What is column agglutination testing?
The common name for various manufacturers’ versions of “column agglutination” testing. Gel testing occurs in small columns filled with a viscous gel. The RBCs and plasma being tested are added to the chamber at the top of the column and incubated, followed by centrifugation to try to force the RBCs through the gel to the bottom of the column.
What is a column agglutination gel card?
DG Gel cards are the original 8-column gel card featuring column agglutination technology (CAT) for blood group typing and investigating unexpected antibodies.
Which column agglutination technologies are used to screen for RBC antibodies?
Gel card (Bio-Rad DiaMed) and glass bead-based (Ortho Clinical Diagnostics) column agglutination technologies were used to screen for antibodies prospectively (group A) and for antibody identification in stored and fresh samples known to contain RBC antibodies retrospectively (group B).
What is involved in the gel testing process?
Gel testing occurs in small columns filled with a viscous gel. The RBCs and plasma being tested are added to the chamber at the top of the column and incubated, followed by centrifugation to try to force the RBCs through the gel to the bottom of the column.
What is column agglutination technology cat and what is it used for?
Historically, CTT has been used as the standard technique for immunohaematological studies, such as direct antihuman globulin test for the diagnosis of autoimmune haemolytic anaemia and in screening for specific antibodies in transfusion medicine.
What is gel column technology?
The gel column acts as a filter that traps agglutinated red blood cells as they pass through the gel column during the centrifugation of the card. The gel column separates agglutinated red blood cells from non-agglutinated red blood cells based on size.
What is AHG test?
Principles of the assay Polyspecific AHG is commonly used in blood banks to perform direct and indirect antiglobulin testing (DAT and IAT). The DAT determines if red blood cells are coated in vivo with immunoglobulin, complement or both. This test is necessary in the investigation of immune-mediated hemolysis.
What is solid phase red cell adherence?
Solid Phase Immune Adherence Assay is an immunological technique in which one of the reactants, either the antigen or antibody, is immobilised onto a solid medium and assay for either the antibody or antigen in question. Indicators of end point can be a fluorescein, an enzyme or red cells.
Which gel is used in the column agglutination procedure?
The gel agglutination test (GEL) detects RBC antigen–antibody reactions using a chamber filled with polyacrylamide gel.
What is the disadvantage of gel technology?
Gel technology also provides standardization and automation to blood bank testing. Disadvantages of gel testing include the inability to perform testing on hemolyzed, icteric, or lipemic samples because color interference can lead to false- positive results.
What is Coombs reagent?
The Coombs Reagent (also known as anti-human globulin) is used to distinguish the presence or absence of immunoglobulin on the surface of red blood cells.
What is DCT test?
What is it? This is a blood test commonly performed in newborn babies. Blood may be taken from your baby by a heal prick test or a needle. It tests for evidence of a reaction between the blood groups of the baby and his/her mother.
What is Coombs test used for?
The direct Coombs test is used to detect antibodies that are stuck to the surface of red blood cells. Many diseases and drugs can cause this to happen. These antibodies sometimes destroy red blood cells and cause anemia.
Which is more sensitive gel method or solid phase adherence method?
Conclusion: Solid-phase red cell adherence assay is more precise and capable of detecting red cell adherence assay than tube method and indirect Coombs test gel technology.
What is antibody screen negative?
A negative antibody test tells you that you don't have harmful antibodies in your blood. If you're also Rh-positive, you can safely carry a baby with either a + or - blood type.
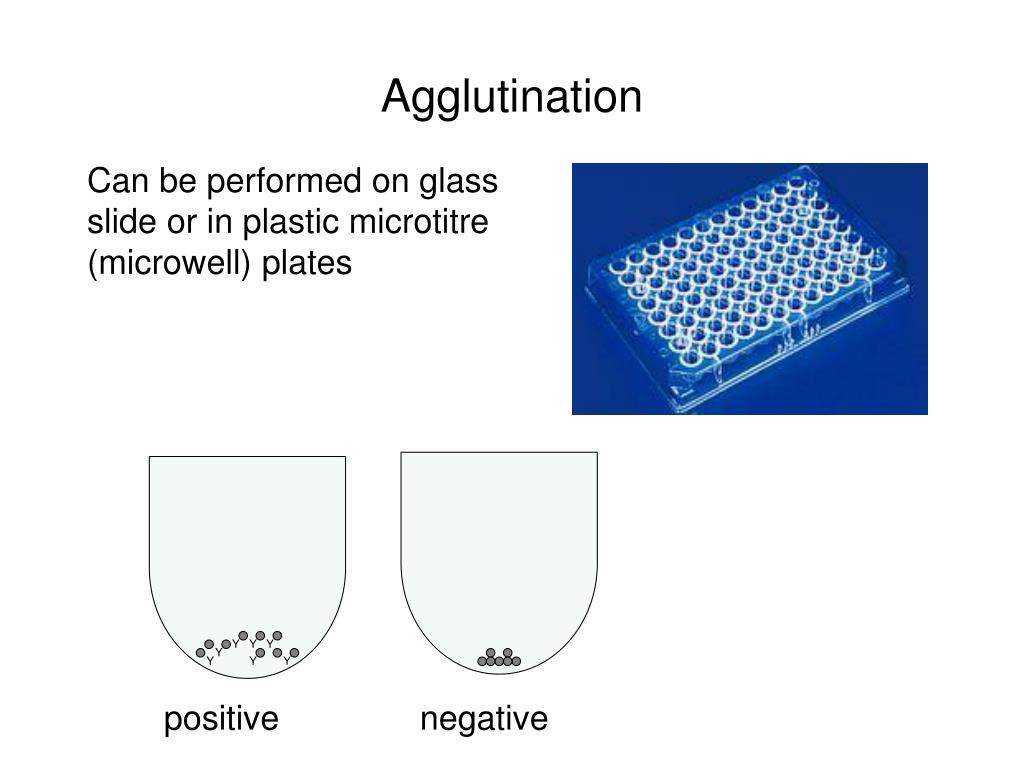
What is solid phase testing?
A method of testing for incompatibility between plasma antibodies and target RBC antigens. Solid phase testing occurs in small microwells, where antigens are bound to the bottom of the well and the patient's plasma is incubated in the well.
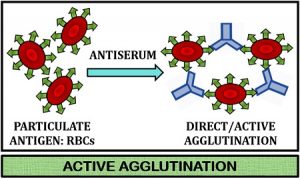
What is agglutination test?
The common name for various manufacturers’ versions of “column agglutination” testing. Gel testing occurs in small columns filled with a viscous gel. The RBCs and plasma being tested are added to the chamber at the top of the column and incubated, followed by centrifugation to try to force the RBCs through the gel to the bottom of the column. Gel makes positive reactions obvious (usually) in two ways: First, RBCs that are agglutinated will be stopped earlier in the gel than those that are not agglutinated. Second, the gel (when performing an antibody screening test) contains anti-IgG, which binds to the IgG coating RBCs in positive reactions, and further inhibits transport of the RBCs through the gel.
Does gel bind to IgG?
Second, the gel (when performing an antibody screening test) contains anti-IgG, which binds to the IgG coating RBCs in positive reactions, and further inhibits transport of the RBCs through the gel. Back to Glossary List. Full Glossary List.
Universal
Use DG Gel Cards to simplify stock management and easily upgrade laboratory instruments.
Flexible
Customize testing with gel cards designed for a wide range of laboratory needs.
Reliable
Easily interpret results from clear, consistent, and stable measurements.