Full Answer
What diseases are caused by nondisjunction?
Some of the important examples are:
- Down’s syndrome – Trisomy of autosomes, i.e. chromosome 21. ...
- Edwards syndrome – Trisomy of chromosome 18 th.
- Patau syndrome – Trisomy of chromosome 13 th.
- Klinefelter syndrome – Trisomy of sex chromosomes. Here cells have one extra X chromosome (XXY)
- Turner syndrome – Monosomy. ...
- Nondisjunction is also seen to cause malignancy. ...
Which genetic disorder can only result from nondisjunction?
Turner syndrome (TS) is a genetic disorder caused by the partial or complete absence of one X chromosome. This is called monosomy and is typically caused by chromosomal nondisjunction. It is a very common abnormality among the sex chromosome disorders, with an incidence of 1 in 2000 liveborn females. Is Down syndrome caused by nondisjunction?
What are the consequences of nondisjunction?
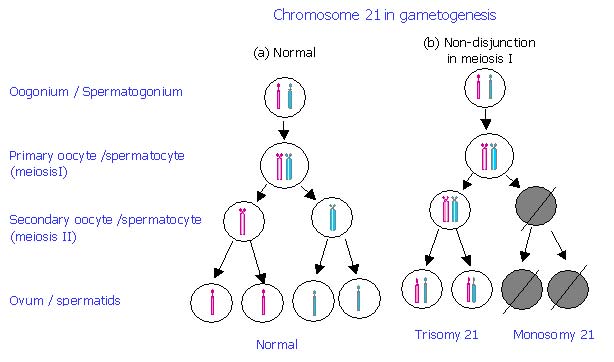
Nondisjunction results in an uneven distribution of chromosomes during cell replication. If nondisjunction occurs during meiosis I, the homologous chromosomes do not separate. If nondisjunction happens in meiosis II, sister chromatids do not separate.
What problem can nondisjunction cause in genetics?
What genetic disorders result from nondisjunction? Nondisjunction causes errors in chromosome number, such as trisomy 21 (Down syndrome) and monosomy X (Turner syndrome). It is also a common cause of early spontaneous abortions.

What is meant by nondisjunction of chromosome?
Nondisjunction is the failure of the chromosomes to separate, which produces daughter cells with abnormal numbers of chromosomes. [ 1][2][3]
What is non-disjunction in simple terms?
Nondisjunction is defined as the failure of chromosomes or chromatids to segregate during cell division. It leads to daughter cells with abnormal numbers of chromosomes, which is known as aneuploidy.
What is non-disjunction vs disjunction?
During anaphase 1 chromosome separate and go to opposite poles while during anaphase 2 sister chromosomes separate. It is called is disjunction. Sometimes the separation is not normal and it is called non-disjunction.
What is nondisjunction of chromosomes during cell division?
Nondisjunction, in which chromosomes fail to separate equally, can occur in meiosis I (first row), meiosis II (second row), and mitosis (third row). These unequal separations can produce daughter cells with unexpected chromosome numbers, called aneuploids.
What is nondisjunction and why does it occur?
Nondisjunction occurs when chromosomes fail to segregate during meiosis; when this happens, gametes with an abnormal number of chromosomes are produced. The clinical significance is high: nondisjunction is the leading cause of pregnancy loss and birth defects.
What are the 3 nondisjunction disorders?
Conditions that arise from non-disjunction events include: Patau's Syndrome (trisomy 13) Edwards Syndrome (trisomy 18) Down Syndrome (trisomy 21)
Why can nondisjunction cause a genetic disorder?
Nondisjunction is the failure of homologous chromosomes to disjoin correctly during meiosis. This results in the production of gametes containing a greater or lesser chromosomal amount than normal ones. Consequently the individual may develop a trisomal or monosomal syndrome.
When can nondisjunction occur?
Non-disjunction of chromosomes during mitosis occurs during anaphase. If a somatic cell undergoes mitosis and experiences non-disjunction, the two daughter cells formed will be aneuploid. In meiosis, nondisjunction can take place either during anaphase I or during anaphase II.
Can nondisjunction occur in males?
Theoretically, non-disjunction may occur in both the male and female germ cells at either the first or second meiotic division and may give rise to a considerable variety of non-disjunctional types in the progeny.
Why is nondisjunction more common in older females?
One explanation for why meiotic segregation errors are more prevalent in older women is that cohesion between sister chromatids deteriorates with age and renders recombinant chromosomes susceptible to missegregation.
What happens during nondisjunction and the effect on the resulting cells?
