What are the 5 cognitive domains?
And yet there are many cognitive domains that contribute to overall cognitive health [4]. The present research addresses five common domains of function [5]: Episodic memory, speed-attention-executive, visuospatial ability, fluency, and numeric reasoning.
What are the 6 cognitive domains?
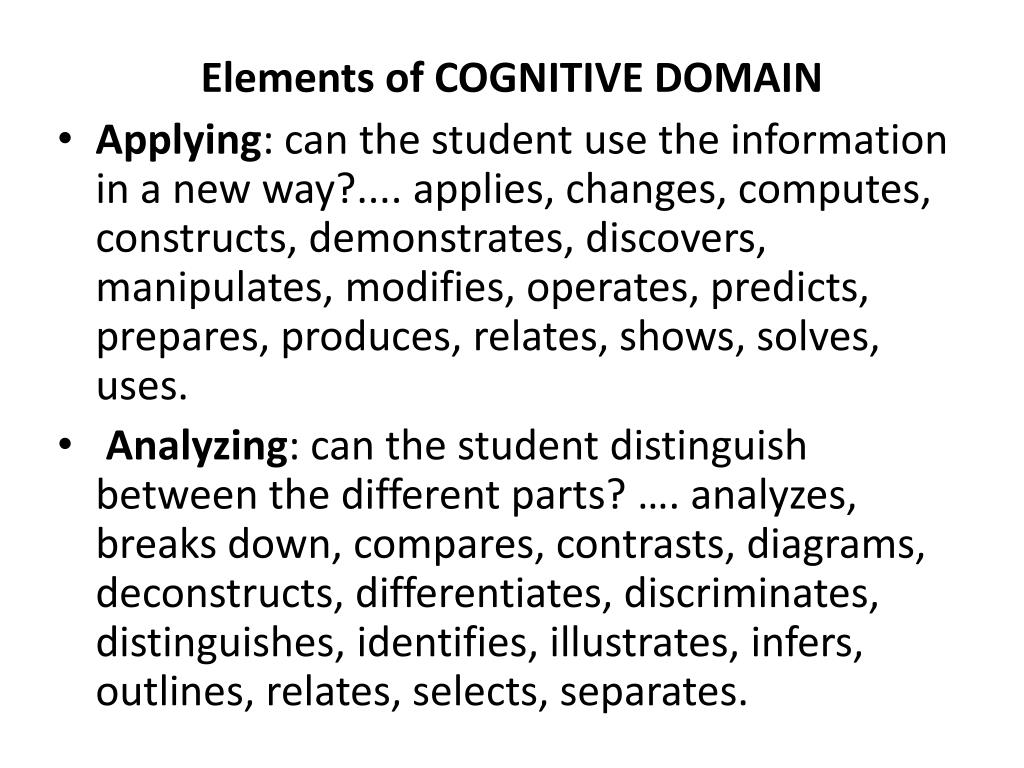
I. Knowledge. Remembering information.II. Comprehension. Explaining the meaning of information.III. Application. Using abstractions in concrete situations.IV. Analysis. Breaking down a whole into component parts.V. Synthesis. Putting parts together to form a new and integrated whole.VI. Evaluation.
What are the activities of cognitive domain?
Cognitive DomainAssessmentsEvaluate Make judgements based on evidence foundAssessments Argumentative or persuasive essay Debates Discussions Presentation Provide alternative solutions Report5 more rows
What is a cognitive domain?
The Cognitive Domain: The cognitive domain of learning involves thinking about facts, terms, concepts, ideas, relationships, patterns, conclusions, etc. A common taxonomy utilized to document learning within the cognitive. domain is Bloom's Taxonomy (as revised by Krathwohl, et al.).
What are the example of affective domain?
Definitions of the affective domain Responding is committed in some small measure to the ideas, materials, or phenomena involved by actively responding to them. Examples are: to comply with, to follow, to commend, to volunteer, to spend leisure time in, to acclaim.
What is cognitive domain in education?
Cognitive Domain. The cognitive domain (Bloom, 1956) involves knowledge and the development of intellectual skills. This includes the recall or recognition of specific facts, procedural patterns, and concepts that serve in the development of intellectual abilities and skills.
What are the example of cognitive objective?
