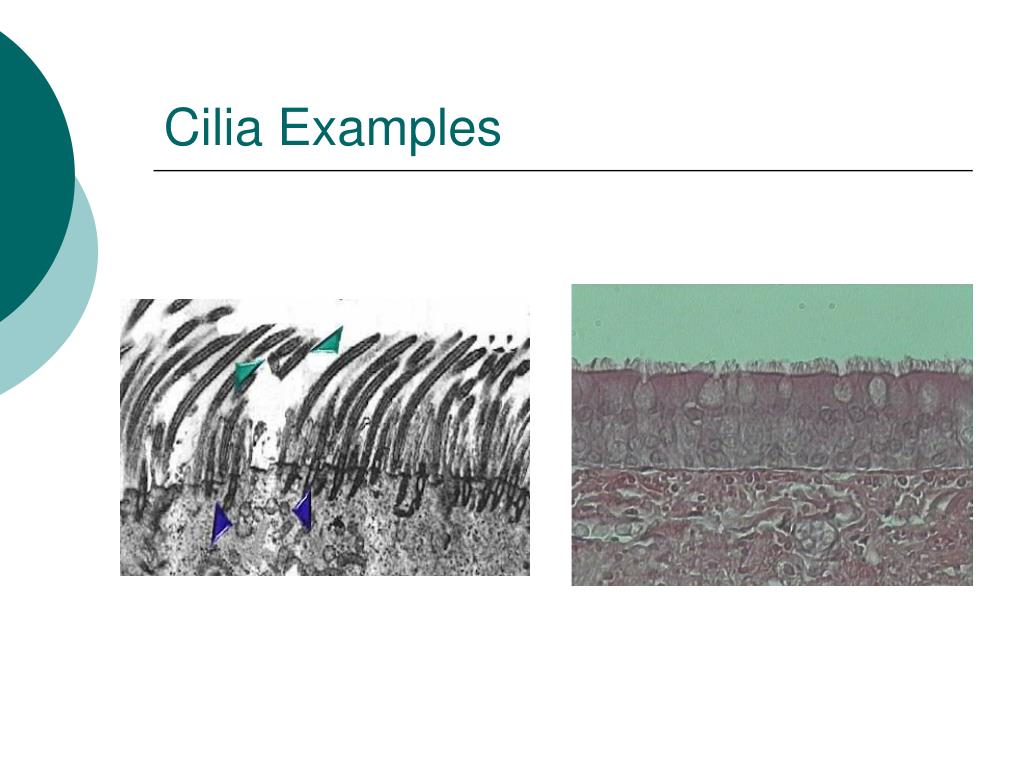
What are the outer pairs of cilia made of?
The nine outer pairs are made up of motor proteins called dynein. These are large and flexible that allows the cilia to move. Cilia are attached to the cell at the basal body that is made up of microtubules arranged in nine triplets. They are very minute structures ranging from 0.25μm in diameter to 20μm in length.
What is the size of cilia?
Cilia are attached to the cell at the basal body that is made up of microtubules arranged in nine triplets. They are very minute structures ranging from 0.25μm in diameter to 20μm in length. Cilia Function
What is the function of the cilia?
Cilium, plural cilia , short eyelashlike filament that is numerous on tissue cells of most animals and provides the means for locomotion of protozoans of the phylum Ciliophora.
What are cilia and flagella?
This colored scanning electron micrograph (SEM) of a section through the wall of a trachea (wind pipe) shows ciliated epithelial cells. Steve Gschmeissner/Science Photo Library/Getty Images What Are Cilia and Flagella? Both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells contain structures known as cilia and flagella.

What protein is cilia made of?
tubulinDirect imaging revealed that proteins of the ciliary matrix, membrane, and axoneme including tubulin, the major structural protein of cilia, move via IFT (Fig. 2E).
What is cilia and its composition?
The cilium is a microtubule-based structure consisting of a basal body with nine triplet microtubules that extend into an axoneme with nine doublet microtubules ensheathed within a ciliary membrane. Typically 2–10 µm long, cilia can reach exceptional lengths of 200 µm in olfactory neurons.
Are cilia made of microtubules?
Cilia are conserved organelles that are built around a sophisticated bundle of microtubules, the axoneme. With few exceptions, motile cilia have a 9+2 axoneme containing nine outer and two central pair (CP) microtubules, while most sensory cilia have a 9+0 axoneme that lacks the CP.
What is inside of cilia?
A cilium, like a flagellum, is composed of a central core (the axoneme), which contains two central microtubules that are surrounded by an outer ring of nine pairs of microtubules.
Are cilia hair?
The bronchus in the lungs are lined with hair-like projections called cilia that move microbes and debris up and out of the airways. Scattered throughout the cilia are goblet cells that secrete mucus which helps protect the lining of the bronchus and trap microorganisms.
How cilia is formed?
Generation of cilia, termed ciliogenesis, occurs in several stages. First, cells must exit the mitotic cycle to free centrioles for axoneme nucleation. Centrioles are called basal bodies upon addition of distal appendages and docking to a ciliary vesicle that fuses with the plasma membrane.
