What are the early signs of respiratory failure?
- labored and rapid breathing.
- muscle fatigue and general weakness.
- low blood pressure.
- discolored skin or nails.
- a dry, hacking cough.
- a fever.
- headaches.
- a fast pulse rate.
What are the 4 types of respiratory failure?
What are the 4 types of respiratory failure? Acute Respiratory Failure: Type 1 (Hypoxemic ) - PO 2 < 50 mmHg on room air. Usually seen in patients with acute pulmonary edema or acute lung injury. Type 2 (Hypercapnic/ Ventilatory ) - PCO 2 > 50 mmHg (if not a chronic CO 2 retainer). Type 3 (Peri-operative).
What are the risk factors for respiratory failure?
Risk factors for respiratory failure. – Alterations in the mechanics of the chest wall: severe kyphoscoliosis, obesity, flail injury with multiple rib fractures, paralysis of the thoracic muscle and diaphragm, immobility of the chest wall, as in progressive systemic sclerosis. – Pleural disorders: large pleural fluid, pneumothorax and ...
Can You recover from respiratory failure?
Treatments for respiratory failure may include oxygen therapy, medicines, and procedures to help your lungs rest and heal. Chronic respiratory failure can often be treated at home. If you have serious chronic respiratory failure, you may need treatment in a long-term care center. If you have respiratory failure, you may receive oxygen therapy.
See 7 key topics from this page & related content

What happens when you have chronic respiratory failure?
Chronic respiratory failure usually happens when the airways that carry air to your lungs become narrow and damaged. This limits air movement through the body, which means that less oxygen gets in and less carbon dioxide gets out.
Can you survive respiratory failure?
Though there is no cure for ARDS, it's not uniformly fatal. With treatment, an estimated 60% to 75% of those who have ARDS will survive the disease. “We know how to support people through ARDS very well,” says Lauren Ferrante, MD, MHS, a Yale Medicine pulmonary and critical care specialist.
How do you get chronic respiratory failure?
An injury to your chest or ribs. A drug or alcohol overdose, which can harm your brain and breathing. Lung damage from breathing in fumes or smoke. Lung disease or infection, like chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), cystic fibrosis, or pneumonia.
What are the 4 types of respiratory failure?
Acute Respiratory Failure:Type 1 (Hypoxemic ) - PO2 < 50 mmHg on room air. Usually seen in patients with acute pulmonary edema or acute lung injury. ... Type 2 (Hypercapnic/ Ventilatory ) - PCO2 > 50 mmHg (if not a chronic CO2 retainer). ... Type 3 (Peri-operative). ... Type 4 (Shock) - secondary to cardiovascular instability.
What is the treatment for chronic respiratory failure?
Treatments for respiratory failure may include oxygen therapy, medicines, and procedures to help your lungs rest and heal. Chronic respiratory failure can often be treated at home. If you have serious chronic respiratory failure, you may need treatment in a long-term care center.
What are the early signs of respiratory failure?
Symptoms include shortness of breath or feeling like you can't get enough air, extreme tiredness, an inability to exercise as you did before, and sleepiness.
How long can I live with chronic respiratory failure?
The time-to-death is around five years in patients with CWD and slowly progressive NMD, around two to three years in those with OHS and Overlap Syndrome, around one to two years in COPD patients and those with other diseases that lead to chronic hypercapnic respiratory failure.
What are three signs of respiratory failure?
This grunting is the body's way of trying to keep air in the lungs so they will stay open. Nose flaring. The openings of the nose spreading open while breathing may mean that a person is having to work harder to breathe. Retractions.
What are the two main causes of respiratory failure?
Damage to the tissues and ribs around the lungs. An injury to the chest can cause this damage. Drug or alcohol overdose. Inhalation injuries, such as from inhaling smoke (from fires) or harmful fumes.
What is the most common type of respiratory failure?
The most common cause is chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD).
How is respiratory failure diagnosed?
A test done on a sample of blood taken from an artery confirms the diagnosis of respiratory failure when it shows a dangerously low level of oxygen and/or a dangerously high level of carbon dioxide. Chest x-rays and usually other tests are done to determine the cause of respiratory failure.
Is respiratory failure death painful?
Dying patients spent an average of 9 days on a ventilator. Surrogates indicated that one out of four patients died with severe pain and one out of three with severe confusion. Families of 42% of the patients who died reported one or more substantial burden.
Is respiratory failure always fatal?
