
Explore
The body can rid itself of acute bronchitis in around 3 weeks for as long as exposure to irritants is kept to a minimum. Although bronchitis can definitely go away by itself, it is generally much better to be on the side of caution and to have yourself undergone treatment for better results.
Will bronchitis go away on its own?
In acute bronchitis, symptoms occur more than five days, and can last up to three weeks. In chronic bronchitis, symptoms last for at least three months of the year during two consecutive years. If your cold symptoms and cough last more than three weeks, cause chest pain, shortness of breath, or fever, see your doctor immediately.
How long does bronchitis last and when should you see a doctor?
Recovery from acute bronchitis may take up to two weeks. One of the most common types of bronchitis—acute bronchitis—is caused by a viral infection. In many cases, the virus is the same or similar to the cold or flu viruses. In some instances, breathing chemicals, dust, and other allergens can cause acute bronchitis.
How long does it take to recover from bronchitis?
Lifestyle Risk Factors
- Smoking: Smoking is the leading cause of chronic bronchitis. ...
- Chemical inhalants: Close and frequent exposure to concentrated inhaled chemicals in the air can cause bronchitis. ...
- Pollution: Exposure to pollution, unlike exposure to inhalants in close proximity, affects people who dwell in the vicinity of high levels of pollution. ...
What are dangers of bronchitis?
What is chronic bronchitis?
How to treat bronchitis?
How is chronic bronchitis diagnosed?
How long do you have to cough for bronchitis?
What are the two most common conditions of COPD?
What is the difference between restrictive and obstructive airways?
What is it called when you cough up mucus?
See 4 more
About this website

What are the signs of chronic bronchitis?
Symptoms may include: Cough, often called smoker's cough. Coughing up mucus (expectoration) Wheezing....Other symptoms may include:Bluish fingernails, lips, and skin because of lower oxygen levels.Wheezing and crackling sounds with breathing.Swollen feet.Heart failure.
Can chronic bronchitis be cured?
Chronic bronchitis is not curable but there are a number of treatments that can help you manage your symptoms. These include bronchodilators that open your airways, steroids to reduce inflammation, oxygen therapy and pulmonary rehabilitation.
What happens when you have chronic bronchitis?
Chronic bronchitis fills your airways with thick mucus. The small hairs that normally move phlegm out of your lungs are damaged. That makes you cough. As the disease goes on, it's harder for you to breathe.
Is chronic bronchitis life threatening?
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is a category of conditions that includes emphysema and chronic bronchitis. It is a progressive condition that gets steadily worse. Over time, the body becomes less able to take in enough oxygen. This can ultimately result in death.
Can you live a long life with chronic bronchitis?
Many people will live into their 70s, 80s, or 90s with COPD.” But that's more likely, he says, if your case is mild and you don't have other health problems like heart disease or diabetes. Some people die earlier as a result of complications like pneumonia or respiratory failure.
How do you get chronic bronchitis?
What causes chronic bronchitis? The cause of chronic bronchitis is usually long-term exposure to irritants that damage your lungs and airways. In the United States, cigarette smoke is the main cause. Pipe, cigar, and other types of tobacco smoke can also cause chronic bronchitis, especially if you inhale them.
What is the best medicine for chronic bronchitis?
What is the best medication for bronchitis?Best medications for bronchitisAdvil (ibuprofen)NSAIDOralXopenex (levalbuterol hydrochloride solution)BronchodilatorInhalationDeltasone (prednisone)CorticosteroidOralMucinex (guaifenesin ER)Mucoactive agentOral4 more rows•Oct 5, 2020
How do you test for chronic bronchitis?
Chest X-Ray Chest X-rays can help confirm a diagnosis of chronic bronchitis and rule out other lung conditions. Sputum Examination Analysis of cells in your sputum can help determine the cause of some lung problems.
What is the first line treatment for chronic bronchitis?
