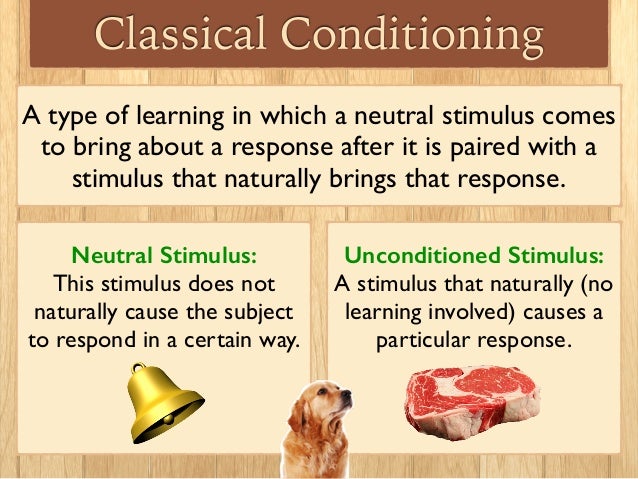
Key Principles of Classical Conditioning Theory
- Acquisition. : This is the starting stage of learning during which a response is established firstly and then gradually strengthened.
- Extinction. : Extinction is expected to take place when the intensity of a conditioned response decreases or disappears completely.
- Spontaneous Recovery. ...
- Stimulus Generalization. ...
- Stimulus Discrimination. ...
What is conditioning method of learning?
What is conditioning? Conditioning is a type of learning that links some sort of trigger or stimulus to a human behavior or response. When psychology was first starting as a field, scientists felt they couldn’t objectively describe what was going on in people’s heads.
What is an example of learning theory?
The new behavioral pattern can be repeated so it becomes automatic. The change in behavior of the learner signifies that learning has occurred. Teachers use Behaviorism when they reward or punish student behaviors. Examples and applications of behaviorist learning theory: Drill / Rote work ; Repetitive practice
How do you explain classical conditioning theory?
Learning Theories: Classical Conditioning, Operant Conditioning and Learning by Observation
- Classical Conditioning Theory and Learning. ...
- Key Principles of Classical Conditioning Theory. ...
- Operant Conditioning Theory and Learning. ...
- Key Components of Operant Conditioning. ...
- Learning by Observation. ...
- Key Steps involved in Observational Learning. ...
How do we learn by classical conditioning?
Key Principles
- Acquisition. Acquisition is the initial stage of learning when a response is first established and gradually strengthened. ...
- Extinction. Extinction is when the occurrences of a conditioned response decrease or disappear. ...
- Spontaneous Recovery. ...
- Stimulus Generalization. ...
- Stimulus Discrimination. ...

What is the meaning of conditioning in learning theory?
Conditioning is a form of learning in which either (1) a given stimulus (or signal) becomes increasingly effective in evoking a response or (2) a response occurs with increasing regularity in a well-specified and stable environment. The type of reinforcement used will determine the outcome.
What is an example of conditioning learning?
For example, whenever you come home wearing a baseball cap, you take your child to the park to play. So, whenever your child sees you come home with a baseball cap, he is excited because he has associated your baseball cap with a trip to the park. This learning by association is classical conditioning.
What is conditioning theory in psychology?
Conditioning in behavioral psychology is a theory that the reaction ("response") to an object or event ("stimulus") by a person or animal can be modified by 'learning', or conditioning.
What is the main idea of classical conditioning theory?
Classical conditioning refers to learning that occurs when a neutral stimulus (e.g., a tone) becomes associated with a stimulus (e.g., food) that naturally produces a behaviour. After the association is learned, the previously neutral stimulus is sufficient to produce the behaviour.
How conditioning helps in the learning process?
The conditioning theory of learning describes a form of learning where learning occurs as a result of associating a condition or stimulus with a particular reaction or response. Human behavior is shaped by habits we pick up in response to certain situations in life and is the outcome of learning by conditioning theory.
What are some examples of classical conditioning in the classroom?
Conditioning in the Classroom: 4 Examples Perhaps students have music class before lunch every day. Halfway through music class, their stomachs may begin to rumble, similar to the salivation of the dogs in Pavlov's experiment. The children may actually start to associate music class with hunger.