Nondisjunction Produces Abnormal Gametes If nondisjunction occurs during anaphase I of meiosis I, this means that at least one pair of homologous chromosomes did not separate. The end result is two cells that have an extra copy of one chromosome and two cells that are missing that chromosome.
Is Down syndrome caused by nondisjunction in meiosis 1 or 2?
Trisomy 21 or Down syndrome (DS) is one of the most common chromosomal abnormalities. The majority of full trisomy 21 is caused by chromosomal nondisjunction occurring during maternal meiotic division (∼90%). Errors occur more frequently in the first maternal meiotic division than the second (73% vs.
What is disjunction in meiosis?
In meiosis, disjunction happens when homologous chromosomes move apart toward the opposite poles of the cell in anaphase I. Disjunction again occurs when sister chromatids separate and move away from each other during anaphase II.
What is nondisjunction in biology?
Nondisjunction is when homologous chromosomes or sister chromatids fail to separate properly during cell division. Such inequitable separation of chromosomes can occur during:
What is the net result of nondisjunction?
The net result of nondisjunction is that the daughter cells have an abnormal number of chromosomes ( aneuploidy ), which can be more or less than normal.
What is the most common chromosomal abnormality in humans?
Down syndrome (Trisomy 21) results, as its name implies, from trisomy of chromosome 21, and this is considered the most common chromosomal abnormality in humans. Most cases arise due to nondisjunction of the egg at meiosis I. Advancing maternal age heightens the risk of these genetic disorders, which is one reason why women over 40 who become pregnant are encouraged to undergo amniocentesis (where fluid is removed from the amnion region) to screen for this genetic disorder. Down syndrome is one of the most common causes of mental retardation.
What are the diseases that are caused by non-disjunction?
Key genetic diseases due to nondisjunction to be examined include Klinefelter's Syndrome, Turner's Syndrome, and Triple X Syndrome . Updated: 01/21/2021
What does it mean to enroll in a course?
Enrolling in a course lets you earn progress by passing quizzes and exams.
What is Turner's syndrome?
Turner's Syndrome is where an individual only has a single X chromosome, XO genotype, or X chromosome monosomy. The resulting individual will be female.
Do you have to be a Study.com member to unlock this lesson?
To unlock this lesson you must be a Study.com Member.
What is nondisjunction in biology?
In genetics, nondisjunction is a failed separation of chromosomes during cell division that results in daughter cells containing an abnormal number of chromosomes (aneuploidy). It refers to either sister chromatids or homologous chromosomes improperly separating during mitosis, meiosis I, or meiosis II. The excess or deficit chromosomes alters cell ...
What happens if you have nondisjunction in mitosis?
Nondisjunction in meiosis leads to a loss of a chromosome (monosomy) or extra single chromosome (trisomy).
Why are oocytes arrested during meiosis?
The two main risk factors for nondisjunction are age and chemical exposure. In humans, nondisjunction in meiosis is much more common in egg production than in sperm production. The reason is that human oocytes remain arrested before completing meiosis I from before birth until ovulation. The cohesin complex holding replicated chromosomes together eventually degrades, so the microtubules and kinetochores may not properly attach when the cell finally divides. Sperm are produced continuously, so problems with the cohesin complex are rare.
What is the cause of chromosomes not separating properly?
When Chromosomes Don't Separate Properly in Cell Division. Trisomy 21 or Down syndrome is a condition caused by nondisjunction in meiosis. Dr. Helmenstine holds a Ph.D. in biomedical sciences and is a science writer, educator, and consultant. She has taught science courses at the high school, college, and graduate levels.
How does DNA replicate in a cell?
DNA replicates prior to cell division. The chromosomes line up in the middle plane of the cell during metaphase and the kinetochores of sister chromatids attach to microtubules. At anaphase, the microtubules pull sister chromatids in opposite directions. In nondisjunction, the sister chromatids stick together, so both get pulled to one side. One daughter cell gets both sister chromatids, while the other gets none. Organisms use mitosis to grow and repair themselves, so nondisjunction affects all descendants of the affected parent cell, but not all of the cells in an organism unless it occurs in the first division of a fertilized egg.
What is the difference between euploidy and nondisjunction?
In contrast, euploidy is when a cell contains the normal chromosome complement. Nondisjunction may occur any time a cell divides, ...
Why are sperm and kinetochores not attached?
The cohesin complex holding replicated chromosomes together eventually degrades, so the microtubules and kinetochores may not properly attach when the cell finally divides. Sperm are produced continuously, so problems with the cohesin complex are rare.