Fluoroquinolones are recommended as first-line therapy for patients with chronic bronchitis who have risk factors; gatifloxacin, gemifloxacin, and levofloxacin are highly active against commonly encountered pathogens.
How long does it take for chronic bronchitis to go away?
According to the American Lung Association, acute bronchitis usually lasts for between 3–10 days, although some symptoms, such as coughing, can last longer. Chronic bronchitis lasts longer than acute bronchitis. Symptoms of chronic bronchitis last for at least 3 months out of the year.
Can bronchitis damage your lungs?
Complications. Pneumonia is the most common complication of bronchitis. It happens when the infection spreads further into the lungs, causing air sacs inside the lungs to fill up with fluid. 1 in 20 cases of bronchitis leads to pneumonia.
How did I get bronchitis?
Bronchitis (Acute) Bronchitis is the sudden development of inflammation in bronchial tubes—the major airways into your lungs. It usually happens because of a virus or breathing in something that irritates the lungs such as tobacco smoke, fumes, dust and air pollution.
How is chronic bronchitis treated?
Bronchodilator Medications Inhaled as aerosol sprays or taken orally, bronchodilator medications may help to relieve symptoms of chronic bronchitis by relaxing and opening the air passages in the lungs. Steroids Inhaled as an aerosol spray, steroids can help relieve symptoms of chronic bronchitis.
How do you get rid of chronic bronchitis naturally?
Luckily, there are home remedies that can help ease acute and chronic bronchitis.Using a humidifier. ... Drinking warm liquids. ... Wearing a face mask in cold weather. ... Honey. ... Pursed-lip breathing techniques. ... Essential oils. ... Ginseng extract. ... N-acetylcysteine (NAC)More items...
What is the most common complication of chronic bronchitis?
Pneumonia. Pneumonia is the most common complication of viral acute bronchitis, occurring in roughly 5% of people. Among children aged 5 and over, as well as adults, the most common cause is Streptococcus pneumonia.
Does chronic bronchitis go away after quitting smoking?
Endobronchial findings showed that macroscopic signs of chronic bronchitis (oedema, erythema and mucus) decreased within 3 months after smoking cessation, and totally disappeared after 6 months 115.
Chronic Bronchitis: Symptoms, Causes, Diagnosis, Treatment - WebMD
Your constant coughing, wheezing, and shortness of breath could be a sign of a serious illness called chronic bronchitis. Learn more about the symptoms, causes, diagnosis, and treatment of chronic ...
Chronic Bronchitis: Signs, Symptoms, and Complications - Verywell Health
A Word From Verywell . Chronic bronchitis is a lifelong condition that can affect not just your airways, but other parts of your body too. If you have a chronic cough, be sure to tell your doctor about any other symptoms you have—especially if you are coughing up blood, becoming confused, passing out, or having chest pain.
Chronic Bronchitis Pathophysiology - Verywell Health
Charday Penn / Getty Images. How the Lungs Work . To understand chronic bronchitis, it is helpful to understand how the lungs work. The primary function of the lungs is to bring oxygen into the body and get rid of waste gases.
Bronchitis - Symptoms and causes - Mayo Clinic
Symptoms. For either acute bronchitis or chronic bronchitis, signs and symptoms may include: Cough; Production of mucus (sputum), which can be clear, white, yellowish-gray or green in color — rarely, it may be streaked with blood
Chronic Bronchitis Treatment | UCSF Health
The goal of therapy for chronic bronchitis is to relieve symptoms, prevent complications and slow the progression of the disease. Quitting smoking is also essential for patients with chronic bronchitis, since continuing to use tobacco will only further damage the lungs.
What are the symptoms of chronic bronchitis?
Other symptoms of chronic bronchitis may include: fatigue. a fever.
How long does bronchitis last?
It’s characterized by recurrent episodes of bronchitis that last for several months or years.
How to get rid of bronchitis?
