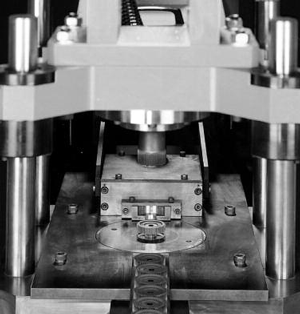
What is a powder compaction die?
Mar 11, 2020 · Powder compaction is the process of compacting metal powder in a die through the application of high pressures. Typically the tools are held in the vertical orientation with the punch tool forming the bottom of the cavity. The powder is then compacted into a shape and then ejected from the die cavity. Click to see full answer.
What is the role of powder compaction in the pharmaceutical industry?
May 11, 2020 · Powder compaction is the process of compacting metal powder in a die through the application of high pressures. Typically the tools are held in the vertical orientation with the punch tool forming the bottom of the cavity. The powder is then compacted into a shape and then ejected from the die cavity.
What is powder compaction of rhodium?
May 19, 2020 · Compaction is crucial in powder metallurgy processing because it allows free metal powders to be formed into desired forms with sufficient strength to survive until sintering is done. Compaction is often performed without the use of heat.
How does powder compaction work in MIM?
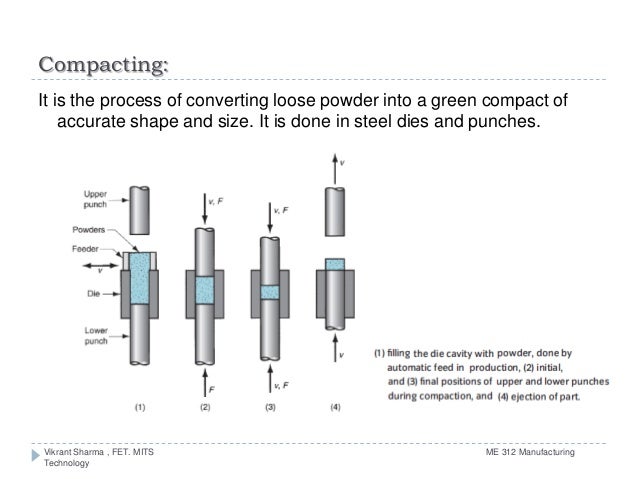
Apr 17, 2014 · This phase of powdered metallurgy is referred to as compacting or pressing. Compacting or pressing of metal powders is divided into the following two areas: Hot Pressing Cold Pressing Hot pressing is the compaction of powder at elevated temperatures. It is usually a dual technique where the metal powders are compacted and sintered at the same time.
What do you mean by sintering and compacting in powder metallurgy?
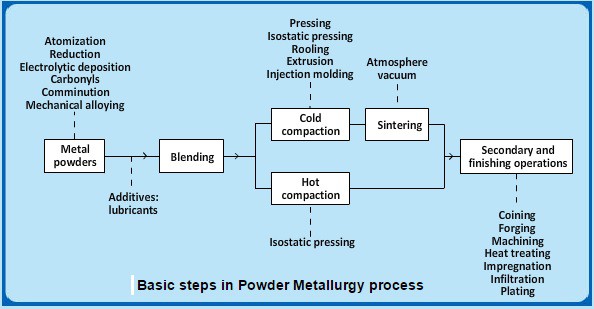
Powder metallurgy is the process of blending fine powdered materials, pressing them into a desired shape or form (compacting), and then heating the compressed material in a controlled atmosphere to bond the material (sintering).Aug 15, 2017
Why compacting and sintering are essential steps in powder metallurgy?
'Compacting process' used in powder metallurgy is done: The powder metallurgy process enables to produce parts in their final shape, thus eliminating the need for any additional machining. Blending and Mixing: In this process, metallic powders in the required proportion are mixed uniformly.
What is crushing in powder metallurgy?
3.3.3. Reduction. Crushing. Process of passing the metal powders against two rollers so that the metal powders are crushed to required size. Crushing requires equipments such as stamp, hammers, and jaw crushers.Apr 29, 2014
What are the different methods of compacting metal powders?
Methods of Compacting / Powder MetallurgyPressing.Centrifugal Casting.Slip Casting.Extruding.Gravity Casting.Rolling.Iso-static Moulding.Explosive Compacting.More items...
What is compacting process?
The compacting process is the compressing of fine-sized powders between a roll compactor. The compacted material is then typically reduced in size and screened to specification. The compacting process includes these steps. Materials are fed and mixed from the material silo into the compactor.
