
Conditioned Stimulus Examples
- 1. The Recess Bell Stimulus: The recess bell Response: Students can leave class Every child sits in class just waiting. ...
- 2. Rote Learning Math Stimulus: 2×2 Response: 4 A conditioned stimulus can also be a simple answer to a math quiz. ...
- 3. The Bicycle Bell Stimulus: Bicycle bell Response: Jump out of the way ...
- 4. Learned Phobias
What are some examples of unconditioned stimuli?
Unconditioned stimulus examples
- Touching a hot iron Touching a hot iron makes you withdraw your hand right away. The hot iron is the UCS.
- Eating Putting food into your mouth causes your mouth to water. The food is the UCS.
- Hurting your foot Dropping a rock on your foot makes you scream in pain. The rock is the UCS.
- Inhaling dust Dust entering your nose causes you to sneeze. ...
What is an example of a conditioned emotional response?
Which experience is an example of a conditioned emotional response? For example, the smell of food is an unconditioned stimulus, a feeling of hunger in response to the smell is an unconditioned response, and the sound of a whistle when you smell the food is the conditioned stimulus.
What is a conditional stimuli?
Simply put, a conditioned stimulus makes an organism react to something because it is associated with something else. Conditioned stimuli begin as neutral stimuli that do not illicit a response until conditioning has occurred via repeated stimulation.
What are three examples of stimulus and response?
What are three examples of stimulus and response?
- Stimulus = strike of patellar ligament with reflex hammer; response = knee jerk, that is, lower leg extends.
- Stimulus = touch a pill bug; response = pill bug rolls into a ball.
- Stimulus = dog sees food; response = dog sits.
- Stimulus = dog sees mailman; response = dog barks.
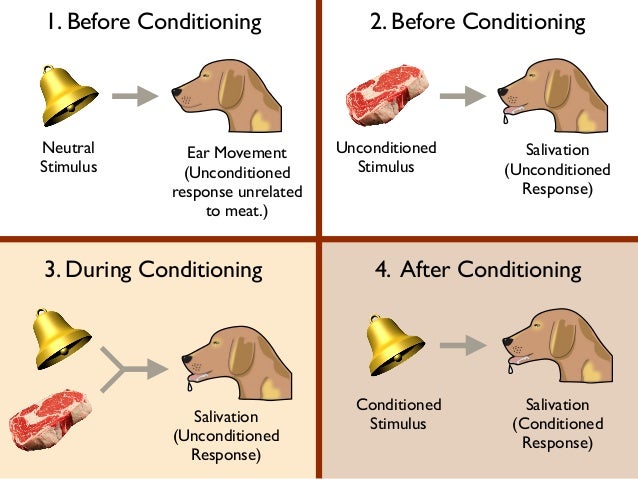
What is a conditioned stimulus simple definition?
In classical conditioning, the conditioned stimulus is a previously neutral stimulus that, after becoming associated with the unconditioned stimulus, eventually comes to trigger a conditioned response.
What is a conditioned stimulus response?
A conditioned stimulus is a stimulus that can eventually trigger a conditioned response. In the described experiment, the conditioned stimulus was the ringing of the bell, and the conditioned response was salivation. It is important to note that the neutral stimulus becomes the conditioned stimulus.
What is conditioned stimulus and unconditioned stimulus?
Conditioned Stimulus. An unconditioned stimulus causes a response without any prior learning on the part of the subject. The response is automatic and occurs without thought. In contrast, a conditioned stimulus produces a reaction only after the subject has learned to associate it with a given outcome.
What is conditioning give an example?
For example, whenever you come home wearing a baseball cap, you take your child to the park to play. So, whenever your child sees you come home with a baseball cap, he is excited because he has associated your baseball cap with a trip to the park. This learning by association is classical conditioning.
How do you identify a conditioned stimulus?
In classical conditioning, a conditioned response is a learned response to a previously neutral stimulus. For example, the smell of food is an unconditioned stimulus, a feeling of hunger in response to the smell is an unconditioned response, and the sound of a whistle when you smell the food is a conditioned stimulus.
Why is it called conditioned stimulus?
A conditioned stimulus is a neutral cue or event that produces an involuntary response after repeatedly being paired with an unconditioned stimulus that naturally elicits that behavior. This term originated in a learning process called classical conditioning.
Is pain an unconditioned stimulus?
Pain is not an unconditioned stimulus, it is a negative reinforcement. It is used in operant conditioning to deter someone from engaging in a behavior.
Why is food an unconditioned stimulus?
