
What are some examples of complementary base pairs?
Complementary sequence: Nucleic acid sequence of bases that can form a double- stranded structure by matching base pairs. For example, the complementary sequence to C-A-T-G (where each letter stands for one of the bases in DNA) is G-T-A-C.
Which shows the incorrect complementary base pairing?
Which shows the incorrect complementary base pairing? human proteins. radioactive isotopes. bacterial cell walls. plant proteins. bacterial cell walls. are found in areas outside the nucleus known as orbitals. may gain energy but do not lose energy.
Which nitrogenous bases make up a complementary base pair?
The four nitrogenous bases of DNA are thymine, adenine, guanine, and cytosine. Guanine and cytosine are bonded together by three hydrogen bonds; whereas, adenine and thymine are bonded together by two hydrogen bonds. This is known as complementary base pairing.
What is the significance of the base pairing?
Complementary base pairing is important in DNA as it allows the base pairs to be arranged in the most energetically favourable way; it is essential in forming the helical structure of DNA. It is also important in replication as it allows semiconservative replication.
What are the four nitrogenous bases?
What are some examples of purine bases?
How many nitrogenous bases are there in DNA?
Why can't you swap which purine bonds with which pyrimidine?
Is RNA complementary to DNA?
See 2 more
About this website
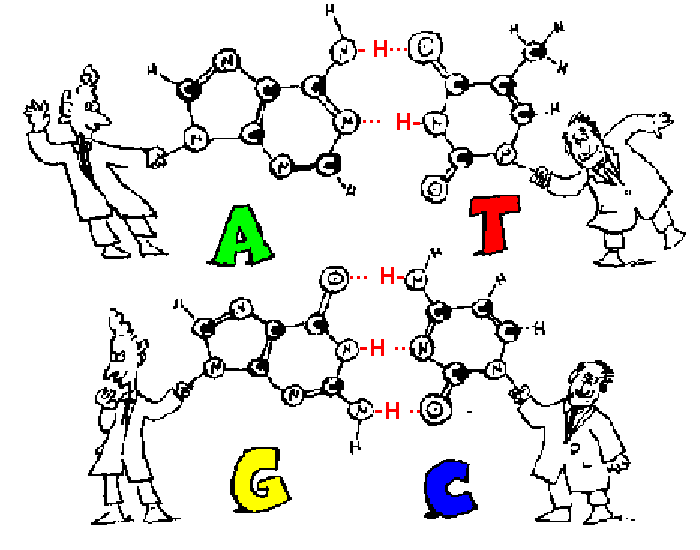
What is a complementary base pair simple definition?
What is a complementary base? A complementary base is either of the two nitrogen-containing sections of a nucleotide that bond together to connect strands of DNA or RNA. DNA and RNA are complex molecules that are central to genetics and both are made of things called nucleotides.
What is complementary base pairing of DNA?
Adenine binds to thymine and guanine binds to cytosine as they are complementary base pairs. The complementary bases can form a bond with each other. This helps to hold the two antiparallel strands of the DNA molecule together to form the helix. This is known as the complementary base pairing rule.
What is complementary base pairing and why is it important?
Complementary base pairing describes the manner in which the nitrogenous bases of the DNA molecules align with each other. Complementary base pairings are also responsible for the double-helix structure of DNA.
What is A complementary strand of DNA example?
Recall that adenine nucleotides pair with thymine nucleotides, and cytosine with guanine. This means that the two strands are complementary to each other. For example, a strand of DNA with a nucleotide sequence of AGTCATGA will have a complementary strand with the sequence TCAGTACT (Figure 9.8).
How is complementary base pairing different in DNA and RNA?
However, the “bases” of RNA differ from those of DNA in that thymine (T) is replaced by uracil (U) in RNA. DNA and RNA bases are also held together by chemical bonds and have specific base pairing rules. In DNA/RNA base pairing, adenine (A) pairs with uracil (U), and cytosine (C) pairs with guanine (G).
Why complementarity between base pairs in a DNA strand is possible?
Complementarity of DNA strands in a double helix make it possible to use one strand as a template to construct the other. This principle plays an important role in DNA replication, setting the foundation of heredity by explaining how genetic information can be passed down to the next generation.
What does complementary mean in biology?
In molecular biology, complementarity is a property of double-stranded nucleic acids such as DNA and RNA as well as DNA:RNA duplexes. Each strand is complementary to the other in that the base pairs between them are non-covalently connected via two or three hydrogen bonds.
What is base pairing in biology?
Listen to pronunciation. (bays payr) Two nitrogen-containing bases (or nucleotides) that pair together to form the structure of DNA. The four bases in DNA are adenine (A), cytosine (C), guanine (G), and thymine (T).
Why are DNA bases complementary?