What is the concept of conditioning?
Definition of conditioning 1 : the process of training to become physically fit by a regimen of exercise, diet, and rest also : the resulting state of physical fitness. 2 : a simple form of learning involving the formation, strengthening, or weakening of an association between a stimulus and a response.
Why is conditioning important in psychology?
Classical conditioning emphasizes the importance of learning from the environment, and supports nurture over nature. However, it is limiting to describe behavior solely in terms of either nature or nurture, and attempts to do this underestimate the complexity of human behavior.
Who introduced the theory of conditioning of learning?
physiologist Ivan PavlovOne, which was first studied by the Russian physiologist Ivan Pavlov, is known as classical, or Pavlovian conditioning. In his famous experiment, Pavlov rang a bell and then gave a dog some food.
What is the simple definition of classical conditioning?
Classical conditioning definition Classical conditioning is a type of learning that happens unconsciously. When you learn through classical conditioning, an automatic conditioned response is paired with a specific stimulus. This creates a behavior.
What is an example of a conditioned response?
In classical conditioning, a conditioned response is a learned response to a previously neutral stimulus. For example, the smell of food is an unconditioned stimulus, a feeling of hunger in response to the smell is an unconditioned response, and the sound of a whistle when you smell the food is a conditioned stimulus.
What are the two types of conditioning?
Classical conditioning involves associating an involuntary response and a stimulus, while operant conditioning is about associating a voluntary behavior and a consequence.
What Is Classical Conditioning Theory?
In the Ivan Pavlov theory, there is a stimulus and a response. How the subject reacts to a stimulus depends on whether they’ve been conditioned or unconditioned. For instance, an infant wouldn’t know that a tiger in the wild can be dangerous. It’s only when they watch something educational or read about predators that they’ll find out.
Elements Of The Classical Conditioning Theory
The Pavlov theory of learning is built on unconditioned/conditioned stimulus and response. The first time you experience a stimulus, it has little to no impact on you. But after repetition, it will elicit a specific response from you. These stages are before and after conditioning.
Unlearn, Learn, Relearn With Harappa
As professionals, it’s important to keep learning and growing. You don’t need to restrict yourself to a particular career path or a certain skill set. You can always reach for more. Unlearning and relearning is a liberating and empowering process where you have the chance to gain new perspectives.
Join the Thrive Tribe
Stay ahead at work with smart stories, videos and podcasts delivered straight to your inbox.
What is conditioning theory?
Definition: The Conditioning Theory refers to the behavioral process, whereby a reaction (response) becomes more frequent to a given object (stimulus) as a result of reinforcement, which is a reward for the response in a given situation.
What is the process of learning that makes the hidden responses clearly visible to all?
In other words, conditioning is a process in which the ineffective object or event becomes so much effective that it makes the hidden responses clearly visible to all. The conditioning theory is based on the premise that learning is establishing the relationship between the stimulus and response.
What is the definition of permanent behavior?
Simply, an individual develops the permanent behavior for a given stimulus, if some rewards are associated with it. Example: If your Mother has given some work and on the completion of it, she gave you some monetary reward, and you learned that for doing the same work, again and again, you get the reward.
Who created the Law of Effect?
The first contributor to this field was Edward.L.Thorndike, who gave the “Law of Effect”. According to this law, any behavioral responses that are followed by rewards or satisfactory results are most likely to become the established pattern and occurs again and again in response to the same stimulus.
What is classical conditioning?
An Introduction to Classical and Operant Conditioning in Psychology. Conditioning in behavior al psychology is a theory that the reaction ("response") to an object or event ("stimulus") by a person or animal can be modified by 'learning' , or conditioning. The most well-known form of this is Classical Conditioning (see below), ...
Who invented the classic conditioning?
An extension of Classical Conditioning was devised by Edward Thorndike (1874-1949), who placed cats in a puzzle box. The incentive of a fish as food was placed outside of the box, giving the cats a reason to try to escape from the box. Initially, they had trouble escaping, and only gained freedom by knocking the latch of the box. Over time, they learnt that the undoing of the latch would enable their escape, and so the time spend being trapped in the puzzle box decreased as their knowledge of how to leave it increased.