What type of cell is cilia?
Cilia are found on eukaryotic cells. Prokaryotes, such as bacteria, have flagella for locomotion. Eukaryotic flagella are similar to cilia in both structure and function.
Is cilia made of actin or microtubules?
Microtubules are also the structural elements of flagella, cilia, and centrioles (the latter are the two perpendicular bodies of the centrosome).
Is cilia a cell or tissue?
Cilia are microtubule-based hair-like organelles that extend from the cell surface. However, the existence and distribution of cilia in each organ and tissue at the postnatal stage in vivo remain largely unknown.
What is the function of a cilia?
Like tiny brooms, cilia sweep mucus, bacteria, and dust particles from your lungs and airways toward your throat and out of your body.
Is cilia a plant or animal cell?
Cilia are found in most animal cells but only in some plant cells.
Where is cilia found in a cell?
Cilia are hair-like structures that extend from the cell body into the fluid surrounding the cell. They are found on many types of single-celled eukaryotes, in which they are adapted for moving the cells through their surrounding fluid, for food uptake, and for sensing the environment.
What is cilia and its function?
Cilia and flagella are motile cellular appendages found in most microorganisms and animals, but not in higher plants. In multicellular organisms, cilia function to move a cell or group of cells or to help transport fluid or materials past them.
What is a cilia simple definition?
plural cilia ˈsi-lē-ə : a minute short hairlike process often forming part of a fringe. especially : one on a cell that is capable of lashing movement and serves especially in free unicellular organisms to produce locomotion or in higher forms a current of fluid. : eyelash.
What are called cilia?
What are Cilia? Cilia are small, slender, hair-like structures present on the surface of all mammalian cells. They are primitive in nature and could be single or many. Cilia play a major role in locomotion. They are also involved in mechanoreception.
What is the best definition of cilia?
Cilia are slender, microscopic, hair-like structures or organelles that extend from the surface of nearly all mammalian cells.
What is Cilia?
Cilia are small appendages that whip back and forth in eukaryotic cells. The primary purpose of cilia is to help a cell move in cellular fluid and help particles move past the cell in one direction, accomplishing this by their back and forth movements. However, cilia are only about 0.1 millimeters in size.
Cilia Molecular Structure and Composition
Tubulin and basal bodies make up the two main structures of cilia. Tubulin are the hair-like structure of the cilia and are composed of small protein pieces connected to the cell by basal bodies. These protein pieces are made in the cell and delivered to the tubulin.
Types of Cilia
There are various types of cilia, and they can be classified based on their motility and arrangement of their microtubular pairs found inside the axoneme. The two main types of cilia are motile cilia and non-motile, or primary cilia, and there is a subtype of motile cilia called nodular cilia.
What Are Cilia and Flagella?
Both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells contain structures known as cilia and flagella. These extensions from the cell surface aid in cell movement. They also help to move substances around cells and direct the flow of substances along tracts. Cilia and flagella are formed from specialized groupings of microtubules called basal bodies.
What Are Their Distinguishing Characteristics?
Cilia and flagella have a core composed of microtubules that are connected to the plasma membrane and arranged in what is known as a 9 + 2 pattern. The pattern is so named because it consists of a ring of nine microtubule paired sets (doublets) that encircle two singular microtubules.
What Is Their Function?
The primary function of cilia and flagella is movement. They are the means by which many microscopic unicellular and multicellular organisms move from place to place. Many of these organisms are found in aqueous environments, where they are propelled along by the beating of cilia or the whip-like action of flagella.
Where Can Cilia and Flagella Be Found?
Both cilia and flagella are found in numerous types of cells. For instance, the sperm of many animals, algae, and even ferns have flagella. Prokaryotic organisms may also possess a single flagellum or more.
More Cell Structures
Cilia and flagella are two of the many types of internal and external cell structures. Other cell structures and organelles include:
Define Flagella and Cilia
Flagella (singular = flagellum) are long, hair-like structures that extend from the plasma membrane and are used in the movement of an entire cell.
Structure of Flagella and Cilia
Both Flagella and Cilia are structurally similar and possess similar parts, i.e., basal body, rootlets, basal plate and shaft.
Structure of Prokaryotic Flagella
The flagella structure and chemical composition are different in eukaryotes and prokaryotes. The bacterial flagella have the following features:
Types of Flagella Arrangement in Bacteria
Based on the number and arrangement of flagella, there are the following types of bacteria:
What is the Main Function of Flagella?
Some of the functions of flagella and cilia are as follows: i. These help in locomotion in flagellated and ciliated organisms. ii. The flagella or cilia also help capture food in many protozoans and some animals. iii. They create water currents in certain aquatic animals for obtaining food. iv.
Summary
Through this article, we understood the structure and functions of flagella and cilia and the difference between them. These are the microscopic contractile and filamentous structure of the cytoplasm. It creates food currents, acts as sensory organs and performs many mechanical functions of the cell.
FAQs
Q.1. Write one function of cilia. Ans: The cilia also help in capturing food in many protozoans and some animals. They also help in feeding, locomotion, aeration, circulation, etc.