Cognitive objectives relate to understandings, awareness, insights (e.g., "Given a description of a planet, the student will be able to identify that planet, as demonstrated verbally or in writing, with 100% accuracy." or "The student will be able to evaluate two different theories of the origin of the solar system as ...
What is the cognitive domain of development?
The cognitive domain of development refers to the ability to mentally process information — to think, reason, and understand what's happening around you. Developmental psychologist Jean Piaget divided cognitive development into four distinct stages.
Why is cognitive domain important in assessment?
The learning domains are cognitive, affective, and psychomotor. The cognitive domain is where intellect is developed. Within the cognitive domain, students process new information, store knowledge, and retrieve it to apply to new circumstances.
What is the difference between cognitive and affective domain?
The affective domain refers to emotional and attitudinal engagement with the subject matter while the cognitive domain refers to knowledge and intellectual skills related to the material.
What is cognitive domain in lesson plan?
The COGNITIVE DOMAIN involves knowledge of information, facts and concepts, and the ability to apply, analyze, synthesize and evaluate. It is the area that is most focused on in these days of basic skills, proficiency testing and exit exams.
WHO classified cognitive domain?
Benjamin BloomThe cognitive domain list has been the primary focus of most traditional education and is frequently used to structure curriculum learning objectives, assessments and activities. The models were named after Benjamin Bloom, who chaired the committee of educators that devised the taxonomy.
What are the 6 cognitive processes of Bloom's taxonomy?
There are six levels of cognitive learning according to the revised version of Bloom's Taxonomy. Each level is conceptually different. The six levels are remembering, understanding, applying, analyzing, evaluating, and creating.
What are the six levels of Bloom's taxonomy with examples?
The six cognitive levels of Bloom's taxonomyLevel one – Remembering.Level two – Understanding.Level three – Applying.Level four – Analysing.Level five – Evaluating.Level six – Creating.Example 1: Primary English-language classroom.Example 2: Secondary school biology class.
What are the main domains of cognitive functioning in psychology?
They include encoding, storage, and retrieval, all of which are required for successful memory performance. In these domains, there are multiple important features required for understanding the processes involved.
What are the 4 cognitive domains?
The Cognitive Domain of Bloom's TaxonomyKnowledge.Comprehension.Application.Analysis.Synthesis.Evaluation.
What is cognitive domain?
Subscribe. What is the cognitive domain? The cognitive domain is one of the three domains of measuring learning. It focuses on acquisition, retention and usage of knowledge, whereas the affective domain covers emotions and values and the psychomotor domain includes physical movement and coordination.
What is the lowest tier of cognitive domain?
Take, for example, the lowest tier of the cognitive domain, remembering . Learners can demonstrate factual, conceptual, procedural and/or metacognitive remembering, each stage progressively more advanced. One way metacognitive remembering can be achieved is if your students are able to identify general strategies for retaining information.
How can metacognitive remembering be achieved?
One way metacognitive remembering can be achieved is if your students are able to identify general strategies for retaining information. In practice, these overlapping ladders of the cognitive domain and the knowledge dimension do have limits and need interpretation.
How to teach metacognition to students?
Explicitly teach metacognition to your students, and develop a classroom discourse about learning. Set aside time to teach for and assess metacognitive skills, and identify and label metacognitive practices for students while they are engaging in them. Here are some phrases you can use or adapt.
What are the four stages of knowledge?
This means four stages—collectively known as the knowledge dimension—can be added to each layer of the pyramid: factual, conceptual, procedural and metacognitive knowledge. The knowledge dimension in the cognitive domain. When we apply the knowledge dimension to the pyramid, we get a matrix that allows educators to not just assess how far up ...
What is metacognition in psychology?
Metacognition is something that can be taught and tested for in any category of the cognitive domain: you don’t need to wait until your students are at the upper layers of the pyramid (creating or understanding). Take, for example, the lowest tier of the cognitive domain, remembering.
What is the highest level of knowledge?
The highest level in the knowledge dimension is metacognition, or knowledge about knowing. Metacognition involves awareness of one’s own thinking and its limits, especially in relation to general ideas about how learning happens.
What is cognitive development?
Cognitive development involves how children think, explore, and figure things out. It refers to things such as memory, and the ability to learn new information. This domain includes the development of knowledge and skills in math, science, social studies, and creative arts. Research shows that even at a young age, ...