What is green compact in powder metallurgy?
Powder Metallurgy (PM) deals with products and processes which use raw material in the form of powders that are compacted into the required shape and size using suitable moulds. These compacted powders are called „Green Compacts‟.
What is compaction and sintering?
After compaction, powdered materials are heated in a controlled atmosphere in a process known as sintering. During this process, the surfaces of the particles are bonded and desirable properties are achieved.
What is densification in powder metallurgy?
The densification of powdered materials is a process of pore elimination whereby the porosity of these sintered alloys decreases with the increase of the time and correct sintering temperature (German, 2005. Princeton, USA: Metal Powder Industries Federation, 2005.
What is atomization in powder metallurgy?
Atomization involves the formation of powder from molten metal using a spray of either a gas or liquid.
What are some of the disadvantages of powder metallurgy methods?
Disadvantages of Powder Metallurgy:There are often size limitations to PM parts that can make certain designs impossible to produce. ... Complex-shaped parts can also be challenging to make. ... Parts are generally not as strong or as ductile as cast irons or forged parts.Apr 11, 2019
What are the functions of metal powder compaction?
The compaction of metal powders has the following major functions: to consolidate the powder into desired shape. to impart, to as high a degree as possible, the desired final dimensions with due consideration to any dimensional changes resulting from sintering. to impart the desired level and type of porosity.
What are the advantages of powder metallurgy?
Advantages of the Powder Metallurgy ProcessMinimizes machining by producing parts at, or close to, final dimensions.Minimizes scrap losses by typically using more than 97% of the starting raw material in the finished part.Permits a wide variety of alloy systems.Produces good surface finish.More items...
What is a P/M compacting press?
The majority of P/M parts are compacted by mechanical means. Mechanical presses, in general, are used for making parts in the lower pressure range because their speed exceeds those of hydraulic presses in most cases. The two basic categories of P/M compacting presses are mechanical and hydraulic. The main difference between the two are ...
What are the physical properties of metal powders?
Pressing of metal powders depend upon their physical characteristics and properties. These include particle size, shape, composition, and size distribution. The type of powder and its method of manufacture also influences its behavior under pressure in a cold die.
Why did stamping presses require a lot of set up time?
They also required quite a bit of set up time to change dies and punches because of the lack of adjustability and controls.
Why do P/M parts need to be repressed?
When extremely accurate dimensions are required the P/M part or parts must be repressed because of dimensional changes during the sintering operation. This is a rapid operation usually performed on high speed presses.
Why is density uneven in compacts?
Uneven distribution of density in a compact is caused by pressure not being transmitted through the green shape without a drop (loss) due to friction.
Do powders behave under pressure?
It has been found that powders do not behave under pressure, in a cold die, in the same way as a liquid. Pressure exerted on a liquid in a closed container is transmitted evenly in all directions. This is not the case with metal powder. When metal powders are pressed in a closed die they flow mainly in the direction off the applied pressure.
What is PM in metal?
In other words, PM is a metal shaping process that creates near-net parts from powdered metal.
Is powder metallurgy a high volume process?
It is suitable for high-volume production with very little wastage of material. Secondary machining is virtually eliminated. Powder metallurgy is a continually and rapidly evolving technology embracing most metallic and alloy materials, and a wide variety of shapes.
What is powder compaction?
Powder compaction is becoming an increasingly important industrial manufacturing process where components of rather complicated geometry are being manufactured. Today, complex parts can be produced by multi-level tools that were inconceivable just a few years ago.
How is MIM powder compaction performed?
As stated previously, in MIM powder compaction is performed by sintering. This means the material is uniformly heat treated at high temperatures for a long time and slowly cooled down. Thus, the formation of a homogenous material with isotropic properties and low internal stress after processing is promoted. However, the grains tend to grow at high temperatures; therefore, sintered materials typically show a homogenous but comparably coarse microstructure that might deteriorate strength and ductility. Furthermore, sintering leads to some residual porosity as mentioned before. These pores are small but nevertheless influence the mechanical properties. However, because the pores are isolated, as discussed before they can easily be closed by a subsequent HIP process commonly applied after casting. Typically, the mechanical properties of MIM components are between cast and forged material.
Why do green compacts need sintering?
Most of powder compaction techniques lead to green compacts require sintering in order to gain high density and strength of the product. By using dynamic compaction systems, it is possible to attain a density very close to the theoretical density of the material without needs to sintering process [1–4].
Is powder manufactured a major route for processing composite materials?
