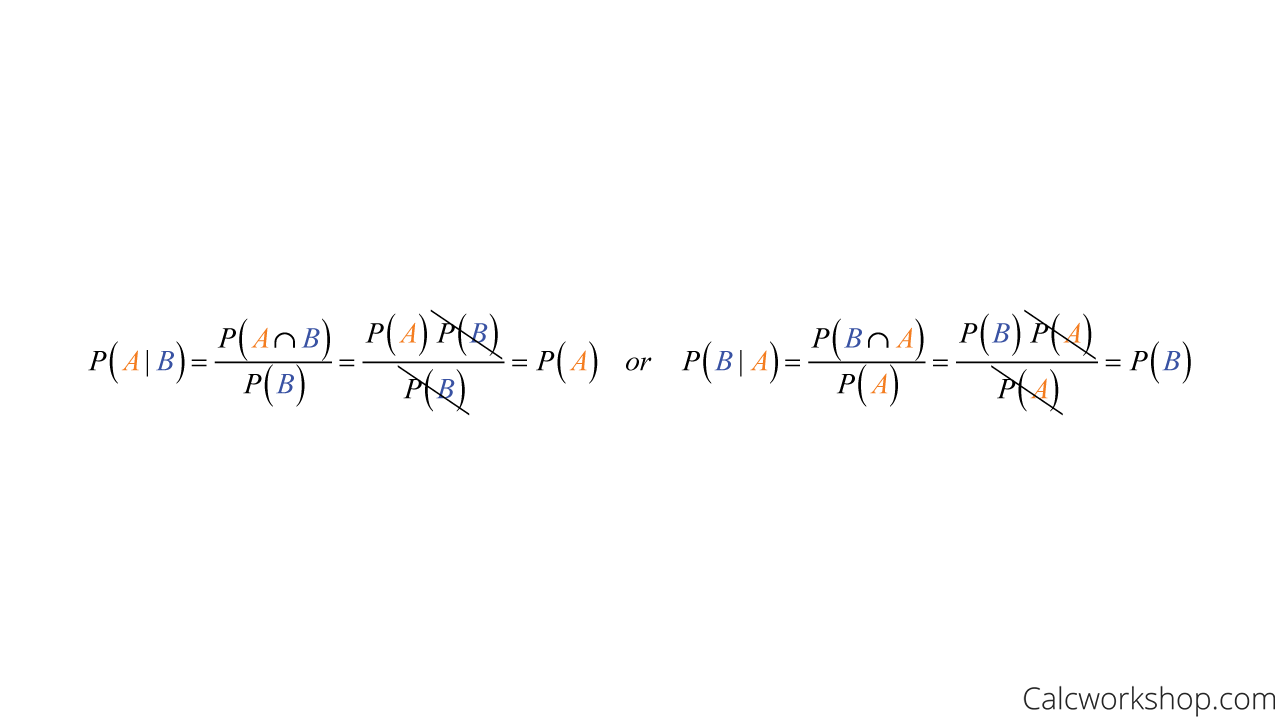
The conditional probability, as its name suggests, is the probability of happening an event that is based upon a condition. For example, assume that the probability of a boy playing tennis in the evening is 95% (0.95) whereas the probability that he plays given that it is a rainy day is less which is 10% (0.1).
How do you calculate conditional probability?
Where:
- P in the formula represents the probability.
- Variables A and B are the events where the formula measures the probability of event B occurring, given that event A occurs first.
- The expression P (B|A) in the formula denotes the conditional probability statement "the probability of event B given the probability of event A."
How to compute conditional probability?
The formula for conditional probability can be represented as P(A|B) = P(A ∩ B) / P(A) This is valid only when P(A)≠ 0 i.e. when event A is not an impossible event.
What are some real life examples of probability?
What are some real life examples of probability? Some examples of probability include: There is a 20 percent chance of rain tomorrow. Based on how poorly the interview went, it is unlikely I will get the job. Since it is 90 degrees outside, it is impossible it will snow. After flipping this coin 10 times and having it land on heads 8 times, the probability of landing on heads is still 50 percent.
What are the basic rules of probability?
- Probability Rule One (For any event A, 0 ≤ P (A) ≤ 1)
- Probability Rule Two (The sum of the probabilities of all possible outcomes is 1)
- Probability Rule Three (The Complement Rule)
- Probabilities Involving Multiple Events
- Probability Rule Four (Addition Rule for Disjoint Events)
- Finding P (A and B) using Logic

What is conditional probability real life examples?