The condition can be acute or chronic. With acute respiratory failure, you experience immediate symptoms from not having enough oxygen in your body. In most cases, this failure may lead to death if it's not treated quickly.
Is respiratory failure a cause of death?
Acute hypoxemic respiratory failure (AHRF) is among the most common causes of critical illness, with a hospital mortality of approximately 30% [1]. In patients meeting the definition of acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS), mortality is approximately 40% [2].
Is death by respiratory failure painful?
Dying patients spent an average of 9 days on a ventilator. Surrogates indicated that one out of four patients died with severe pain and one out of three with severe confusion. Families of 42% of the patients who died reported one or more substantial burden.
What does respiratory failure feel like?
The symptoms of respiratory failure depend on the cause and the levels of oxygen and carbon dioxide in your blood. A low oxygen level in the blood can cause shortness of breath and air hunger (the feeling that you can't breathe in enough air). Your skin, lips, and fingernails may also have a bluish color.
What Is Chronic Respiratory Failure?
Chronic respiratory failure (CRF) is a long-term condition that happens when your lungs cannot get enough oxygen into your blood. Your heart, brain...
What Causes Chronic Respiratory Failure?
1. Heart conditions such as left-sided heart failure or mitral stenosis 2. Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) 3. A problem with the nerve...
What Are The Symptoms of CRF?
1. Rapid breathing 2. Shortness of breath, especially with activity 3. Feeling like you cannot get enough air 4. A bluish color on your skin, finge...
When Should I Contact My Healthcare Provider?
1. Your have new symptoms. 2. Your symptoms get worse. 3. You have questions or concerns about your condition or care.
What is chronic respiratory failure?
Chronic respiratory failure is a condition that results in the inability to effectively exchange carbon dioxide and oxygen, and induces chronically low oxygen levels or chronically high carbon dioxide levels. The condition is usually caused by chronic respiratory diseases, such as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), ...
What is respiratory insufficiency?
Chronic respiratory insufficiency, or the inability to breathe independent ly, has a profound impact on the affected individual, his or her family, and the healthcare community as a whole. The treatment of chronic respiratory insufficiency in spinal cord injury (SCI) has been traditionally performed with mechanical positive pressure ventilation (MPPV) through a ventilator. MPPV, while life preserving, has the psychosocial stigma of the ventilator tubing for patients and also leads to posterior lobe atelectasis, barotrauma, and pneumonia. Respiratory complications are the leading cause of death in spinal cord injured patients on ventilators (Krause et al., 2004; Shavelle et al., 2006 ).
What causes respiratory alkalosis?
In many cases of gas exchange failure, respiratory alkalosis occurs secondary to dyspnea-associated increases in ventilatory drive and minute ventilation. In chronic respiratory failure, hypoxemia can be caused by one or more of the following basic mechanisms: •. Ventilation-perfusion mismatch.
How often should a child be seen for respiratory failure?
For instance, an adolescent with Type 2 spinal muscular atrophy (SMA) might require only semiannual visits once growth has stopped and progression of the underlying disease is slow. An infant with Type 1 SMA is likely to require visits every 2 to 3 months to reassess adequacy of ventilation and airway clearance.
Can a ventilatory support be used for nighttime hypoxemia?
Nocturnal ventilatory support can enhance the quality of life in many patients with nighttime hypoxemia and hypercarbia. Supplemental oxygen by nasal cannula may suffice in patients with hypoxemia caused by chronic lung disease without hypercarbia. The physiology of chronic respiratory muscle fatigue and its treatment with respiratory muscle rest are discussed earlier in this chapter.
Why is chloride supplementation required for respiratory failure?
When the Pco 2 is reduced by mechanical ventilation, chloride supplementation is often required in order to promote excretion of the retained HCO 3 −.
Is hypercapnia a sign of gas exchange failure?
Thus, in the absence of superimposed ventilatory pump failure, hypercapnia is not a feature of gas exchange failure. In many cases of gas exchange failure, respiratory alkalosis occurs secondary to dyspnea-associated increases in ventilatory drive and minute ventilation. In chronic respiratory failure, hypoxemia can be caused by one or more of the following basic mechanisms:
What is chronic care?
Chronic. You’ll get ongoing care in your home, which typically includes medication you take every day -- either inhaled medicine or drugs you take by mouth. In severe cases, you might need oxygen therapy.
What is the condition where your lungs have a hard time loading your blood with oxygen or removing carbon dioxide?
Respiratory Failure. Respiratory failure is a condition in which your lungs have a hard time loading your blood with oxygen or removing carbon dioxide. It can leave you with low oxygen, high carbon dioxide, or both.