What is the failure of chromosomes to go to opposite poles during nuclear division?
the failure of chromosomes (in eukaryotes) to go to opposite poles during nuclear division, leading to unequal numbers of chromosomes in the daughter cells (see ANEUPLOIDY ). See Fig. 230 . Nondisjunction produces abnormal numbers of both AUTOSOMES (e.g. DOWN'S SYNDROME) and SEX CHROMOSOMES (e.g. TURNERS SYNDROME ).
What happens if one daughter cell has two chromosomes?
If this happens during meiosis, an aneuploid individual (for example, a child with Down syndrome) may develop following fertilization.
What is the failure of one or more pairs of chromosomes to separate at the meiotic stage of?
Failure of one or more pairs of chromosomes to separate at the meiotic stage of karyokinesis, with the result that both chromosomes are carried to one daughter cell and none to the other.
How many chromosomes are in an egg?
A genetic term referring to an event which takes place during cell division, in which a genetic accident causes an egg or sperm cell to have 24 chromosomes, rather than the normal 23.
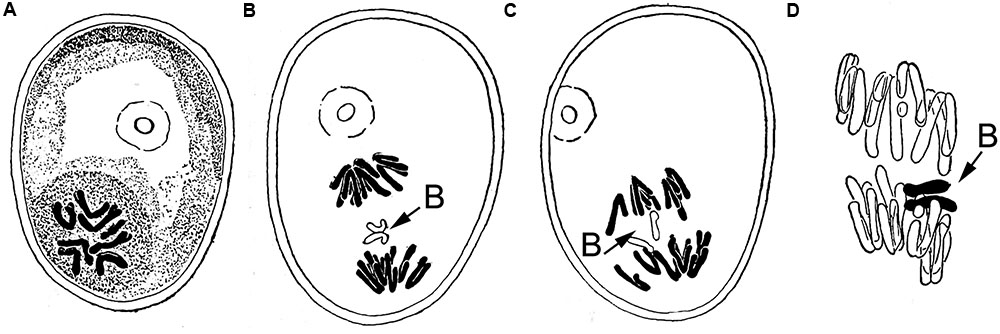
Is normal meiosis nondisjunction?
Nondisjunction. Normal meiosis (A) is contrasted with failure of homologous chromosomes to separate in meiosis I (B) or of sister chromatids to separate in meiosis II (C). From Dorland's, 2000.
Is Gale Encyclopedia of Medicine copyrighted?
Gale Encyclopedia of Medicine. Copyright 2008 The Gale Group, Inc. All rights reserved.
What causes nondisjunction?
Nondisjunction is caused due to inactivation of topoisomerase II, separase or condensin. During anaphase, the cohesin which binds the sister chromatids together is broken by separase. Catenation is removed by condensin and topoisomerase II.
What is the term for loss of one or more chromosomes?
Meiotic nondisjunction leads to chromosomal disorders known as aneuploidy, where there is loss or gain of one or more chromosomes. Meiosis I nondisjunction is a more common cause of aneuploidy than meiosis II nondisjunction. Aneuploidy can be monosomy (2n-1), trisomy (2n+1), nullisomy (2n-2), disomy (n+1).
What happens to homologous chromosomes during meiosis I?
In the first type, due to nondisjunction during meiosis I, homologous chromosomes fail to segregate at anaphase I and lead to all the haploid cells with an abnormal number of chromosomes. The second type of nondisjunction occurs during meiosis II when sister chromatids fail to segregate. It leads to half of the haploid cells with abnormal ...
What is nondisjunction in biology?
Nondisjunction is defined as the failure of chromosomes or chromatids to segregate during cell division. It leads to daughter cells with abnormal numbers of chromosomes, which is known as aneuploidy. The irregular distribution of chromosomes during cell division leads to one cell with an extra chromosome and the other with a less chromosome.
What is the result of Mitotic Nondisjunction?
It leads to half of the haploid cells with abnormal chromosomes. Mitotic nondisjunction leads to somatic mosaicism as only the daughter cells lineage originating from the defective cell contains an abnormal set of chromosomes. It can lead to various forms of cancer such as retinoblastoma.
How to diagnose nondisjunction?
Nondisjunction can be diagnosed by karyotyping. Amniocentesis is carried out to take out amniotic fluid, which is analysed and any chromosomal abnormalities in the foetus can be diagnosed.
When does nondisjunction occur in oocytes?
Nondisjunction is more common in oocytes as the oocyte meiotic division gets arrested first at diplotene of prophase I and then later at metaphase II, which resumes only after fertilization. Most of the aneuploidy in children is derived from the mother.