You may want to consider the following: Breathing in warm, moist air from a humidifier can ease coughs and loosen the mucus in your airways.
What is the inflammation of the lining of the bronchial tubes?
Bronchitis is an inflammation of the lining of the bronchial tubes. These are the tubes that carry air to and from your lungs. People who have bronchitis often have a persistent cough that brings up thickened, discolored mucus. They may also experience wheezing, chest pain, and shortness of breath. Bronchitis may be either acute or chronic.
Why does bronchitis make my lungs swell?
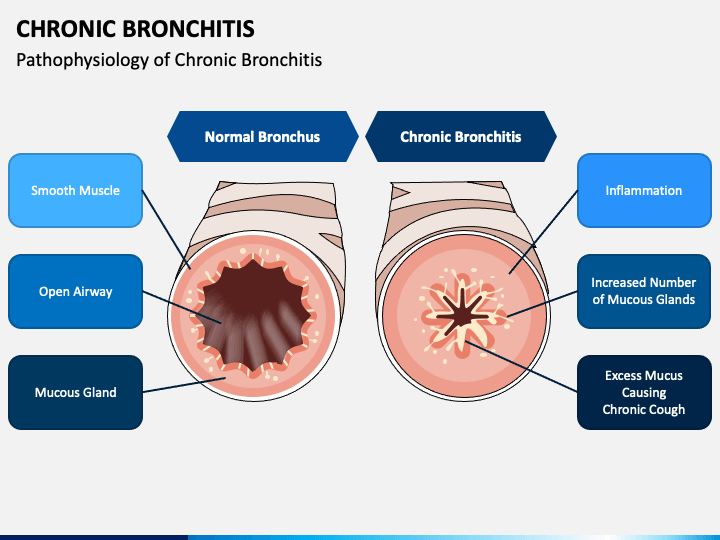
Chronic bronchitis occurs when the lining of the bronchial tubes repeatedly becomes irritated and inflamed. The continuous irritation and swelling can damage the airways and cause a buildup of sticky mucus, making it difficult for air to move through the lungs. This leads to breathing difficulties that gradually get worse.
What does it mean when you cough up mucus?
After a long period of inflammation and irritation in the bronchial tubes, chronic bronchitis can result in several hallmark symptoms, including a persistent, heavy cough that brings up mucus from the lungs. The mucus may be yellow, green, or white. As time passes, the amount of mucus gradually increases due to the increased production ...
What is the name of the condition where the lungs are blocked?
Together, the two conditions are referred to as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, or COPD.
What is chronic bronchitis?
Chronic bronchitis is a type of COPD (chronic obstructive pulmonary disease). COPD is a group of lung diseases that make it hard to breathe and get worse over time. The other main type of COPD is emphysema. Most people with COPD have both emphysema and chronic bronchitis, but how severe each type is can be different from person to person.
What are the treatments for chronic bronchitis?
There is no cure for chronic bronchitis. However, treatments can help with symptoms, slow the progress of the disease, and improve your ability to stay active. There are also treatments to prevent or treat complications of the disease. Treatments include:
What causes mucus to build up in the lungs?
These tubes are the airways that carry air to and from the air sacs in your lungs. The irritation of the tubes causes mucus to build up. This mucus and the swelling of the tubes make it harder for your lungs to move oxygen in and carbon dioxide out of your body.
How old do you have to be to get bronchitis?
Age. Most people who have chronic bronchitis are at least 40 years old when their symptoms begin. Genetics. This includes alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency, which is a genetic condition. Also, smokers who get chronic bronchitis are more likely to get it if they have a family history of COPD.
What is the genetic condition that causes chronic bronchitis?
Rarely, a genetic condition called alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency can play a role in causing chronic bronchitis.
What is the best treatment for bronchitis?
Oxygen therapy, if you have severe chronic bronchitis and low levels of oxygen in your blood. Oxygen therapy can help you breathe better. You may need extra oxygen all the time or only at certain times.