Conditional probability could describe an event like: Event A is that it is raining outside, and it has a 0.3 (30%) chance of raining today. Event B is that you will need to go outside, and that has a probability of 0.5 (50%).
What is meant by conditional probability?
The probability of occurrence of any event A when another event B in relation to A has already occurred is known as conditional probability.
What is the formula for conditional probability?
If A and B are two events in a sample space S, then the conditional probability of A given B is defined as P(A|B)=P(A∩B)P(B), when P(B)>0.
What is a conditional probability question?
Conditional probability formula gives the measure of the probability of an event given that another event has occurred. If the event of interest is A and the event B is known or assumed to have occurred, “the conditional probability of A given B”, or “the probability of A under the condition B”.
What is conditional probability PDF?
Conditional Probability. Definition. The conditional probability of an event given another is the probability of the event given that the other event has occurred. If P(B) > 0, P(A|B) = P(A and B) P(B) With more formal notation, P(A|B) = P(A ∩ B) P(B) , if P(B) > 0.
Why is conditional probability important in statistics?
A conditional probability is the likelihood of an event occurring given that another event has already happened. Conditional probabilities allow you to evaluate how prior information affects probabilities.
What are the properties of conditional probability?
Conditional Probability Properties Property 1: Let E and F be events of a sample space S of an experiment, then we have P(S|F) = P(F|F) = 1. Property 2: f A and B are any two events of a sample space S and F is an event of S such that P(F) ≠ 0, then P((A ∪ B)|F) = P(A|F) + P(B|F) – P((A ∩ B)|F).
How do you solve conditional probability problems?
The formula for the Conditional Probability of an event can be derived from Multiplication Rule 2 as follows:Start with Multiplication Rule 2.Divide both sides of equation by P(A).Cancel P(A)s on right-hand side of equation.Commute the equation.We have derived the formula for conditional probability.
What is conditional probability and Bayes Theorem?
Conditional probability is the likelihood of an outcome occurring, based on a previous outcome having occurred in similar circumstances. Bayes' theorem provides a way to revise existing predictions or theories (update probabilities) given new or additional evidence.
What is conditional probability PPT?
With our new notation for conditional probabilities, we can now formalize this definition: Events A and B are independent whenever P(B|A) = P(B). ( Equivalently, events A and B are independent whenever P(A|B) = P(A).)
What is conditional probability Mcq?
In probability theory, the probability measure of an event is made if another event has already occurred is referred to as conditional probability.
How do you calculate probability with examples?
Using the example of the rolling dice, you'd calculate your total probability by multiplying the 1/6 chances you calculated: P(A and B) = 1/6 x 1/6 = 1/36. Using these results, there's a 1/36 chance of rolling "6" on one die at the same time you roll a "6" with the other.
What is conditional probability?
Probability is a branch of Mathematics which deals with the study of occurrence of an event. There are several approaches to understand the concept of probability which include empirical, classical and theoretical approaches. The conditional probability of an event is when the probability of one event depends on the probability of occurrence ...
When does conditional probability come into existence?
The conditional probability of an event is when the probability of one event depends on the probability of occurrence of the other event. When two events are mutually dependent or when an event is dependent on another independent event, the concept of conditional probability comes into existence.
What is conditional probability of occurrence of two events?
Conditional probability of occurrence of two events A and B is defined as the probability of occurrence of event ‘A’ when event B has already occurred and event B is in relation with event A.
How to find the probability that an event does not occur?
So, the probability that the event does not occur can be found by subtracting the probability of occurrence of an event from 1. 2.
How to calculate probability?
The branch of Mathematics which deals with the computation of likelihood of an event being true is called the probability. There are a few important facts that should be known before solving any problem related to probability. They are: 1 The probability of an event ranges from 0 to 1, 0 being the lowest range and 1 being the highest range. 2 If the probability of an event is zero, then it is called an impossible event. 3 If the probability of an event is one, then it is called a sure or a certain event. 4 The sum of the probabilities of occurrence and nonoccurrence of an event is equal to unity. So, the probability that the event does not occur can be found by subtracting the probability of occurrence of an event from 1.
What is the probability of occurrence of an event when the other event has already occurred?
If the probability of occurrence of an event when the other event has already occurred is equal to 1, then both the events are identical.
Which branch of mathematics deals with the computation of likelihood of an event being true?
The branch of Mathematics which deals with the computation of likelihood of an event being true is called the probability. There are a few important facts that should be known before solving any problem related to probability. They are:
What is conditional probability?