3:144:03DNA: Complementary Base Pairing - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipIt allows something called complementary base pairing. You see cytosine can form three hydrogenMoreIt allows something called complementary base pairing. You see cytosine can form three hydrogen bonds with guanine. And adenine can form two hydrogen bonds with thymine. Or more simply c bonds with g.
What is complementary nature of DNA?
In nature complementarity is the base principle of DNA replication and transcription as it is a property shared between two DNA or RNA sequences, such that when they are aligned antiparallel to each other, the nucleotide bases at each position in the sequences will be complementary, much like looking in the mirror and ...
How do you find complementary base pairs?
Chargaff's rule, also known as the complementary base pairing rule, states that DNA base pairs are always adenine with thymine (A-T) and cytosine with guanine (C-G). A purine always pairs with a pyrimidine and vice versa. However, A doesn't pair with C, despite that being a purine and a pyrimidine.
How do you find the complementary base sequence of DNA?
You can determine the sequence of a complementary strand if you are given the sequence of the template strand. These two strands are complementary, with each base in one sticking to its partner on the other. The A-T pairs are connected by two hydrogen bonds, while the G-C pairs are connected by three hydrogen bonds.
What is the complementary base pairing rule for DNA?
Complementary base pairs refer to the nitrogenous bases adenine, thymine, cytosine, and guanine. in a double strand of DNA, adenine will always pai...
What is a base pair in genetics?
A base pair in genetics refers to complementary nitrogenous bases that are paired in a double strand of DNA. Here, adenine is with thymine and cyto...
How are complementary bases in DNA held together?
DNA complementary bases are held together by hydrogen bonds. An attraction exists between the hydrogen molecules in the complementary bases.
Why is complementary base pairing important for DNA replication?
DNA replication is a necessary step in the cell cycle. In order for cells to divide, they must have a complete set of chromosomes for each cell. Re...
What is an example of complementary base pair?
An example of a base pair found in a double helix of DNA would be adenine bonding with thymine. Another example is cytosine bonding with guanine.
Complementary Base Pairing | Rule & Examples - Video & Lesson ...
This lesson will explain nitrogenous bases, types of bases, and complementary base pairs in both DNA and RNA. It will also cover the rules of base pairing and provide examples.
Complementary Base Pairing: Definition & Explanation
Complementary Base Pairing in the DNA Molecule. While working on the structure of DNA, Watson and Crick not only figured out that the two polynucleotides in the DNA (i.e., the DNA strands ...
DNA complementary base pairing | Discovering the Genome
Credit: Madeleine Price Ball Remember that nucleotides of the DNA have the property of base pairing, where the letter A (Adenine) forms a hydrogen bond with the letter T (Thymine) and the letter C (Cytocine) forms a hydrogen bond with the letter G (Guanine).Let’s use an example of a string of DNA like this:. 5′-ACGT-3′ The DNA string shown above will form hydrogen bonds with a ...
DNA and RNA Base Pairing Rules - Peekskill City School District
DNA and RNA Base Pairing Rules DNA to DNA • Possible Bases: Adenine, Thymine, Cytosine, Guanine • G↔C, A↔T • A and G are purines (double‐ring), C and T are pyrimidines (single‐ring)
What is complementary strand of DNA of the following single strand DNA ...
3'T-A-G-T-A-C-G-5' DNA is a double helix structure made of phosphate, sugar and 4 nitrogen bases. Your 4 bases are guanine (G), cytosine (C), adenine (A) and thymine (T). Now, your nitrogen bases actually come in pairs so remember your pairs as GC and AT which means that guanine pairs with cytosine and cytosine pairs with guanine and similarly with adenine and thymine.
What is Complementary Base Pairing
Complementary base pairing refers to the match-up of specific nitrogenous bases in the strands of genetic material. There are certain rules that must be followed when connecting two strands of genetic material into the double helix configuration of DNA.
Complementary Base Pairing in DNA: Rules
The double helix structure of DNA was first hinted at by a scientist named Rosalind Franklin. She used x-rays to create images that suggested that DNA formed the double-stranded, twisted structure that James Watson and Francis Crick later determined to be true.
What is complementary base pairing?
Complementary base pairing describes the manner in which the nitrogenous bases of the DNA molecules align with each other. Complementary base pairings are also responsible for the double-helix structure of DNA. If you imagine yourself looking at a closet with four pairs of shoes that are all mixed up, complementary base pairing would be the set ...
How do bases interact in DNA?
How is it that the bases interact in the DNA to form its characteristic double helix structure? Well, the bases are interacting through hydrogen bonds, which are a form of weak chemical interaction taking place between hydrogen and an atom of negative charge, or polarity. Examining the base pairs in DNA, researchers figured out that there are three hydrogen bonds between C and G and only two between A and T. This difference is due to the actual shape and composition of each of the nucleotides but has consequences in the stability of the DNA. Because the interactions between C and G are stronger, a DNA molecule with a high proportion of CG over AT will tend to be more stable than one of the opposite composition. In fact, researchers can look at a DNA sequence and predict how easy or hard it would be to separate the two strands using this property.