What is pulmonary rehabilitation?
Pulmonary rehabilitation, which is a program that helps improve the well-being of people who have chronic breathing problems. It may include. If you have chronic bronchitis, it's important to know when and where to get help for your symptoms.
What is the cause of chronic bronchitis?
The cause of chronic bronchitis is usually long-term exposure to irritants that damage your lungs and airways. 1 Cigarette smoke is the main cause of this disease in the United States. Pipe, cigar, and other types of tobacco smoke can also cause chronic bronchitis.
How to help bronchitis?
You can support your health and keep your chronic bronchitis from becoming worse if you: 1. Exercise . Eat a healthy diet.
What is the term for inflammation of the bronchial tubes?
Chronic bronchitis refers to inflammation and irritation of the bronchial tubes. It is a type of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), which is an umbrella term for lung diseases that make it hard to breathe and get worse over time.
How many people have COPD?
About 10 million people—mostly aged 44 to 65—are affected by chronic bronchitis. 2 Roughly three-quarters of the people around the world diagnosed with COPD struggle with chronic bronchitis. This condition is usually caused by prolonged exposure to irritants that damage your lungs and airways, such as cigarette smoke.
What are the best ways to treat bronchitis?
Medications that may be used to treat or control chronic bronchitis include: 1. Antibiotics for bacterial and viral lung infections. Bronchodilators, which relax the muscles around your airways and help make breathing easier.
What is the best treatment for breathing problems?
Oxygen therapy, which also helps make breathing easier. Pulmonary rehabilitation therapy, a program that helps improve the well-being of people who have chronic breathing problems and may include an exercise program, disease management training, nutritional counseling, and psychological counseling.
What to do if you have a cough that produces mucus?
If you have a frequent or lasting cough, especially one that produces mucus, you should see your doctor.
What is the number one cause of bronchitis?
Cigarette smoking is by far the No. 1 cause of chronic bronchitis. More than 90% of people with the disease smoke or used to smoke. Other things that raise your chances for it include:
How to stop bronchitis from getting worse?
Many people live with moderate symptoms for a long time, and breathe on their own without supplemental oxygen.
How long does coughing last?
That’s when the air tubes in your lungs called bronchi get irritated and inflamed, and you have coughs for at least 3 months a year for 2 years in a row. It’s a long-term illness that keeps coming back or never fully goes away. It’s a type of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). The other type is emphysema.
What to do if you smoke and have bronchitis?
Your first step, if you smoke, is to quit. Your lungs will not fully recover, but the rate of decline will be much slower. Airway openers ( bronchodilators ): These drugs relax your air passages to make it easier to breathe and relieve your bronchitis symptoms.
How do you know if you have bronchitis?
Other signs of chronic bronchitis may include: Cough, often with mucus. Wheezing. Tight chest. Shortness of breath. Feeling tired. Your symptoms may be worst in the winter, when humidity and temperatures drop.
What is the best treatment for a swollen lungs?
Anti-inflammatory drugs: Steroids lessen the swelling that narrows your air passages. Oxygen therapy: This is for serious cases, where your lungs are so damaged that blood oxygen levels are extremely low. You can inhale oxygen from a portable machine at home as needed.
Does bronchitis make it easier to catch colds?
Chronic bronchitis may make it easier for you to catch respiratory infections like colds, the flu, and pneumonia.
How long does it take for bronchitis to go away?
Unlike acute bronchitis, which usually develops from a respiratory infection such as a cold and goes away in a week or two, chronic bronchitis is a more serious condition that develops over time. Symptoms may get better or worse, but they will never completely go away.
What tests are used to diagnose bronchitis?
Tests used to diagnose chronic bronchitis include pulmonary function tests, chest X-rays or CT scans. Chronic bronchitis is not curable but there are a number of treatments that can help you manage your symptoms.
What causes mucus to build up in the airways?
