Connective Tissue
- Epithelial- provides covering or lining
- Muscular- helps in movement
- Neural- responds to stimuli
- Connective- supports, links and cushions
What are the three characteristics of connective tissue?
What three characteristics does connective tissue provide to skin quizlet?
- Storage.
- Protect and Bind Organs.
- Support.
- Transport.
- Immune Protection.
What is the main function of connective tissue?
The primary functions of connective tissues include:
- Transportation of nutrients and metabolites through direct diffusion between organs and connective tissue proper.
- Immunological defense (fights invading cells via inflammation)
- Structural support.
- Tissue repair (after injury)
What does the connective tissue do in the body?
Connective tissues perform many functions in the body, but most importantly, they support and connect other tissues; from the connective tissue sheath that surrounds muscle cells, to the tendons that attach muscles to bones, and to the skeleton that supports the positions of the body.
Which is the function of connective tissue?
The function of connective tissue is either to join bodily structures like bones and muscles to one another or hold tissues like muscles, tendons, or even organs in their proper place in the body. It also gives reinforcement to joints, strengthening and supporting the articulations between bones.

What is the connective tissue?
Connective tissues bind structures together, form a framework and support for organs and the body as a whole, store fat, transport substances, protect against disease, and help repair tissue damage. They occur throughout the body.
What is connective tissue kid definition?
Connective Tissue Connective tissues protect, support, and bind, or connect, the parts of the animal's body. Connective tissues are composed of cells, extracellular fibers, and a matrix of nonliving gel-like material called ground substance.
Where are the connective tissues?
Connective tissue is found in between other tissues everywhere in the body, including the nervous system. The three meninges, membranes that envelop the brain and spinal cord are composed of connective tissue.
What are 5 examples of connective tissue?
The connective tissues include several types of fibrous tissue that vary only in their density and cellularity, as well as the more specialized and recognizable variants—bone, ligaments, tendons, cartilage, and adipose (fat) tissue.
Which statement best describes connective tissue?
Answer and Explanation: The statement that best describes connective tissue is (a) usually contains a large amount of matrix. The presence of a large amount of extracellular matrix is one of the defining characteristics of connective tissue, which is not found in any of the other three major tissues of the body.
Why is connective tissue called so?
Connective tissues, as the name implies, support and connect different tissues and organs of the body. They are widely distributed in every part of the body. They originate from the mesoderm (the middle germinal layer of the embryo).
How do you remember connective tissue?
Remember where the loose tissues are by thinking of skin and its elasticity. Dense tissue is found in ligaments and tendons; make a correlation between the strong and dense tendons to the name "dense connective tissue." Cartilage is packed into tight spaces, much like cargo on an airplane.
Why blood is a connective tissue?
Blood is one of the connective tissues. As a connective tissue, it consists of cells and cell fragments (formed elements) suspended in an intercellular matrix (plasma). Blood is the only liquid tissue in the body that measures about 5 liters in the adult human and accounts for 8 percent of the body weight.
How do you identify connective tissue?
3:3512:46Identifying Connective Tissue | Review and Practice - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipAnd in a lymph node you have lots of these circular cells so those circular cells you're seeing areMoreAnd in a lymph node you have lots of these circular cells so those circular cells you're seeing are also a hint that this is reticular. So all these ones on the top are loose connective tissues.
What are connective tissue cells?
The common cell types in connective tissue include: fibroblasts, mast cells, plasma cells, macrophages, adipocytes, and leukocytes. Slide 72 Tendon. Fibroblasts are the most common cell type of connective tissue. They produce both fibers and amorphous ground substance. Typically only the oval nuclei are visible.
What is an example of connective tissue?
Examples of specialized connective tissues are adipose tissue, cartilage, bone, blood, and lymph.
What are the 7 functions of connective tissue?
MatchEnclosing and separating.Connecting tissues to one another.Supporting and moving.Storing.Cushioning and insulating.Transporting.Protecting.
What is a tissue in science definition?
Tissue is a group of cells that have similar structure and that function together as a unit. A nonliving material, called the intercellular matrix, fills the spaces between the cells.
How important are connective tissues in the body?
Connective tissue fibers form capsules and membranes which surround organs, and form ligaments and tendons which bind bones to each other or to muscles. They also form the 3-dimensional fibrous mesh which supports cells inside large soft organs such as the liver and spleen. Bone and cartilage support body organs.
Why is blood a connective tissue?
Blood is considered a connective tissue for two basic reasons: (1) embryologically, it has the same origin (mesodermal) as do the other connective tissue types and (2) blood connects the body systems together bringing the needed oxygen, nutrients, hormones and other signaling molecules, and removing the wastes.
What is the definition of muscle tissue?
Muscle tissue is composed of cells that have the special ability to shorten or contract in order to produce movement of the body parts. The tissue is highly cellular and is well supplied with blood vessels.
What is the function of connective tissue?