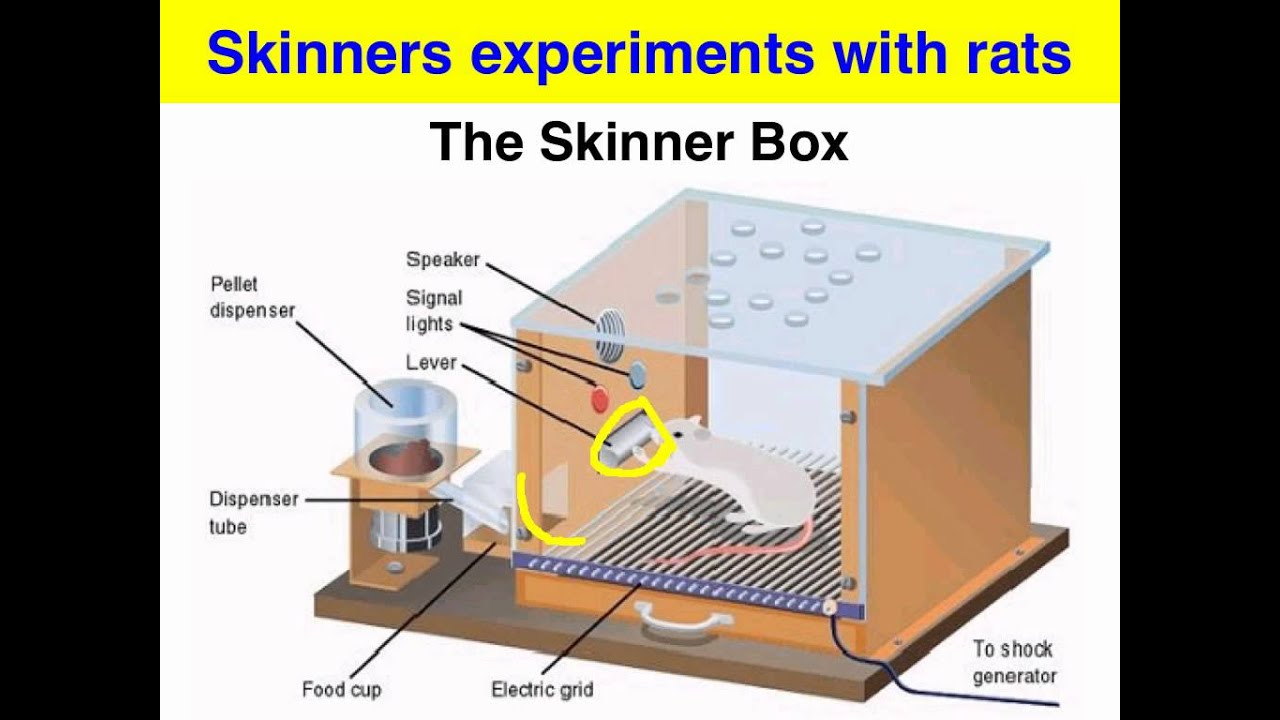
What did Skinner learn from the experiment?
Skinner carried out an experiment with caged rats in an "operant conditioning chamber" - Skinner's Box - who learnt through Operant Conditioning that if they pressed on a lever, food would be released for them. Under Operant Conditioning, reinforcement plays a key role:
What is the stimulus response of a dog?
This is known as a stimulus-response (SR), when salivation becomes a responsive action to the stimulus of the person feeding the dogs: At the start of the experiments: The Unconditioned/Neutral Stimulus (US/NS) is the person arriving to feed the dogs before the salivation as a result of their presence had began.
What is the difference between operant and classical conditioning?
The key difference between operant conditioning and classical conditioning is that the former creates association based on the result of a subject's behavior and the outcome that it generates as a secondary effect, whereas classical conditioning more primitively concentrates on the behavior itself.
What does a dog learn from a stick?
A dog receiving positive attention after fetching a stick back to its owner, learns to associate bringing the object back with favorable attention - positive reinforcement. A rat in a cage with an electrified floor learns that by pressing a lever, the electrical shock will stop - negative reinforcement.
Who was the first physiologist to use classical conditioning?