Conditional Probability for Mutually Exclusive Events. In probability theory, mutually exclusive events. Mutually Exclusive Events In statistics and probability theory, two events are mutually exclusive if they cannot occur at the same time. The simplest example of mutually exclusive. are events that cannot occur simultaneously.
What is conditional probability of two independent events?
Two events are independent if the probability of the outcome of one event does not influence the probability of the outcome of another event. Due to this reason, the conditional probability of two independent events A and B is:
What is the total probability rule?
Total Probability Rule The Total Probability Rule (also known as the law of total probability) is a fundamental rule in statistics relating to conditional and marginal. . Note that conditional probability does not state that there is always a causal relationship between the two events, as well as it does not indicate that both events occur ...
What does P mean in probability?
P (A|B) – the conditional probability; the probability of event A occurring given that event B has already occurred
What is Bayes' rule?
Bayes' Theorem In statistics and probability theory, the Bayes theorem (also known as the Bayes’ rule) is a mathematical formula used to determine the conditional. , which is one of the most influential theories in statistics.
Example 1: Weather Forecasting
One of the most common real life examples of using conditional probability is weather forecasting.
Example 2: Sports Betting
Conditional probability is frequently used by sports betting companies to determine the odds they should set for certain teams to win certain games.
Example 3: Sales Forecasting
Retail companies use conditional probability to predict the chances that they’ll sell out of a certain product based on product promotions.
Example 4: Traffic
Traffic engineers use conditional probability to predict the likelihood of traffic jams based on stop light failures.
Additional Resources
The following tutorials provide additional information about probability:
What Is Conditional Probability?
Conditional probability is defined as the likelihood of an event or outcome occurring, based on the occurrence of a previous event or outcome. Conditional probability is calculated by multiplying the probability of the preceding event by the updated probability of the succeeding, or conditional, event.
What is prior probability?
Prior probability is the probability of an event occurring before any data has been gathered to determine the probability. It is the probability as determined by a prior belief. Prior probability is a component of Bayesian statistical inference.
What is the probability of drawing a blue marble?
First, the probability of drawing a blue marble is about 33% because it is one possible outcome out of three. Assuming this first event occurs, there will be two marbles remaining, with each having a 50% chance of being drawn. So the chance of drawing a blue marble after already drawing a red marble would be about 16.5% (33% x 50%). ...
How many equally likely outcomes are there in a fair die?
There are six equally likely outcomes, so your answer is 1/6.
What is Bayes' theorem?
Bayes' theorem is also called Bayes' Rule or Bayes' Law and is the foundation of the field of Bayesian statistics. This set of rules of probability allows one to update their predictions of events occurring based on new information that has been received, making for better and more dynamic estimates.
What is conditional probability?
The probability of occurrence of any event A when another event B in relation to A has already occurred is known as conditional probability. It is depicted by P (A|B).
What is the common portion of the probability of occurrence of events?
Common portion of the events is depicted by the intersection of both the events A and B i.e. A ∩ B.
What is the property of a sample space?
Property 1: Let E and F be events of a sample space S of an experiment, then we have P (S|F) = P (F|F) = 1.
What is conditional probability?
Then, the probability of A's occurrence under the condition that B has already occurred and P (B) ≠ 0 is called the Conditional Probability. It is denoted by P (A/B). Thus, you have
What is the probability of happening in a random experiment?
If there are n elementary events associated with a random experiment and m of them are favorable to an event A, then the probability of happening or occurrence of A is denoted by P (A) and is defined as the ratio mn.
What is it called when an experiment is repeated under identical conditions?
If an experiment, when repeated under identical conditions, does not produce the same outcome every time but the outcome in a trial is one of the several possible outcomes, then such an experiment is called a random experiment or a probabilistic experiment.
What does P mean in math?
P (A/B) = Probability of occurrence of A given that B has already occurred.
How many elementary events are associated with a given random experiment?
You will observe that there are two elementary events, H,T associated with a given random experiment. Out of these two events, only one is favorable i.e. H.
What Is Conditional Probability?
Essentially, conditional probability is the likelihood of an event occurring, assuming a different one has already happened. Otherwise said, there must be some sort of relationship with the past. Moreover, its formula, which we will expand on in this tutorial, is based on the Bayes’ Theorem.
What Are Independent and Dependent Events?
There are two types of events that can influence conditional probability:
The Conditional Probability Formula
By definition, the conditional probability equals the probability of the intersection of events A and B over the probability of event B occurring:
Conditional Probability in Real Life: An Example
Many scientific papers rely on conducting experiments or surveys. They often provide summarized statistics we use to analyze and interpret how certain factors affect one another.