How do DNA strands attach to each other?
If we go back to our zipper analogy, the two strands in DNA attach to each other through the nitrogenous bases in a similar manner to which the two strips of fabric in the zipper interlock to each other through the small metal pieces.
What is the phenomenon where the nitrogen-based molecules in DNA tend to align with one another?
The phenomenon where the nitrogen-based molecules in DNA tend to align with one another is referred to as complementary base pairing. Learn about the structure and composition of the DNA molecule, the Chargaff Rule on the structure of DNA, and how complementary base pairing occurs. Updated: 08/25/2021
Why is CG more stable than AT?
Because the interactions between C and G are stronger, a DNA molecule with a high proportion of CG over AT will tend to be more stable than one of the opposite composition. In fact, researchers can look at a DNA sequence and predict how easy or hard it would be to separate the two strands using this property.
What is the Chargaff Parity Rule?
This rule, %A = %T and %G = %C, is known as Chargaff Parity Rule 1 and played a key role in Watson's ...
Can you remember which base associates with which?
You can remember which base associates with which by using the mnemonic GCAT. One of the cool consequences of complementary base pairing is that, if we know the nucleotides that are present in one DNA strand, we actually already know the nucleotides present in both strands. Try it!
What is complementary base pairing?
Complementary base pairing is a phenomenon in which nitrogenous bases of the nucleotides get paired with the bases that are complementary to them. Adenine pairs with thymine, and guanine pairs with cytosine in DNA. So, adenine is complementary to thymine, and guanine is complementary to cytosine.
What pairs with cytosine?
Pairing between nitrogenous bases follows Chargaff’s rule. This rule states that in DNA, adenine always pairs with thymine, and guanine pairs with cytosine. Adenine never pairs with cytosine even though this is also a pairing between purine and pyrimidine.
What are the two types of nitrogenous bases?
Nitrogenous bases are of two types, purine, and pyrimidine. Adenine and guanine are purine bases. Thymine and cytosine are pyrimidine bases. A purine always pairs with pyrimidine and vice versa. But no bond forms between purine-purine and pyrimidine-pyrimidine in DNA. There are two hydrogen bonds between A-T and three hydrogen bonds between G-C.
Answer
A complimentary base pairing is how adenine can only bond with thymine and how guanine and cytosine through hydrogen bonding. It is necessary to maintain the double helix shape. Because it is opposite, that is why the DNA is that shape. It is anti parallel due to the Complementary base pairing.
New questions in Biology
Circulatory System1. Describe how blood flows through the heart. - 2, What controls heartbeat? - 3. How do arteries differ from veins? - 4. What is bl …
What are the four nitrogenous bases?
In DNA, there are four nitrogenous base options: adenine (A), thymine (T), cytosine (C) and guanine (G). Each base can only bond with one other, A with T and C with G. This is called the complementary base pairing rule or Chargaff's rule.
What are some examples of purine bases?
Adenine and guanine are examples of purine bases. This means their structure is a nitrogen-containing six atom ring joined with a nitrogen-containing five atom ring that share two atoms to combine the two rings. Thymine and cytosine are examples of pyrimidine bases.
How many nitrogenous bases are there in DNA?
The Four Nitrogenous Bases. In DNA nucleotide subunits, there are four nitrogenous bases: Adenine (A) Thymine (T) Cytosine (C) Guanine (G) Each of these bases can be divided into two categories: purine bases and pyrimidine bases. Adenine and guanine are examples of purine bases. This means their structure is a nitrogen-containing six atom ring ...
Why can't you swap which purine bonds with which pyrimidine?
But why can't you swap which purine bonds with which pyrimidine? The answer has to do with hydrogen bonding that connects the bases and stabilizes the DNA molecule.
Is RNA complementary to DNA?
RNA strands are also complementary with the exception that RNA uses uracil instead of thy mine. So, you can also infer the mRNA strand that would be produced from that first DNA strand. It would be:

Composition of The DNA Molecule
Structure of The DNA Molecule
- When people first realized that DNA contained all of our genetic information, they became very interested in understanding how it was organized and structured. While it was known that the DNA molecule contained two polynucleotide molecules, no one knew how they were organized together. Some people believed that they interacted through the phosphate part of the nucleotid…
Chargaff Rule 1: More Insight Into The Structure of DNA
- While Watson and Crick worked on the problem of the structure of the DNA molecule, Erwin Chargaff, an Austrian biochemist who emigrated to the U.S. during the Nazi era, was studying the actual composition of DNA. It was known that DNA consisted of A, G, T, C, but what Chargaff found was that the proportion of each of these bases in DNA was not random. In fact, across dif…