
Competitive trait anxiety (CTA) is a personality disposition which reflects the tendency to experience stress in situations involving competitive sport (20).
What is competitive trait anxiety (CTA)?
Competitive trait anxiety (CTA) is a personality disposition which reflects the tendency to experience stress in situations involving competitive sport (20).
Do you have sports performance anxiety?
Sports performance anxiety, also called sports anxiety or competitive anxiety, is incredibly common. Estimates suggest anywhere from 30 to 60 percent of athletes experience it, according to a 2019 review.
What is trait anxiety in football?
Trait anxiety refers to an innate part of an athlete’s personality characteristic, which represents a predisposition to perceive situations as threatening and respond with an increase in state anxiety. State anxiety is a temporary response to a specific situation, such as when our footballer is taking a penalty.
How can we measure anxiety in sport?
There are three questionnaires we can use to measure anxiety in sport, these include the State Trait Anxiety Inventory (STAI), Competitive State Anxiety Inventory-2 (CSAI-2) and the Sport Competition Anxiety Test (SCAT). The table below provides a brief description of each questionnaire:
What is competitive anxiety in sport?
Competition anxiety is the term for when an athlete experiences anxiety symptoms when faced with what they consider high-stakes competition. In these situations, they might show the physical manifestations of anxiety, such as sweaty palms, shallow breathing, pounding heart, and negative mind chatter.
What is trait and state anxiety in sport?
Trait anxiety is a personality characteristic that remains relatively stable over time, while state anxiety is activated in response to certain situations, such as an athletic Page 5 ANXIETY AND ATHLETIC PERFORMANCE 5 competition.
What is trait anxiety in sport psychology?
Trait anxiety relates to innate characteristics that humans are born with. For example, having a tendency to throw up before important competition. A second form of anxiety is related to the state, which is situational specific. For example, a performer may feel anxious when free-throwing in basketball.
What causes competitive anxiety?
The factors that influence competitive anxiety in athletes include fear of failure in a match, fear of social consequences for the quality of performance, fear of injury or injury of an opponent, physical fear of not being able to complete their duties to compete properly, and demands to change something without ...
What causes trait anxiety in sport?
Uncertainty is a major cause of anxiety, whether in sports or any other aspect of life. The significance of the event also affects anxiety levels. The higher the stakes, the higher your anxiety is likely to rise. Expectations also play a role in how anxious you feel.
How does competitive anxiety affect performance?
When feeling overwhelming fear, the athlete may be unable to move, talk or act at all. Pre-competitive anxiety also develops as an inability to concentrate before an upcoming event or competition. The athlete is unable to concentrate on the task at hand and therefore cannot give their performance full attention.
What is the meaning of trait anxiety?
Definition. Trait anxiety refers to the stable tendency to attend to, experience, and report negative emotions such as fears, worries, and anxiety across many situations. This is part of the personality dimension of neuroticism versus emotional stability.
What is the difference between state and trait anxiety?
State anxiety reflects the psychological and physiological transient reactions directly related to adverse situations in a specific moment. In contrast, the term trait anxiety refers to a trait of personality, describing individual differences related to a tendency to present state anxiety.
What is trait anxiety and how is it related to arousal?
There are two main types of anxiety: Trait anxiety – this is the personality core, State anxiety – this is changeable and varies depending upon the situation. Arousal is referred to as a psychological state of alertness and anticipation that prepares the body for action.
What is an example of trait anxiety?
Competitive Trait Anxiety For example, if a footballer taking a penalty high in CTA is predisposed to view the situation as threatening, then thoughts would direct to the shot, which could lead to a greater somatic (bodily) response, which could result in impaired performance (Weinberg & Gould, 2011).
How do you manage competitive anxiety?
Coping With Pre-Competition NervousnessVisualization.Goal Setting.Relaxation Techniques.Cognitive Restructuring.Develop Self-Confidence.Distract Yourself.Focus on What You Can Control.
How do you overcome sports anxiety?
5 Tips for Overcoming Sports Performance AnxietyIdentify when your student-athlete is feeling anxious. ... Acknowledge and normalize feelings of anxiety. ... Make a game plan. ... Remember to breathe. ... Stay positive.
What is the difference between state and trait anxiety?
State anxiety reflects the psychological and physiological transient reactions directly related to adverse situations in a specific moment. In contrast, the term trait anxiety refers to a trait of personality, describing individual differences related to a tendency to present state anxiety.