What are some examples of unfamiliar phenomena?
For example, two objects may look the same but one floats and one sinks in water. Throughout your day, be mindful of opportunities to show your child an unfamiliar phenomenon. For example, if you are washing dishes, show your child what happens when you add dish soap to water. As you do this, explain what you are seeing.
What is cognitive domain?
The cognitive domain involves knowledge and the development of intellectual skills. This includes the recall or recognition of specific facts, procedural patterns, and concepts that serve in the development of intellectual abilities and skills. There are six major categories, which are listed in order below, starting from ...
How many categories are there in psychology?
There are six major categories, which are listed in order below, starting from the simplest behavior to the most complex. The categories can be thought of as degrees of difficulties. That is, the first one must be mastered before the next one can take place.
What is the cognitive dimension of the IE?
The cognitive dimension is a cohort’s collective perception of an information set. By extension therefore, this dimension is a warfighting domain (also known as an operating domain), albeit one with a higher level of abstraction than the maritime or land domains. The argument rests on the assertion that a strategic competition can be won in the cognitive domain before the vanquished party even recognises that its interests are threatened. Wars can be lost in the cognitive domain without a shot being fired. This point is not lost on the People’s Liberation Army, whose doctrine includes no fewer than three types of warfare in the IE, among them “public opinion warfare.”
What are the five domains of war?
The UK’s Ministry of Defence (MOD) recognizes five warfighting domains: land, maritime, air, space, and cyberspace. However, none of these five domains account satisfactorily for the territory fought over in the battle for hearts and minds. Julie “Pistol” Janson and Laura Elkins separately argue in this journal for recognition ...
What is the convergence of social networks?
The convergence of the internet, mobile computing, and social network sites represents the perfection of a machinery of communication of such ubiquity and agility that the potential now exists for public discourse to be manipulated at machine speed. This raises the stakes in the battle of strategic narratives being waged between liberal democracies and rising, revanchist states. Yet there is no consensus among security scholars or officials as to where this battle is taking place.
Is cyber warfare a cognitive domain?
As cyber warfare is to the cyber domain, then cognitive warfare is to the cognitive domain.
Can a war be lost in the cognitive domain?
The argument rests on the assertion that a strategic competition can be won in the cognitive domain before the vanquished party even recognises that its interests are threatened. Wars can be lost in the cognitive domain without a shot being fired.
Is the citizenry's hive mind a domain?
A citizenry’s ‘hive mind’ is therefore vital territory. Thus, the cognitive dimension qualifies as a domain — and, inductively, since its protection will be the preserve of the national security enterprise, as a warfighting (or operating) domain.
Is cognitive warfare hard power?
When a party wages it intensely, characterised by malign intent or in the defence thereof, cognitive warfare is an instrument of hard power since it is seeking to coerce a party into a course of action. Seeding disinformation to distract or deceive a target audience so that it acts against its best interests would be such an employment of hard power. Yet actors may also use the cognitive domain as a manoeuvre space for soft power projection. International cooperation in higher education is a good example, ranging from the European Union’s Erasmus+ scheme to China’s more controversial Confucius Institutes. The online conspiracy-debunking services, particularly those offered by well-reputed and non-partisan institutions are another good example of soft power projection in the cognitive domain. The Associated Press and the British Broadcasting Corporation’s both enjoy global reach and cultivated reputations for reporting news and current affairs impartially. They are significant soft power assets for the US and UK respectively. Other public information providers are available.
How many levels of knowledge are there in Bloom's cognitive domain?
In all there are six different levels ...
What are the three domains of learning?
These are called the Cognitive domain, the Psychomotor domain, and the Affective domain .
How many levels of knowledge are there?
In this post, we’re going to consider the “knowledge” domain of learning more closely–things you can know. We’ll find that there are actually six different levels of knowledge, from simplest to most complex, and we will give a list of behaviors that learners must perform to show they’ve mastered each type of knowledge. This will help you pick the verb you’ll use when writing learning objectives dealing with knowledge. We’ll look at the Skills and Attitudes domains in following posts.
What is the original cognitive domain?
Based on the 1956 work, The Handbook I-Cognitive Domain, behavioral objectives that dealt with cognition could be divided into subsets. These subsets were arranged into a taxonomy and listed according to the cognitive difficulty — simpler to more complex forms.