It is important to understand densification behavior of mixed powders, since powder manufactured has been considered as a major route for processing composite materials. Except for the very simplest part geometries it is not possible to achieve a homogeneous green density distribution by die compaction.
What is isostatic powder compacting?
Isostatic powder compacting is a mass-conserving shaping process. Fine metal particles are placed into a flexible mould and then high fluid pressure is applied to the mold, in contrast to the direct pressure applied by the die faces of a die pressing process. The resulting article is then sintered in a furnace which increases the strength of the part by bonding the metal particles. This manufacturing process produces very little scrap metal and can be used to make many different shapes. The tolerances that this process can achieve are very precise, ranging from +/- 0.008 inches (0.2 mm) for axial dimensions and +/- 0.020 inches (0.5 mm) for radial dimensions. This is the most efficient type of powder compacting (the following subcategories are also from this reference). This operation is generally only applicable on small production quantities, although the cost of a mold much lower than that of pressing dies it is generally not reusable and the production time is much longer.
What is the dominant technology for the forming of products from powder materials?
The dominant technology for the forming of products from powder materials, in terms of both tonnage quantities and numbers of parts produced, is die pressing. There are mechanical, servo-electrical and hydraulic presses available in the market, whereby the biggest powder throughput is processed by hydraulic presses. This forming technology involves a production cycle comprising:
What is electro sintering?
Spark plasma sintering and electro sinter forging are two modern, industrial commercial ECAS technologies. Additive manufacturing (AM) is a relatively novel family of techniques which use metal powders (among other materials, such as plastics) to make parts by laser sintering or melting.
What are the steps of powder metallurgy press?
The powder metallurgy press and sinter process generally consists of three basic steps: powder blending (pulverisation), die compaction, and sintering. Compaction is generally performed at room temperature, and the elevated-temperature process of sintering is usually conducted at atmospheric pressure and under carefully controlled atmosphere composition. Optional secondary processing such as coining or heat treatment often follows to obtain special properties or enhanced precision.
What is sintering metal?
Sintering involves the production of a hard solid metal or ceramic piece from a starting powder. The ancient Incas made jewelry and other artifacts from precious metal powders, though mass manufacturing of PM products did not begin until the mid or late 19th century. In these early manufacturing operations, iron was extracted by hand from metal sponge following reduction and was then reintroduced as a powder for final melting or sintering.
How are air and powder streams segregated?
Air and powder streams are segregated using gravity or cyclonic separation. Most atomized powders are annealed, which helps reduce the oxide and carbon content. The water atomized particles are smaller, cleaner, and nonporous and have a greater breadth of size, which allows better compacting.
What are the hazards of powder metallurgy?
The special materials and processes used in powder metallurgy can pose hazards to life and property. The high surface-area-to-volume ratio of the powders can increase their chemical reactivity in biological exposures (for example, inhalation or ingestion), and increases the risk of dust explosions.
Chapter One - What is Powder Metallurgy?
Powder metallurgy is a manufacturing process that produces precision and highly accurate parts by pressing powdered metals and alloys into a rigid die under extreme pressure.
Chapter Two - The Powder Metallurgy Process
The process of powder metallurgy is an ancient, unique method for forming shapes and designs from ferrous and non-ferrous metals. Powder metallurgy has been used for thousands of years as a way to produce household items and tools. It began as a method for mass producing products and parts in the middle of the first industrial revolution.
Chapter Three - Parts and Products Made Using Powder Metallurgy
After its return in the middle of the first industrial revolution, the use of powder metallurgy has steadily grown to become an essential part of the production of a wide variety of parts and products.
Chapter Four - Types of Metals Used in Powder Metallurgy
There are few limitations to the types of metals that can be used in the powder metallurgy process. Though there is a wide selection available, certain metals are used repeatedly due to their properties and characteristics. There are certain factors producers consider when making their metal selection.
Chapter Five - Equipment Used for Powder Metallurgy
Each step of the powder metallurgy process requires special equipment that varies according to the process being used. Powder metallurgy is a method for producing structural parts and bearings using a variety of techniques and equipment.
Chapter Six - Benefits of Using the Powder Metallurgy Process
To many, the steps of the powder metallurgy process may seem like a waste of time considering there are other methods less time consuming. Though there are negative factors regarding powder metallurgy, its many benefits have made it one of the most popular production methods.
Conclusion
Powder metallurgy is a manufacturing process that produces precision and highly accurate parts by pressing powdered metals and alloys into a rigid die under extreme pressure.