In Pavlov's classic experiment, the food represents what is known as the unconditioned stimulus (UCS). The UCS naturally and automatically triggers a response. 1 Pavlov's dogs salivating in response to the food is an example of the unconditioned response.
What's an unconditioned stimulus?
a stimulus that elicits an unconditioned response, as in withdrawal from a hot radiator, contraction of the pupil on exposure to light, or salivation when food is in the mouth. Also called unconditional stimulus.
What are the three types of conditioning?
Three Major Types of Learning Learning through association - Classical Conditioning. Learning through consequences – Operant Conditioning. Learning through observation – Modeling/Observational Learning.
What are the 2 main types of conditioning?
Classical conditioning involves associating an involuntary response and a stimulus, while operant conditioning is about associating a voluntary behavior and a consequence.
What are some examples of classical conditioning in everyday life?
10 Classical Conditioning Examples in Everyday LifeSmartphone Tones and Vibes. ... Celebrities in Advertising. ... Restaurant Aromas. ... Fear of Dogs. ... A Good Report Card. ... Experiences in Food Poisoning. ... Excited for Recess. ... Exam Anxiety.More items...
What is conditioned stimulus quizlet?
Conditioned stimulus. A stimulus that causes a response that is learned. Conditioned response. A learned response to a stimulus that was previously neutral. Extinction.
What are the 5 major conditioning responses?
Classical conditioning: Extinction, spontaneous recovery, generalization, discrimination.
What is conditioned and unconditioned response?
The unconditioned response is innate and requires no prior learning. The conditioned response will occur only after an association has been made between the UCS and the CS. The conditioned response is a learned response.
What do you mean by a conditioned stimulus?
A conditioned stimulus is a thing or sound that starts out without an associated response, but then is conditioned to have a specific response base...
Is money a conditioned stimulus?
It can be, almost anything can be a conditioned stimulus. Since most conditioned stimuli don't have a typical or natural response but are taught to...
Can a person be a conditioned stimulus?
Yes, a person can be a conditioned stimulus if the response to the person is not a natural or usual response. For example, a child may react to a p...
What's the difference between unconditioned stimulus and conditioned stimulus?
An unconditioned stimulus is different from a conditioned stimulus because it has a naturally occurring response that is like a reflex or automatic...
How does a conditioned stimulus work?
A conditioned stimulus starts as a neutral stimulus, meaning it does not elicit a response or at least not the desired response. Once the desired r...
What is an example of conditioning?
Pavlov's dogs drooling at the sound of a bell rather than the presentation of food is an example of conditioning.
What is a Conditioned Stimulus?
The dumbbell is the conditioned stimulus. Conditioned stimulus is when a neutral object, action, or person is connected to a specific response over time. The dumbbell has no meaning alone but over time of using it to work out, your brain has formed a conditioned stimulus for exercise when you see it. There are also unconditioned stimuli. Unconditional stimuli have a natural response paired with them. A loud crash that makes someone jump or pull away from something that is hot are both examples of unconditional stimuli. The jump is a natural response to the sound, humans are born to respond to loud noise. Humans are also born to instinctively avoid or pull away when something is hot and could harm them.
How is an unconditioned stimulus different from a conditioned stimulus?
An unconditioned stimulus is different from a conditioned stimulus because it has a naturally occurring response that is like a reflex or automatic response that does not have to be taught . A conditioned stimulus starts out without any natural response , it is neutral, then the subject is trained to respond with a conditioned response.
What is classical conditioning?
Classical conditioning allows for attaching a specific, desired response to a conditioned stimulus that started out neutral.
Can conditioning happen unintentionally?
Conditioning can happen intentionally like with Pavlov's and Watson's experiments. Conditioning can also happen unintentionally when two unrelated things get accidentally connected like the restaurant example or the car accident example. Classical Conditioning was the starting point for most behavioral psychology. Later as new theories were developed, they built off the base of classical conditioning and the distinction of unconditional and conditional stimuli and responses.
Can a person be a conditioned stimulus?
Yes, a person can be a conditioned stimulus if the response to the person is not a natural or usual response. For example, a child may react to a person coming into a room which would be a natural response, however, they may get excited when their grandparents come in because they know that they will be getting a treat. The specific grandparents are the conditioned stimuli.
How Does Conditioned Stimulus Work?
Ivan Pavlov first discovered the process of classical conditioning in his experiments on the digestive response of dogs. He noticed that the dogs naturally salivated in response to food, but that the animals also began to drool whenever they saw the white coat of the lab assistant who delivered the food.
How can a neutral stimulus become a conditioned stimulus?