These extended periods of inflammation cause sticky mucus to build up in the airways, leading to long-term breathing difficulties. Along with emphysema, chronic bronchitis is one of the lung diseases that comprise COPD (chronic obstructive pulmonary disease).
Why do I cough so much?
This irritation can cause severe coughing spells that bring up mucus, wheezing, chest pain and shortness of breath. There are two main types, acute and chronic.
What are the factors that increase the risk of developing bronchitis?
Other factors that increase your risk of developing this disease include exposure to air pollution as well as dust or toxic gases in the workplace or environment. It may also occur more frequently in individuals who have a family history of bronchitis.
Is chronic bronchitis a COPD?
Key Facts about Chronic Bronchitis. Chronic bronchitis is included in the umbrella term COPD (chronic obstructive pulmonary disease). Your doctor may refer to your disease as either chronic bronchitis or COPD. Cigarette smoking is a major cause of chronic bronchitis. Other factors that increase your risk of developing this disease include exposure ...
What is the inflammation of the lining of the bronchial tubes?
Bronchitis is an inflammation of the lining of your bronchial tubes, which carry air to and from your lungs. People who have bronchitis often cough up thickened mucus, which can be discolored. Bronchitis may be either acute or chronic.
Can you get bronchitis from a heartburn?
Your risk of developing bronchitis is greater if you work around certain lung irritants, such as grains or textiles, or are exposed to chemical fumes. Gastric reflux. Repeated bouts of severe heartburn can irritate your throat and make you more prone to developing bronchitis.
Can bronchitis cause pneumonia?
Although a single episode of bronchitis usually isn't cause for concern, it can lead to pneumonia in some people. Repeated bouts of bronchitis, however, may mean that you have chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD).
Can chronic bronchitis cause periods?
If you have chronic bronchitis, you're likely to have periods when your cough or other symptoms worsen. At those times, you may have an acute infection on top of chronic bronchitis.
Can antibiotics kill bronchitis?
Antibiotics don't kill viruses, so this type of medication isn't useful in most cases of bronchitis. The most common cause of chronic bronchitis is cigarette smoking. Air pollution and dust or toxic gases in the environment or workplace also can contribute to the condition.
Can smoking cause bronchitis?
Cigarette smoke. People who smoke or who live with a smoker are at higher risk of both acute bronchitis and chronic bronchitis. Low resistance. This may result from another acute illness, such as a cold, or from a chronic condition that compromises your immune system.
What are the causes of chronic bronchitis?
There are many known causes of chronic bronchitis, but the most important causative factor is exposure to cigarette smoke either due to active smoking or passive inhalation. Many inhaled irritants to the respiratory tract such as smog, industrial pollutants, and toxic chemicals can cause chronic bronchitis. Although bacterial and viral infections usually cause acute bronchitis repeated exposure to infections can cause chronic bronchitis. The predominant viruses that are causative are Influenza type A and B, and the dominant bacterial agents are Staphylococcus, Streptococcus, and Mycoplasma pneumonia. People who have an associated background in respiratory diseases such as asthma, cystic fibrosis, or bronchiectasis have a higher predisposition to develop chronic bronchitis. People who have repeated exposure to environmental pollutants such as dust or airborne chemicals such as ammonia and sulfur dioxide have a higher risk of developing chronic bronchitis. Chronic gastroesophageal reflux is a well documented but less frequent cause of chronic bronchitis. [1]
What is the most common symptom of chronic bronchitis?
The most common symptom of patients with chronic bronchitis is a cough. The history of a cough typical of chronic bronchitis is characterized to be present for most days in a month lasting for 3 months with at least 2 such episodes occurring for 2 years in a row. A productive cough with sputum is present in about 50% of patients. The sputum color may vary from clear, yellow, green or at times blood tinged. The color of sputum may be dependent on the presence of secondary bacterial infection. Very often changes in sputum color can be due to peroxidase released by leucocytes in the sputum. Therefore, color alone is not a definite indication of bacterial infection.