Classical Conditioning. Russian physiologist Ivan Pavlov (1849-1936) became eponymous with his dog conditioning experiments. The most famous experiment by the physiologist related to conditioning followed this research. Commonly referred to as " Pavlov's Dogs ", the experiment aimed to condition the dogs to associate the opening ...
What is conditioning in psychology?
Conditioning, in physiology, a behavioral process whereby a response becomes more frequent or more predictable in a given environment as a result of reinforcement, with reinforcement typically being a stimulus or reward for a desired response. Early in the 20th century, through the study of reflexes, physiologists in Russia, England, ...
What is animal learning?
animal learning: Associative learning: conditioning. The study of animal learning in the laboratory has long been dominated by experiments on conditioning. This domination has been resisted... Conditioning is a form of learning in which either (1) a given stimulus (or signal) becomes increasingly effective in evoking a response or (2) ...
What is the process of stimulus substitution?
The type of reinforcement used will determine the outcome. When two stimuli are presented in an appropriate time and intensity relationship, one of them will eventually induce a response resembling that of the other. The process can be described as one of stimulus substitution.
What is the S-R theory?
Stimulus-response (S-R) theories are central to the principles of conditioning. They are based on the assumption that human behaviour is learned.
Who studied spontaneous behaviour?
American psychologist B.F. Skinner studied spontaneous (or operant) behaviour through the use of rewards (reinforcement) or punishment. For example, a hungry animal will respond to a situation in a way that is most natural for that animal.
Who created the law of effect?
One of the early contributors to the field, American psychologist Edward L. Thorndike, postulated the Law of Effect, which stated that those behavioral responses (R) that were most closely followed by a satisfactory result were most likely to become established patterns and to reoccur in response to the same stimulus (S).
What is classical conditioning theory?
What Is the Classical Conditioning Theory? Behaviorists focus on the effect of the environment on human and non-human behavior. Their focus is on learning, particularly conditioning, to the exclusion of inherited, innate factors (Gross, 2020).
What is the term for the spontaneous transfer of conditioned response?
The spontaneous transfer of conditioned response is known as generalization (Pavlov, 1927).
How did Pavlov's discovery affect behaviorism?
He recognized that by repeatedly pairing a neutral stimulus (bell) with an unconditioned stimulus (food), he was ultimately able to trigger a conditioned response (salivat ing).
What is behaviorism in psychology?
17-05-2021. Until the 1950s, behaviorism was the dominant school of thought in psychology. It attempted to explain behavior based on the effects of the environment and learning rather than innate or inherited factors (Gross, 2020). Classical conditioning theory, discovered by Russian physiologist and Nobel prize winner Ivan Pavlov, ...
Is the theory of automatic responses relevant?
Results can be reliably reproduced. The theory explains automatic responses, though not the influence of other factors such as personality and genetic factors . The theory is highly relevant for animal conditioning (less so for humans, as the theory ignores an individual’s choice or agency).
Does classical conditioning include conscious self awareness?
Classical conditioning and behaviorism do not consider human agency including conscious self-awareness, intentionality, etc. The theory ignores innate and inherited factors. It does not explain how people make procedural decisions, such as choosing between more than one option or goal and how to overcome an obstacle.
How can teachers apply classical conditioning?
Teachers are able to apply classical conditioning in the class by creating a positive classroom environment to help students overcome anxiety or fear. Pairing an anxiety-provoking situation, such as performing in front of a group, with pleasant surroundings helps the student learn new associations.
What are the components of classical conditioning?
Let's take a closer look at the two critical components of this phase of classical conditioning: 1 The unconditioned stimulus is one that unconditionally, naturally, and automatically triggers a response. 4 For example, when you smell one of your favorite foods, you may immediately feel very hungry. In this example, the smell of the food is the unconditioned stimulus. 2 The unconditioned response is the unlearned response that occurs naturally in response to the unconditioned stimulus. 4 In our example, the feeling of hunger in response to the smell of food is the unconditioned response.
What would happen if the smell of food was no longer paired with the conditioned stimulus?
However, if the unconditioned stimulus (the smell of food) were no longer paired with the conditioned stimulus (the whistle), eventually the conditioned response (hunger) would disappear. Extinction in Classical Conditioning.
