism in response to a chemical stimulant while phototaxis is (biology) the movement of an organism either towards or away from a source of light.
What do you mean by phototaxis?
Phototaxis is the ability of organisms to move directionally in response to a light source. Many cyanobacteria exhibit phototaxis, both towards and away from a light source. In the environment, the ability to move into optimal light conditions for photosynthesis is likely to be an advantage.
What does the chemotaxis mean?
Chemotaxis is the directed migration of cells in response to concentration gradients of extracellular signals. In unicellular organisms, such as bacteria and amoebae, chemotaxis is frequently used as a foraging mechanism [1].
What is phototaxis and examples?
A positive phototaxis is exhibited by phototrophic organisms. They move towards the light source to take advantage of the light energy necessary in photosynthesis. Examples of phototrophic organisms exhibiting phototaxis are the phytoflaggellates, e.g. Euglena, and photosynthetic bacteria.
What are the 2 types of chemotaxis?
There are two major types of chemotaxis: (1) positive chemotaxis, i.e. the movement is toward a higher concentration of the diffusible substance, and (2) negative chemotaxis, i.e. the movement is in the opposite direction.
What is chemotaxis in biology?
Chemotaxis is the phenomenon whereby bacterial cells direct their movements according to certain chemicals in their environment.
What is chemotaxis and its types?
Chemotaxis Definition If the movement of the organism occurs in the direction of a higher concentration of the chemical (in the direction of an attractant), it is referred to as positive chemotaxis. However, if the movement occurs in the opposite direction, it is called negative chemotaxis.
What causes phototaxis?
Phototaxis is a kind of taxis, or locomotory movement, that occurs when a whole organism moves towards or away from a stimulus of light. This is advantageous for phototrophic organisms as they can orient themselves most efficiently to receive light for photosynthesis.
Is phototaxis positive or negative?
n. movement toward or away from a light source. Positive phototaxis is movement toward light; negative phototaxis is movement away from light. Some insects display a relationship between muscular activity and light orientation.
What is the difference between phototaxis and phototropism?
Answer. is that phototropism is (biology) the movement of a plant towards or away from light while phototaxis is (biology) the movement of an organism either towards or away from a source of light.
What is chemotaxis and why is it important?
Chemotaxis, the directed migration of cells in response to external chemical gradients is crucial for the survival of single-cell organisms, as it enables them to search for nutrients. Cells in multicellular organisms rely on gradient sensing and chemotaxis during development, and as part of the innate immune response.
What are the steps of chemotaxis?
Step 1: Activation of Phagocytic cells and Chemotaxis. ... Step 2: Recognition of invading microbes. ... Step 3: Ingestion and formation of phagosomes. ... Step 4: Formation of phagolysome. ... Step 5: Microbial killing and formation of residual bodies. ... Step 6: Elimination or exocytosis.
What is the main feature of chemotaxis?
Chemotaxis is the movement of organisms in response to a nutrient source or chemical gradient. Cells with chemotatic capabilities can sense xenobiotic chemicals adsorbed to soil particles and swim toward them, thereby overcoming the mass-transfer limitations in the bioremediation process (Fig. 28.6).
What is chemotaxis in WBC?
leukocyte chemotaxis, A CRITICAL feature of the innate immune response is the movement of neutrophils and macrophages from one site in the body to another to provide effector functions.
What is chemotaxis in inflammation?
Chemotaxis (from chemo- + taxis) is the movement of an organism or entity in response to a chemical stimulus. Somatic cells, bacteria, and other single-cell or multicellular organisms direct their movements according to certain chemicals in their environment.
Why do bacteria use chemotaxis?
Chemotaxis is a mechanism by which bacteria efficiently and rapidly respond to changes in the chemical composition of their environment, approaching chemically favorable environments and avoiding unfavorable ones.
What is chemotaxis in phagocytosis?
Chemotaxis is the directional movement of the phagocyte towards a chemical attractant (chemotaxins). Chemotaxins include bacterial products (e.g. endotoxin), injured tissues, complement proteins (C3a, C4a, C5a) and chemical substances produced by leukocytes (leukotrienes).
What is chemotaxis in a cell?
Chemotaxis involves the cellular reactions of motility and directional sensing, which enable cells to sense and move along extracellular chemical gradients. Dictyostelium discoideum cells display robust chemotactic responses to cAMP. Extensive characterization of these responses has provided insights into the mechanisms of chemotaxis. In this system, chemotaxis is composed of multiple signaling pathways including the TORC2–PDK–PKB module where target of rapamycin complex 2 (TORC2) and phosphoinositide-dependent kinase (PDK) function as upstream activators of protein kinase B (PKBs) through hydrophobic motif (HM) and activation loop (AL) phosphorylations, respectively. This module forms a unique signaling pathway where chemoattractant signals are separated and then converge on substrate phosphorylations mediated by two PKB homologues, phosphatidylinositol (3,4,5)-tris phosphate (PtdIns (3,4,5)P3 )-dependent PKBA and -independent PKBR1. PKBA and PKBR1 contribute minor, redundant and major activities, respectively. Consistently, pkbR1− cells are more severely impaired in chemotaxis than cells lacking PKBA or PtdIns (3,4,5)P 3. The TORC2–PDK–PKB module is selectively activated at the front of morphologically polarized cells by an upstream regulator, RasC, during chemotaxis. Spatial dysregulation of this pathway, exemplified by pten− cells or cells expressing an active form of RasC where PtdIns (3,4,5)P 3 -PKBA or TORC2-dependent PKBR1 is overactivated, respectively, leads to extension of pseudopods all around cells and to severe chemotaxis defects. These results strongly suggest that this pathway has critical roles in linking chemotactic stimuli to cytoskeletal rearrangements. These studies shed light on the function and regulation of the TORC2–PDK–PKB pathway from a new perspective.