The Law of Total Probability
Now that you understand the distinctions between the different conditional probabilities of two events, we can introduce an important concept – the law of total probability.
Conditional Probability: Next Steps
As you can see, there are many benefits to learning how to apply probability in order to solve real-life problems. In fact, the theory is used in branches such as finance, business analytics, healthcare, and many more. In other words, it is indeed an essential skill for everyone looking to work with data.
What is conditional probability?
A conditional probability is the likelihood of an event occurring given that another event has already happened. Conditional probabilities allow you to evaluate how prior information affects probabilities. When you incorporate existing facts into the calculations, it can change the probability of an outcome.
What does P mean in probability?
P (A|B) denotes the conditional probability of event A occurring given that event B has occurred.
What is the numerator of a probability formula?
The numerator of the formula is the joint probability that A and B occur together. We need the joint probability in the numerator because we’re interested in the subset of cases where both events happen.
What is the probability of getting a 6 on a roll?
Because these are independent events, we can use the multiplication rule to calculate the joint probability of P (6 2 ⋂ P 1 ). Each roll has a 1/6 = 0.167 chance of getting a six.
Why are joint probabilities misleading?
The joint probabilities were misleading because they do not account for the fact that days with no rain are three times as likely as rainy days (0.75 vs. 0.25)! In this study, you’re more likely to see people carrying umbrellas when there’s no rain because there are many more days with no rain. The conditional probabilities consider that fact.
What is the probability of someone owning a cat given the presence of an open box on their floor?
This notation indicates that the probability of someone owning a cat given the presence of an open box on their floor is 0.8.
Does probability of B have an effect on the probability of A?
The probability of A given that B occurred equals the probability of A. In other words, whether B occurs or not has no effect on the likelihood of A. That makes sense because the events are independent! There’s also a mathematical proof for it, which I won’t cover.
What is the chance of winning a coin?
The chance is simply 1-in-2, or 50%, just like ANY toss of the coin.
What is the probability of Alex getting Sam?
The probability of getting Sam is 0.6, so the probability of Alex must be 0.4 (together the probability is 1) Now, if you get Sam, there is 0.5 probability of being Goalie (and 0.5 of not being Goalie): If you get Alex, there is 0.3 probability of being Goalie (and 0.7 not):

What Is Conditional Probability?
Understanding Conditional Probability
- Conditional probabilities are contingent on a previous result or event occurring. A conditional probability would look at such events in relationship with one another. Conditional probability is thus the likelihood of an event or outcome occurring based onthe occurrence of some other event or prior outcome. Two events are said to be independent if one event occurring does not affect t…
Examples of Conditional Probability
- As an example, suppose you are drawing three marbles—red, blue, and green—from a bag. Each marble has an equal chance of being drawn. What is the conditional probability of drawing the red marble after already drawing the blue one? First, the probability of drawing a blue marble is about 33% because it is one possible outcome out of three. Assuming...
Conditional Probability vs. Joint Probability and Marginal Probability
- Conditional probability: p(A|B) is the probability of event A occurring, given thatevent B occurs. For example, given that you drew a red card, what’s the probability that it’s a four (p(four|red))...
- Marginal probability: the probability of an event occurring (p(A)) in isolation. It may be thought of as an unconditional probability. It is not conditioned on another event. Example: the proba…
- Conditional probability: p(A|B) is the probability of event A occurring, given thatevent B occurs. For example, given that you drew a red card, what’s the probability that it’s a four (p(four|red))...
- Marginal probability: the probability of an event occurring (p(A)) in isolation. It may be thought of as an unconditional probability. It is not conditioned on another event. Example: the probabili...
- Joint probability: p(A ∩B). Joint probability is that of event A andevent B occurring. It is the probability of the intersection of two or more events. The probability of the intersection of A and...
Bayes' Theorem and Conditional Probability
- Bayes' theorem, named after 18th-century British mathematician Thomas Bayes, is a mathematical formula for determining conditional probability.1 The theorem provides a way to revise existing predictions or theories (update probabilities) given new or additional evidence. In finance, Bayes' theorem can be used to rate the riskof lending money to potential borrowers. Ba…
The Bottom Line
- Conditional probability examines the likelihood of an event occurring based on the likelihood of a preceding event occurring. The second event is dependent on the first event. It is calculated by multiplying the probability of the first event by the probability of the second event.