What Are the Symptoms?
Your symptoms will depend on the cause and whether you have low oxygen, high carbon dioxide, or both. Some things you may notice are:
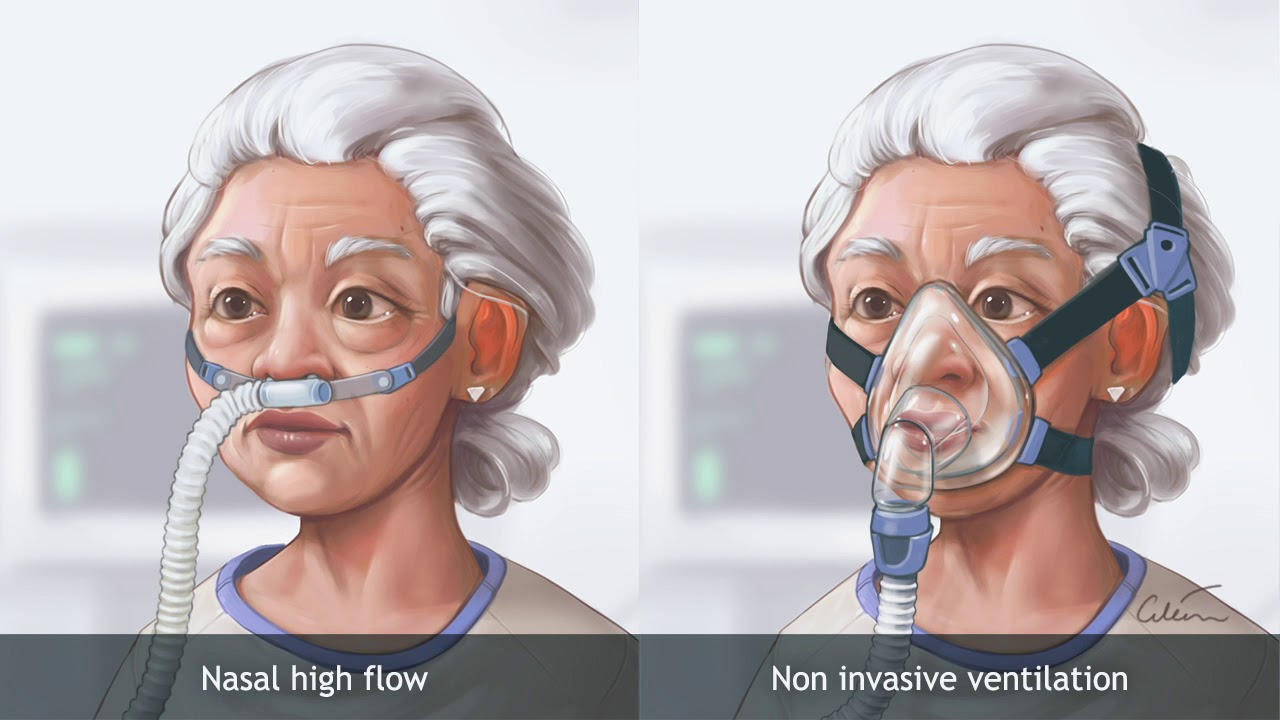
Why do you need a ventilator?
Ventilator. You might need one of these breathing machines if oxygen therapy isn't enough or if you can't breathe on your own. They blow air into your lungs so you get the oxygen you need without having to work so hard for it. They also help lower carbon dioxide levels.
What is it called when you don't get enough oxygen?
If you aren’t getting enough oxygen into your blood, your doctor will call this hypoxemic or type 1 respiratory failure. If you have too much carbon dioxide, it’s called hypercapnic, hypercarbic, or type 2 respiratory failure.
What causes a person to not breathe?
Breathing may seem like a simple act, but there are a lot of moving parts. A problem with any one of them can lead to respiratory failure, including: 1 An injury to your chest or ribs 2 A drug or alcohol overdose, which can harm your brain and breathing 3 Lung damage from breathing in fumes or smoke 4 Lung disease or infection, like chronic obstructive pulmonary disease ( COPD ), cystic fibrosis, or pneumonia 5 Muscle and nerve damage from conditions like amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), spinal cord injuries, and stroke 6 Scoliosis or other spine problems, which can affect bones and muscles involved in breathing 7 Blocked blood flow to your lung, like with a blood clot
What is the most common cause of lung damage?