What is COPD in pulmonary disease?
Chronic bronchitis is a type of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) that is defined as a productive cough of more than 3 months occurring within a span of 2 years. Patients typically present with chronic productive cough, malaise, and symptoms of excessive coughing such as chest or abdominal pain. This activity reviews the evaluation and management of chronic bronchitis and explains the role of the interprofessional team in improving care for patients with this condition.
How long does bronchitis last?
Chronic bronchitis can be defined as a chronic productive cough lasting more than 3 months occurring within a span of 2 years. There is a strong causal association with smoking and is very often secondary to chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). [1]
What is the primary goal of bronchitis treatment?
The primary aim of treatment for chronic bronchitis is to relieve symptoms, prevent complication and slow the progression of the disease. The primary goals of therapy are aimed at reducing the overproduction of mucus, controlling inflammation and lowering cough. These are achieved by pharmacological as well as nonpharmacological interventions. [5][6][7]
What is the best treatment for chronic bronchitis?
Pulmonary rehabilitation is an important part of treatment for chronic bronchitis is pulmonary rehabilitation which consists of education, lifestyle modification, regular physical activity and avoidance of exposure to known pollutants either at work or living environment. [8]
What is the most critical factor in the diagnosis of chronic bronchitis?
The most critical factor in the diagnosis of chronic bronchitis is a typical history to exclude other possible diseases of the lower respiratory tract.
What are the risks of bronchitis?
The risk for developing chronic bronchitis is linked to lifestyle choices, including: 1 Smoking: Up to 75% of people who have chronic bronchitis smoke or used to smoke. 1 2 Long-term exposure to other lung irritants: These include secondhand smoke, air pollution, and chemical fumes and dusts from the environment or workplace. 3 A history of childhood respiratory infection 3
What is the genetic condition that causes chronic bronchitis?
Rarely, a genetic condition called alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency can play a role in causing chronic bronchitis. 1
Why does bronchitis cause breathing problems?
Chronic bronchitis causes excess mucus production which can cause breathing problems when it builds up. It is usually the result of prolonged exposure to irritants that can damage your lungs. Smoking is the leading cause of chronic bronchitis, but other factors may increase a person's risk of developing this condition, ...
What are the chemicals that can cause chronic bronchitis?
Aerosolized paints, pesticides, fuels, and fertilizers are some of the chemicals that can increase your risk of chronic bronchitis. 2 Some jobs that have been linked to a higher risk of chronic bronchitis and COPD include: 2. Coal miners. Hard rock miners. Tunnel workers. Concrete manufacturers and laborers.
How many COPD cases are linked to smoking?
An estimated 85% to 90% of all COPD cases are linked to cigarette smoking. 3. Outside of smoking, there are other ways that toxins can reach your lungs and lead to chronic bronchitis. These include air pollution and chemicals used in the workplace.
What is the role of Alpha-1 in bronchitis?
Alpha-1 is a protein that helps protect the lungs, and people who are deficient in this gene have been found to be at a higher risk of developing chronic bronchitis. 3. Your gender and ethnic background may also play a role. Hereditary cases of chronic bronchitis were found to be more common in women, and women overall have a higher chance ...
How to prevent bronchitis?
You can therefore take steps to reduce your risk of developing chronic bronchitis by choosing not to smoke, quitting smoking, and protecting yourself from harmful dust and chemicals. If you work in an environment that's prone to exposure, wear protective equipment to keep yourself safe on the job.
What is bronchitis in the lungs?
What is bronchitis? Bronchitis occurs when the bronchioles (air-carrying tubes in the lungs) are inflamed and make too much mucus. There are two basic types of bronchitis: Chronic bronchitis is defined as cough productive of sputum that persists for three months out of the year for at least two consecutive years.
How long does bronchitis last?
Episodes of acute bronchitis can be related to and made worse by smoking. Acute bronchitis could last for 10 to 14 days, possibly causing symptoms for three weeks. Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center.