What is the term for when the occurrences of a conditioned response decrease or disappear?
Extinction is when the occurrences of a conditioned response decrease or disappear. In classical conditioning, this happens when a conditioned stimulus is no longer paired with an unconditioned stimulus. 6
What is the conditioned response?
The conditioned response is the learned response to the previously neutral stimulus. In our example, the conditioned response would be feeling hungry when you heard the sound of the whistle. In the after conditioning phase, the conditioned stimulus alone triggers the conditioned response.
What is behaviorism based on?
Behaviorism is based on the assumption that: All learning occurs through interactions with the environment. The environment shapes behavior. Classical conditioning involves placing a neutral signal before a naturally occurring reflex. In Pavlov's classic experiment with dogs, the neutral signal was the sound of a tone and ...
Can a learned response reemerge?
Sometimes a learned response can suddenly reemerge even after a period of extinction. Spontaneous recovery is the reappearance of the conditioned response after a rest period or period of lessened response. 7
What is conditioning in psychology?
Conditioning means modification of the natural response. Natural stimulus results in natural response. But natural stimulus may sometimes be substituted by an artificial stimulus (or conditioned stimulus as it is called). In this way, a new connection of artificial stimulus and natural response is created.
What are some examples of conditioning at home and school?
Examples of conditioning at home and school are not un-wanting. When a parent slaps a child every time the child touches the radio or electrical appliances (for the risk involved in getting electric shock) the child gets conditioned, and is afraid of all electrical appliances.
What is the treatment of delinquent, problem and maladjusted children?
This theory helps the teachers and psychologists to study the conditioned response of fear, phobia, anxiety or emotionally unstable children.
What are the points of deconditioning?
The following points should be noted for the extinction of conditioned reflex or response (Deconditioning): 1. Lack of motivation: If there is no motivation, there will be no learning by conditioning. If no food is given to the dog after ringing the bell, then the dog will not care for ringing the bell. 2.
Is food a stimulus?
Food is the stimulus, as it motives the dog to respond. His response is secretion of saliva. Food is natural or unconditioned stimulus, as it produces the response in a natural manners. Ringing of the bell is artificial or conditioned stimulus.
What is learning theory?
Learning theories establish the conceptual framework for explaining how information absorption, processing and retention take place during learning. Human learning is influenced by a gamut of factors like Emotional, Cognitive, Past Experiences and Environmental factors. Learning theories prescribe the right format or methodologies ...
What is operant conditioning theory?
Renowned Behavioural Psychologist B.F. Skinner was the main proponent of Operant conditioning theory. It is for this reason that the Operant Conditioning is also known as Skinnerian Conditioning and Instrumental Conditioning. Just like Classical Conditioning, Instrumental/Operant Conditioning lays emphasis on forming associations, but these associations are established between behaviour and behavioural consequences. The theory stressed on the role of punishment or reinforcements for increasing or decreasing the probability of the same behaviour to be repeated in the future. But the condition is that the consequences must immediately follow a behavioural pattern. The focus of operant conditioning is on voluntary behavioural patterns.
What are the three theories of learning?
The key learning theories are Classical Conditioning, Operant Conditioning and Social Learning . Let’s have a closer look at all these three major theories of learning.
Why does learning take place?
Learning takes place as a result of the interactions with the environmental forces. The environmental forces play a key role in shaping the behaviour. According to Pavlov’s Classical Conditioning theory, learning takes place because of association which is established between a previously neutral stimulus and a natural stimulus.
What does classical conditioning mean?
It means, not responding to those stimuli which is not similar, but responding only to certain specific stimuli. The theory of Classical Conditioning has several applications in the real-world. It is helpful for various pet trainers for helping them train their pets.
What is retention in learning?
Retention: It is the ability to store the learnt information and recall it later, which is equally affected by a number of factors. Reproduction: It involves practising or emulating the learnt behaviour, which will further lead to the advancement of the skill.
What are the components of operation conditioning?
Key Components of Operant Conditioning. Reinforcement: Reinforcements strengthen or increase the intensity of behaviour. This can be Positive and Negative. Positive Reinforcement: When a favourable event or an outcome is associated with behaviour in the form of a reward or praise, it is called as positive reinforcement.