There are plenty of examples of how neutral stimuli can become a conditioned stimulus through association with an unconditioned stimulus. Let's explore a few more examples. Bad burrito: You eat a burrito for lunch but become ill shortly after. While the food you ate was previously a neutral stimulus, it becomes a conditioned stimulus ...
What stimulus would a dog salivate to?
The dogs in his experiment would salivate in response to food, but after repeatedly pairing the presentation of food with the sound of a bell, the dogs would begin to salivate to the sound alone. In this example, the sound of the bell was the conditioned stimulus. There are plenty of examples of how neutral stimuli can become a conditioned stimulus ...
What happens after a neutral stimulus is associated with an unconditioned stimulus?
After the neutral stimulus had become associated with the unconditioned stimulus, it became a conditioned stimulus capable of triggering the conditioned response all on its own.
Why is the bell a stimulus?
Because the bell has become associated with the sight of customers needing assistance, the bell has become a conditioned stimulus. Lunch bell: Students hear the sound of a bell right before they are released for lunch. Eventually, just the sound of the bell alone causes the students to become hungry.
Who discovered classical conditioning?
Ivan Pavlov first discovered the process of classical conditioning in his experiments on the digestive response of dogs. He noticed that the dogs naturally salivated in response to food, but that the animals also began to drool whenever they saw the white coat of the lab assistant who delivered the food.
Is the sound of a whistle a stimulus?
In this case, the sound of the whistle is the conditioned stimulus.
What are some examples of conditioned stimulus?
One of the most widely known examples of a conditioned stimulus is the research conducted by Russian physiologist Ivan P. Pavlov. His research in classical conditioning was notable for demonstrating how to create associations between the occurrence of one event and the anticipation of another. Source: rawpixel.com.
What is the difference between conditioned and unconditioned stimulus?
The main difference between a conditioned stimulus and an unconditioned one is that the former is a product of learned behavior. Unconditioned stimulus refers to any stimulus that naturally and automatically triggers a specific response in humans or organisms.
What stimulus did dogs salivate when the door opened?
The door opening was a neutral event, but the dogs began to associate the opening door with being fed. Thus, a conditioned stimulus was created when the door opened, and dogs began to salivate. Pavlov continued to test his theory using different conditioned stimuli including bells, metronomes, and even electrical shocks.
How does a neutral stimulus become a conditioned stimulus?
This period is called the acquisition phase. During this time, humans or animals learn to connect the neutral stimulus with the unconditioned response. These repeated connections transform the neutral stimulus into a conditioned stimulus.
What is conditioning in psychology?
What is conditioning? This refers to when some type of reinforcement results in people altering their behavioral processes such that a response becomes more frequent or predictable. This form of learning usually involves one of two parameters: 1 A given stimulus or signal becomes more effective in creating a response. 2 A response occurs with more regularity in a well-specified, stable environment.
Why is the brain optimized?
Our brains are optimized to perceive and respond to the world with automatic associations and pattern matching. This allows us to respond in ways we learn are effective and normal. Our inherited and learned thought patterns allow us to respond to stimuli quickly and subconsciously.
Can a conditioned stimulus fade?
Conditioned Stimuli Can Fade or Become "Extinct.". If the conditioned stimulus no longer follows the unconditioned stimulus, the conditioned response will fade in a process known as extinction. Once Pavlov's dogs associated a specific tone with food, he began making the sound but not providing food.
What is an Unconditioned Stimulus in Psychology
There is a bang! What happens? Usually, a person will jump or take in a sharp breath. The bang is an unconditioned stimulus; it is something that has a natural or automatic response without the person or animal being trained to have that response.
Classical Conditioning
Classical conditioning is where an unconditioned or natural response is conditioned to occur based on a neutral stimulus rather than an unconditioned one. The most common and well-known example of this is Ivan Pavlov and his dogs.
Stimuli
According to Webster's Dictionary Online, a stimulus is "something that causes a change or a reaction." Something like a touch or sound could be a stimulus, or it could be the appearance of a certain person or object that stimulates an action, like an audience becoming quiet when the guest speaker approaches the podium.

Is Fear A Conditioned Response?
What Is The Difference Between The Conditioned Stimulus and Neutral Stimulus?
How Does A Neutral Stimulus Become A Conditioned Stimulus?
- Suppose that the smell of food is an unconditioned stimulus and a feeling of hunger is the unconditioned response. Now, imagine that when you smelled your favorite food, you also heard the sound of a whistle. While the whistle is unrelated to the smell of the food, if the sound of the whistle was paired multiple times with the smell, the sound alon...
Is Generalization A Conditioned Response?