How does chemotaxis work?
Chemotaxis enables microorganisms to locate contaminants and to increase their bioavailability by swimming toward them. Chemotaxis exists for various priority contaminants. Chemotactic behavior may also enable a microbe to escape toxic chemicals (negative chemotaxis) and locate itself in a place where substrate supply is still sufficient while the remaining toxicity is tolerable. Chemotaxis requires at least some solubility of the target chemical, as an aqueous phase concentration gradient needs to be generated. It is nevertheless imaginable that nearly insoluble (extremely hydrophobic) or insoluble (polymeric) chemicals give rise to chemotaxis upon mobilization or processing by solubilizing agents or exoenzymes, respectively. The role of chemotaxis will be treated in more detail in the section about ways to influence bioavailability.
What is the role of chemotaxis in the body?
In multicellular organisms, it ensures that the right cells get to the right place at the right time during development, and plays an essential role in processes such as wound healing and inflammation [2, 3]. Chemotaxis is also a contributing factor to many diseases. For example, metastatic cancer cells migrate toward stereotypic regions of the body that promote further growth, and the unregulated chemotaxis of immune cells can lead to inflammatory diseases such as asthma and arthritis.
What is chemotaxis in microbiology?
Defining Statement. Chemotaxis in microbiology refers to the migration of cells toward attractant chemicals or away from repellents. Virtually, every motile organism exhibits some type of chemotaxis. The chemotaxis responses of eukaryotic microorganisms proceed by mechanisms that are shared by all cells in the eukaryotic kingdom ...
What is the chemotransduction that starts from MCPs?
Chemotaxis signaling, which starts from MCPs, is a special kind of two-component signal transduction that involves a specialized histidine kinase CheA, which directly interacts with MCPs, and a specialized response regulator CheY that consists of stand-alone receiver domain without any output domains.
Why is chemotaxis important?
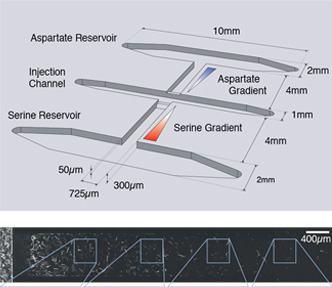
Chemotaxis is an important biological process involved in the development of multicellular organisms, immune response and cancer metastasis. In order to better understand how cells follow chemical cues in their native environments, we recently developed a microfluidics-based chemotaxis device that allows for observation of cells or cell aggregates in 3D networks in response to tunable chemical gradients (Aizel et al., 2017). Here, we describe the methods required for fabrication of this device as well as its use for live imaging experiments and subsequent analysis of imaging data. This device can be adapted to study a number of different cell arrangements and chemical gradients, opening new avenues of research in 3D chemotaxis.
Why is chemo important in multicellular organisms?
In multicellular organisms, it ensures that the right cells get to the right place at the right time during development, and plays an essential role in processes such as wound healing and inflammation [2, 3]. Chemotaxis is also a contributing factor to many diseases.
Which type of pili is used in phototaxis?
We have shown that in the model organism Synechocystis. sp. phototaxis is a surface-dependent phenomenon that requires Type IV pili rather than flagella. Many Gram negative bacteria have Type IV pili, which are long multi-functional, proteinaceous surface appendages.
What is the ability of organisms to move directionally in response to a light source?
Phototaxis is the ability of organisms to move directionally in response to a light source. Many cyanobacteria exhibit phototaxis , both towards and away from a light source. In the environment, the ability to move into optimal light conditions for photosynthesis is likely to be an advantage.
How many tax loci does Synechocystis have?
Synechocystis sp. has three tax loci, two of which are involved in motility responses. Disruption of the tax1 locus (which contains a photoreceptor, TaxD1) produces mutants that are negatively phototactic while tax3 mutants are non-motile and have no pili.
What is Phototaxis?
Phototaxis is derived from the two words ‘Photo’ meaning light and ‘Taxis’ meaning the movement of an organism in response to an external stimulus.
What is Positive Phototaxis?
Positive Phototaxis is defined as the response of an organism in a direction towards the source of light.
What is the innate response of an organism to variation in light intensity and direction?
Phototaxis is the innate response of an organism to variation in light intensity and direction. Meaning that the more the intensity of light in a particular direction the more the phototactic stimulation occurs in the organism. Each and every organism that is phototactic in nature has its own specific biological reason for a phototactic response, ...
Why is phototaxis important?
However, being Phototactic is an advantage to a wide variety of organisms. The advantages of phototaxis include the regulation of light exposure for photosynthesis, ...
What are some examples of phototrophic organisms?
Examples of phototrophic organisms exhibiting phototaxis are the various Phytoflaggellates, Euglena, and photosynthetic bacteria . Positive phototaxis also shows the natural response of chlorophyll-containing green colored plants to move towards the direction of sunlight to prepare their own food by photosynthesis.
Which cells mediate the phototactic response?
There are various light-sensitive cells containing photopigments that mediate the Phototactic response in an organism. These light-sensitive cells are also called photoreceptors and the photopigments they include are retinal (in rhodopsin), flavin (in cryptochrome), bilin (in phytochrome).
What is taxis in biology?
Simply meaning that a taxis is the movement of an organism in response to a stimulus such as light or the presence of food. Here, in the case of Phototaxis, the organism move towards or away from the direction of light, and not food. Phototaxis is the innate response of an organism to variation in light intensity and direction.