Who was the first author of the cognitive domain?
While Bloom was involved in describing both the cognitive and the affective domains, he appeared as first author on the cognitive domain. As a result this bore his name for years and was commonly known among educators as Bloom ’s Taxonomy even though his colleague David Krathwohl also a partner on the 1956 publication.
What are the three domains of learning?
These domains of learning are the cognitive (thinking), the affective (social/emotional/feeling), and the psychomotor (physical/kinesthetic) domain , and each one of these has a taxonomy associated with it.
When was the cognitive taxonomy first described?
In examining the three domains of learning it is interesting to note that while the cognitive taxonomy was described in 1956, and the affective in 1964, the psychomotor domain was not fully described until the 1970s.
When were the domains of learning first described?
The domains of learning were first developed and described between 1956-1972. The cognitive domain had a major revision in 2000-01.
When was the cognitive domain revised?
Many veteran teachers are totally unaware that the cognitive/thinking domain had major revisions in 2000-01. If you are searching the internet for more information on domains of learning, please be sure the sources you find are offering readers information that includes the most recent revisions. Here I have included both the original cognitive domain, and I have also attached it to the newer, revised version so that users can see the differences. The newer version of Bloom’s Taxonomy of Learning has a number of added features that can be very useful to educators as they try to construct optimal learning experiences. I hope readers will explore the differences and additions through the links provided on this page.
What are the differences between the old and new version of cognition?
One of the major changes that occurred between the old and the newer updated version is that the two highest forms of cognition have been reversed. In the older version the listing from simple to most complex functions was ordered as knowledge, comprehension, application, analysis, synthesis, and evaluation. In the newer version the steps change to verbs and are arranged as knowing, understanding, applying, analyzing, evaluating, and the last and highest function, creating.
What are the verbs that represent the cognitive domain?
Instructional verbs that represent this foundational level of the cognitive domain include write, list, label, name and state.
What are the domains of learning?
The domains of learning are a series of learning objectives created in 1956 by educational psychologist Dr. Benjamin Bloom. They involve three categories of education, and each one requires a different instruction style to achieve its intended outcomes. Each domain has specific features and objectives designed to engage students who learn to solve problems, process information and build their skills using different perspectives. This helps make learning easier and more enjoyable.
Why are domains of learning important?
The domains of learning give educators the knowledge to establish teaching methods that emphasize the distinctive strengths of each student. These concepts have influenced the field of education by encouraging a more holistic approach to learning. Holistic educational methods allow students to grow not only academically but also professionally. In this article, we discuss what the domains of learning are, why they're important and the stages of each domain that students use to process information and develop skills.
What is the psychomotor domain?
The psychomotor domain focuses on physical skills, such as the development of hand-eye coordination and the use of motor skills. Psychomotor skills help people perform physical tasks in daily life and at work. The areas of this domain include:
What is affective domain?
The affective domain of learning represents skills that foster appropriate emotional responses. In this domain, individuals understand and develop their feelings, attitudes and values. Like the cognitive domain, Bloom arranged the five areas of emotional response from simple to complex:
What is the cognitive domain?
The cognitive domain is centered on intelligence and developing new knowledge and mental skills. The affective domain is focused on emotional development and learning. All three are pertinent to physical education, which typically includes exercises, games, and organized sports.
What are the three domains of learning?
All education, including physical education, should incorporate the three domains of learning: psychomotor, cognitive, and affective. This lesson will explain each domain and how it can be applied to physical education. Updated: 10/27/2020
Which domain is centered on intelligence and developing new knowledge and mental skills?
Next, we have the cognitive domain, which is centered on intelligence and developing new knowledge and mental skills. Like the other domains, a person's capacity to learn new information increases throughout childhood into adulthood.
Which domain is focused on emotional development?
Finally, we have the affective domain, which is focused on emotional development learning. We have the capacity to acquire new feelings and emotions with age, as well as develop the control to manage how these feelings or emotions are expressed.
What are the three domains of cognitive psychology?
In the field of cognitive psychology, there are, in general, three learning domains. The first domain is the affective domain (e.g., social skills, emotion regulation skills), the second domain is the cognitive domain (e.g., facts, thinking skills) , and the third domain is the psychomotor domain (e.g., physical skills).
What is cognitive psychology?