How many chromosomes are in a Down syndrome egg?
The people infected with Down syndrome, have three copie s of chromosomes 21 in all their somatic cells, two copies from mother and one copy from father.
How many daughter cells are formed in meiosis?
During the process of meiosis I, the gametes are created. One cell divided into four daughter cells by the combined process of both meioses I and meiosis II. The nondisjunction occurs in anaphase of meiosis I when pair of homologous chromosomes not separated. In the result of this problem, one cell copies a chromosome, ...
Why does nondisjunction occur?
Nondisjunction occurs When the chromosomes cannot separate properly. The result of this is that the daughter cells have an incorrect number of chromosomes, as one can have too many, and others may have too few. This problem causes cell function due to a cell cannot function properly without the right numbers of chromosomes.
What happens to somatic cells during mitosis?
During Mitosis: During mitosis, the division of somatic cells takes place. Two identical or similar daughter cells produce from each original parent cell. When the nondisjunction occurs, the chromatids do not separate, and the result comes that one cell gains both chromatids, and gain no one.
What is sex chromosome aneuploidy?
Sex chromosome aneuploidy is the form of abnormal numbers in sex chromosomes. Typically, females consist of two X chromosomes and males consist of one X and one Y chromosome. Nondisjunction is the cause of the individuals to be born female with one X, female with three X chromosomes, males with XXY, or male with XYY.
What happens if the sister chromatids cannot separate?
If the pair of sister chromatids cannot separate accurately during the anaphase of meiosis II, the result will be that one daughter cell has an extra chromosome, and one daughter cel l missed the chromosome.
Why does trisomy 16 occur in the first trimester?
Many other forms of trisomy occur in the result of miscarriage during the first trimester of pregnancy because the fetus cannot survive chromosomal abnormality . The trisomy 16 happens in over 1% of pregnancies and it is the most common trisomy, but many individuals having this trisomy do not survive.
Types of Nondisjunction
Nondisjunction Causes
- Nondisjunction occurs when some aspect of the spindle assembly checkpoint (SAC) fails. The SAC is a molecular complex that holds a cell in anaphase until all of the chromosomes are aligned on the spindle apparatus. Once alignment is confirmed, SAC stops inhibiting anaphasepromoting complex (APC), so the homologous chromosomes separate. Sometimes th...
Risk Factors
- The two main risk factors for nondisjunction are age and chemical exposure. In humans, nondisjunction in meiosis is much more common in egg production than in sperm production. The reason is that human oocytes remain arrested before completing meiosis I from before birth until ovulation. The cohesin complex holding replicated chromosomes together eventually degrades, …
Conditions in Humans
- Nondisjunction in mitosis can result in somatic mosaicism and some types of cancer, such as retinoblastoma. Nondisjunction in meiosis leads to a loss of a chromosome (monosomy) or extra single chromosome (trisomy). In humans, the only survivable monosomy is Turner syndrome, which results in an individual who is monosomic for the X chromosome. All monosomies of aut…
Sources
- Bacino, C.A.; Lee, B. (2011). "Chapter 76: Cytogenetics". In Kliegman, R.M.; Stanton, B.F.; St. Geme, J.W.; Schor, N.F.; Behrman, R.E. (eds.). Nelson Textbook of Pediatrics(19th ed.). Saunders: Phi...
- Jones, K. T.; Lane, S. I. R. (August 27, 2013). "Molecular causes of aneuploidy in mammalian eggs". Development. 140 (18): 3719–3730. doi:10.1242/dev.090589
- Bacino, C.A.; Lee, B. (2011). "Chapter 76: Cytogenetics". In Kliegman, R.M.; Stanton, B.F.; St. Geme, J.W.; Schor, N.F.; Behrman, R.E. (eds.). Nelson Textbook of Pediatrics(19th ed.). Saunders: Phi...
- Jones, K. T.; Lane, S. I. R. (August 27, 2013). "Molecular causes of aneuploidy in mammalian eggs". Development. 140 (18): 3719–3730. doi:10.1242/dev.090589
- Koehler, K.E.; Hawley, R.S.; Sherman, S.; Hassold, T. (1996). "Recombination and nondisjunction in humans and flies". Human Molecular Genetics. 5 Spec No: 1495–504. doi:10.1093/hmg/5.Supplement_1.1495
- Simmons, D. Peter; Snustad, Michael J. (2006).Principles of Genetics(4. ed.). Wiley: New York. ISBN 9780471699392.