An injury to your chest or ribs. A drug or alcohol overdose, which can harm your brain and breathing. Lung damage from breathing in fumes or smoke. Lung disease or infection, like chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), cystic fibrosis, or pneumonia.
What is respiratory failure?
Respiratory failure is a condition in which your blood doesn't have enough oxygen or has too much carbon dioxide. Sometimes you can have both problems. When you breathe, your lungs take in oxygen. The oxygen passes into your blood, which carries it to your organs. Your organs, such as your heart and brain, need this oxygen-rich blood to work well.
Why do you need emergency care for respiratory failure?
Living with respiratory failure may cause fear, anxiety, depression, and stress.
What are the conditions that affect breathing?
Conditions that affect your breathing can cause respiratory failure. These conditions may affect the muscles, nerves, bones, or tissues that support breathing. Or they may affect the lungs directly. These conditions include. Problems with the spine, such as scoliosis (a curve in the spine).
What are the problems with the spine?
Problems with the spine, such as scoliosis (a curve in the spine). They can affect the bones and muscles used for breathing.
What diseases affect the lungs?
Diseases that affect the lungs, such as COPD (chronic obstructive pulmonary disease), cystic fibrosis, pneumonia, pulmonary embolism, and COVID-19. Conditions that affect the nerves and muscles that control breathing, such as amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), muscular dystrophy, spinal cord injuries, and stroke.
Can acute respiratory failure be treated at home?
Acute respiratory failure can be a medical emergency. You may need treatment in intensive care unit at a hospital. Chronic respiratory failure can often be treated at home. But if your chronic respiratory failure is severe, you might need treatment in a long-term care center.
When to query for chronic respiratory failure?
We query often for chronic respiratory failure when patients are on continuous home O2. We carry that further that if the patient is presenting with issues requiring increased FiO2 and other measures above and beyond what is normal maintenance care for the patient at home, we query for acute on chronic respiratory failure. We do include a table defining the difference between acute and chronic respiratory failure on the query.
Which condition requires oxygen dependence?
Review the medical record documentation for the condition that requires the oxygen dependence, e.g., COPD, emphysema, acute-on-chronic systolic heart failure, chronic systolic heart failure, chronic respiratory failure. Query for clarification if condition is not documented.
What does it mean when a patient is dependent on oxygen?
Dependence on supplemental oxygen indicates the patient is on long term oxygen therapy . This can be reported regardless of the amount of time on oxygen each day (e.g., patient uses oxygen only at night). Additionally, although the patient might not be dependent on admission, review the record for need for home O2 at time of discharge.
Is home O2 evaluation done for chronic respiratory failure?
I try to include the Home O2 evaluation when I query for Chronic Respiratory Failure. It is not always done, but the documentation of the patient's Room Air sat and level of oxygen needed to maintain a sat of 90% is very helpful.
Causes
Prognosis
- Respiratory failure may be acute or chronic. Acute respiratory failure is a short-term condition. It occurs suddenly and is typically treated as a medical emergency. Chronic respiratory failure, however, is an ongoing condition. It gradually develops over time and requires long-term treatme…
Classification
- Chronic respiratory failure can also be classified as hypoxemic or hypercapnic respiratory failure. Low blood oxygen levels cause hypoxemic respiratory failure. High carbon dioxide levels cause hypercapnic respiratory failure.
Symptoms
- Symptoms of chronic respiratory failure may not be noticeable at first. They usually occur slowly over an extended period of time. When symptoms do develop, they may include: Chronic respiratory failure is a serious illness that gets worse over time. As the condition increases in severity, people may develop an abnormal heart rhythm, stop breathing, or slip into a coma. Cert…
Diagnosis
- Your doctor will be able to diagnose chronic respiratory failure by performing a physical exam and by asking you about your symptoms and medical history. They may also run certain tests to confirm the diagnosis. Often an ongoing illness or significant injury has occurred prior to its development. Your doctor will ask you about lung diseases or conditions you currently have or h…
Results
- Pulse oximetry is a simple and painless test that evaluates how well oxygen is being sent to various parts of the body. Your doctor will place a small sensor on the tip of your finger or ear lobe to determine whether you are getting enough oxygen. In healthy people, normal oxygen saturation range will be between 96 to 100 percent. Any percentage under 90 indicates an abnormally low …
Treatment
- Although acute respiratory failure is a medical emergency that must be treated in a hospital, chronic respiratory failure may be managed at home, depending on its cause. In severe cases, medical professionals can help you manage the condition in a long-term healthcare center. Treatment options typically include: You may receive oxygen therapy if you dont have enough ox…