What is state anxiety in sport examples?
State anxiety is situation-specific. It is a temporary emotional state in response to a threatening situation. For example, state anxiety can change during a game of football. It might be moderate just before kick-off, lower as the game starts and then high at certain moments, such as when taking a penalty.
What is meant by state anxiety?
State anxiety can be defined as a transitory emotional state consisting of feelings of apprehension, nervousness, and physiological sequelae such as an increased heart rate or respiration (Spielberger 1979). From: International Encyclopedia of the Social & Behavioral Sciences, 2001.
What is the difference between trait and state?
Traits are characteristic patterns of thinking, feeling, and behaving that generalize across similar situations, differ systematically between individuals, and remain rather stable across time. States are characteristic patterns of thinking, feeling, and behaving in a concrete situation at a specific moment in time.
How Can You Manage Anxiety in Sport?
If our athlete is experiencing anxiety that is having a negative impact on their performance, it’s important that we provide them with coping recourses through psychological skills training to help the athlete cope with stressors and be in their optimum zone for performance. These coping recourses include:
What is the stressor of a sport?
The environment or task demands associated with a competition or game can be a stressor for some athletes. According to the Transactional Model of Stress and Coping, if an athlete firstly interprets a stressor as a threat or harmful and secondly that they don’t perceive themselves to have sufficient resources to cope with the stressor, then it results in stress and thus, anxiety.
How to determine the optimal zone for an athlete?
One way to do this, is by measuring the athlete’s anxiety levels (how we can do this will be covered later in this article) and how they performed in a range of conditions. From these measurements, it provides an opportunity for the athlete, coach and/or support team to reflect and have discussions on how the athlete performed in these conditions and the level of anxiety the athlete had (low, moderate or high) when they performed at their best.
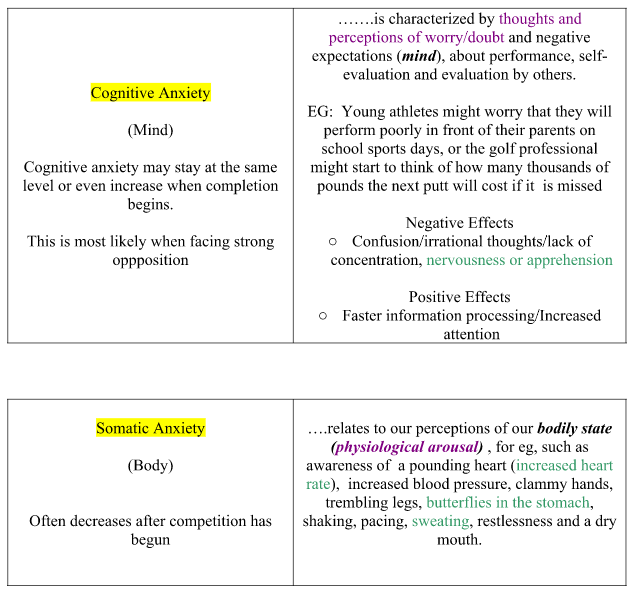
What is anxiety made of?
Anxiety is made up of cognitive and somatic components. It can manifest itself in different ways, this can be through state or trait anxiety. Below we will explore what this means…
What is state anxiety?
State anxiety is a temporary response to a specific situation, such as when our footballer is taking a penalty.
What are the physical symptoms of anxiety?
For example, our footballer taking the penalty may experience an increase in their heart rate, shaking, chest pains, hot flushes or sudden chills, tension in their neck muscles and butterflies in their stomach.
How do we measure anxiety?
The two main ways we can measure anxiety, is through observations and questionnaires. In this next section, I’m going to discuss these methods and their advantages and disadvantages.
Procedure
The athlete answers the 15 questions on the questionnaire below. There is no time limit. The test is good for monitoring the performance anxiety of an athlete, by conducting the rest at regular interval and noting the changes over time.
The SCAT
Read each statement below, decide if you "Rarely", "Sometimes" or "Often" feel this way when competing in your sport, and tick the appropriate box to indicate your response.
Scoring
The SCAT contains 15 items, 10 of which measure symptoms associated with anxiety, with five others that are not scored included to reduce the likelihood of an internal response-set bias. The scores for the 10 items are summed to provide an overall measure, with a high score reflecting a greater tendency to experience competitive anxiety.
Psychology Extra
Try some of these top tips to stay motivated, or these motivational quotes. Psychological assessment also plays an important role in sport psychology.