How does bronchitis spread?
If bronchitis is caused by a viral or bacterial infection, it is spread the same ways that colds are spread—by germs traveling through the air when someone coughs or sneezes. You can breathe the germs in if you are close enough. You could also touch something that has germs on it, like a door, and then transfer the germs by touching your nose, mouth or eyes. That is why good hand washing practices are important for adults and children.
What is the name of the condition that falls in between the common cold and pneumonia in severity?
Bronchitis . The condition that falls in between the common cold and pneumonia in severity is called bronchitis. Symptoms include a frequent cough that produces mucus, fatigue, fever, and a wheezing sound when breathing. Find out how to treat, or better yet, prevent bronchitis. Appointments 216.444.6503.
How long do you stay contagious after taking antibiotics for bronchitis?
If you have begun taking antibiotics for bronchitis, you usually stop being contagious 24 hours after starting the medication. If you have a viral form of bronchitis, antibiotics will not work. You will be contagious for at least a few days and possibly for as long as a week.
What are the similarities between pneumonia and bronchitis?
Bronchitis can sometimes progress to pneumonia. Despite similarities, the conditions are different. First, bronchitis involves the bronchial tubes, while pneumonia affects the alveoli, or the air sacs in the lungs.
What are the drugs used for COPD?
Anti-inflammatory drugs, such as corticosteroids (also called steroids), to reduce swelling and mucus output.
What is chronic bronchitis?
Bronchitis is inflammation of the breathing tubes. These are the airways called bronchi. This inflammation causes too much mucus production and other changes. There are different types of bronchitis. But the most common are acute and chronic.
How to treat bronchitis?
It may include: Quitting smoking. Staying away from secondhand smoke and other lung irritants. Taking medicines by mouth (oral) to open airways and help clear away mucus. Taking inhaled medicines, such as bronchodilators and steroids.
How is chronic bronchitis diagnosed?
Your healthcare provider will take a complete health history and do a physical exam. He or she may order the following tests:
How long do you have to cough for bronchitis?
People with chronic bronchitis tend to get lung infections more easily. They also have episodes of acute bronchitis, when symptoms are worse. To be classified as chronic bronchitis: You must have a cough and mucus most days for at least 3 months a year, for 2 years in a row.
What are the two most common conditions of COPD?
These diseases can block air flow in the lungs and cause breathing problems. The 2 most common conditions of COPD are chronic bronchitis and emphysema.
What is the difference between restrictive and obstructive airways?
Restrictive means less air will get into your lungs. Obstructive means less air will get out of your lungs. Peak flow monitor. This test measures the fastest speed you can blow air out of your lungs. Inflammation and mucus in the large airways in the lungs narrow the airways.
What is it called when you cough up mucus?
Cough, often called smoker’s cough. Coughing up mucus (expectoration) Wheezing. Chest discomfort. People with chronic bronchitis often have a cough and make mucus for many years before they have shortness of breath. Chronic bronchitis may cause: Disability. Frequent and severe infections that affect your airways.
Overview
Epidemiology
Prognosis
Symptoms
Effects
Signs and symptoms
Causes
- Chronic bronchitis occurs when the lining of the bronchial tubes repeatedly becomes irritated and inflamed. The continuous irritation and swelling can damage the airways and cause a buildup of sticky mucus, making it difficult for air to move through the lungs. This leads to breathing difficulties that gradually get worse. The inflammation can also...
Diagnosis
Treatment
Prevention
Chronic Bronchitis Symptoms
Causes
Diagnosis
Treatment
Prognosis
Coping
Summary
- Chronic bronchitis is a type of COPD that causes inflammation and irritation of the bronchial tubes. It’s usually caused by exposure to irritants that damage your lungs over a long period of time. This condition can be managed with lifestyle changes, medications, and specialized forms of therapy.
A Word from Verywell