Cognitive psychology can be regarded as a field of psychology that focuses on the study of human cognition. It is concerned with not only the aspects and functions of our cognition but also the cognitive process involved in various activities (e.g., decision making, judgment).

Overview
- Bloom's taxonomy is a set of three hierarchical models used to classify educational learning objectives into levels of complexity and specificity. The three lists cover the learning objectives in cognitive, affective and sensory domains. The cognitive domain list has been the primary focus of most traditional education and is frequently used to structure curriculum learning objectives, as…
Cognitive Domain
- The cognitive domain involves knowledge and the development of intellectual skills (Bloom, 1956). This includes the recall or recognition of specific facts, procedural patterns, and concepts that serve in the development of intellectual abilities and skills. There are six major categories of cognitive an processes, starting from the simplest to the most complex (see the table below for …
Original Taxonomy
- Lorin Anderson, a former student of Bloom, and David Krathwohl revisited the cognitive domain in the mid-nineties and made some changes, with perhaps the three most prominent ones being (Anderson, Krathwohl, Airasian, Cruikshank, Mayer, Pintrich, Raths, Wittrock, 2000): 1. changing the names in the six categories from noun to verb forms 2. rearranging them as shown in the ch…
- Bloom’s taxonomy was originally published in 1956 by a team of cognitive psychologists at the University of Chicago. It is named after the committee’s chairman, Benjamin Bloom (1913–1999). The original taxonomy was organized into three domains: Cognitive, Affective, and Psychomotor. Educators have primarily focused on the Cognitive model, which includes six different classifica…
- Published in 2001, a revised Bloom's Taxonomy was revealed that intended to address the changing nature of education and a more relevant structure for the 21st century. A former student of Bloom's, Lorin Anderson, facilitated the creation of this revised taxonomy along with cognitive psychologists, curriculum theorists, instructional researchers and testing specialists. Most relev…
Examples
- Below are sample intended course learning outcomes that utilize Bloom’s Taxonomy: 1. At the end of the course, students will be able to: 1. describe the colonization of the Americas by the British, French and Spanish 2. analyze the outcomes of the Civil War 3. identify specific stages of language acquisition 4. describe major theories of language development (e.g. nativist, empirici…
Domains
- Bloom's Taxonomy refers to three different domains of competence but is almost solely known for its framework of the cognitive domain. The cognitive domain is the most relevant in the discussion about educational design.
History
- Although named after Bloom, the publication of Taxonomy of Educational Objectives followed a series of conferences from 1949 to 1953, which were designed to improve communication between educators on the design of curricula and examinations. The first volume of the taxonomy, Handbook I: Cognitive was published in 1956, and in 1964 the second volume Handb…
Criticism Of The Taxonomy
- As Morshead pointed out on the publication of the second volume, the classification was not a properly constructed taxonomy, as it lacked a systematic rationale of construction. This was subsequently acknowledged in the discussion of the original taxonomy in its 2001 revision, and the taxonomy was reestablished on more systematic lines. Some critiques of the taxonomy's co…
- Bloom's Taxonomy is widely cited in K-12 teacher training programs in reference to how students learn and how to teach. However, it has been pointed out that Bloom's Taxonomy is more often than not interpreted incorrectly. Booker (2007) believes that \"Bloom’s Taxonomy has been used to devalue basic skills education and has promoted “higher order thinking” at its expense\" (200…
Definition Of Knowledge
- In the appendix to Handbook I, there is a definition of knowledge which serves as the apex for an alternative, summary classification of the educational goals. This is significant as the taxonomy has been called upon significantly in other fields such as knowledge management, potentially out of context. "Knowledge, as defined here, involves the recall of specifics and universals, the recal…
Connections Across Disciplines
- The skill development that takes place at these higher orders of thinking interacts well with a developing global focus on multiple literacies and modalities in learning and the emerging field of integrated disciplines. The ability to interface with and create media would draw upon skills from both higher order thinking skills including analysis, evaluation, and creation and lower order thin…
Implications
- Bloom's taxonomy serves as the backbone of many teaching philosophies, in particular, those that lean more towards skills rather than content. These educators view content as a vessel for teaching skills. The emphasis on higher-order thinking inherent in such philosophies is based on the top levels of the taxonomy including analysis, evaluation, synthesis and creation. Bloom's ta…