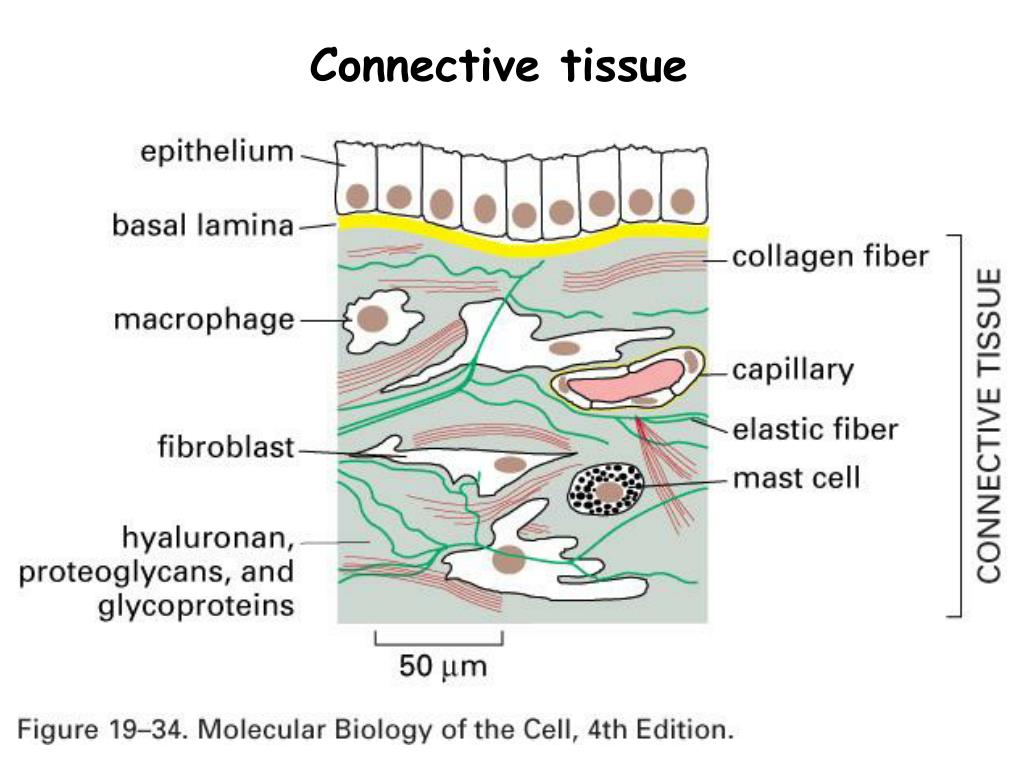
As the name implies, connective tissue serves a connecting function: It supports and binds other tissues in the body. Unlike epithelial tissue, which has cells that are closely packed together, connective tissue typically has cells scattered throughout an extracellular matrix of fibrous proteins and glycoproteins attached to a basement membrane. The primary elements of connective tissue include a ground substance, fibers, and cells.
What is dense regular connective tissue?
Dense regular: Tendons and ligaments are examples of dense regular connective tissue. Dense irregular: Much of the dermis layer of the skin is composed of dense irregular connective tissue. The membrane capsule surrounding several organs is also dense irregular tissue.
What is the color of collagenous fibers?
This image of the dermis of the skin shows dense fibrous connective tissue. Irregular collagenous fibers (pink) and fibroblast nuclei (purple) can be seen. Ed Reschke/Photolibrary/Getty Images
What is the ground substance in connective tissue?
The ground substance acts as a fluid matrix that suspends the cells and fibers within the particular connective tissue type. Connective tissue fibers and matrix are synthesized by specialized cells called fibroblasts. There are three main groups of connective tissues: loose connective tissue, dense connective tissue, and specialized connective tissue.
Why is spongy bone called cancellous bone?
Spongy bone, also called cancellous bone, gets its name because of its spongy appearance. The large spaces, or vascular cavities, in this type of bone tissue contain blood vessels and bone marrow. Spongy bone is the first bone type formed during bone formation and is surrounded by compact bone.
Why is loose connective tissue called loose connective tissue?
Loose connective tissue is named so because of the "weave" and type of its constituent fibers. These fibers form an irregular network with spaces between the fibers. The spaces are filled with ground substance. The three main types of loose connective fibers include collagenous, elastic, and reticular fibers.
What is the insulating layer of fat tissue?
This image shows a sample of fat tissue with fat cells (adipocytes, blue) surrounded by fine strands of supportive connective tissue. Adipose tissue forms an insulating layer under the skin, storing energy in the form of fat. Steve Gschmeissner/Science Photo Library/Getty Images
What are loose connective tissue?
Loose regular tissue has a fluid matrix and low proportions of arranged (regular) fibers. The loose form is sometimes called areolar connective tissue and is found: 1 Surrounding blood vessels 2 Between muscle fascia (as sliding tissue) 3 As the endomysium of muscle around muscle fibers 4 Below the dermis 5 Below epithelial cell layers 6 In the form of the lamina propria of several organs (see above) 7 In the form of the mesentery 8 As mucous membranes 9 In glands
Why is connective tissue dense?
Dense connective tissue is dense because of the high proportion of fibers that run parallel to each other. Dense regular tissue is found in tendons, ligaments, and muscle fascia. In many sources, this type is listed as connective tissue proper; however, it is found in specific locations and can fit into either category.
What is the lace-like network of reticular fibers?
The lace-like network of reticular fibers. All extracellular fibers are contained within a gel-like solution called ground substance. The combination of ground substance and extracellular fibers makes up the extracellular matrix. Add cells to the extracellular matrix and you have connective tissue.
How is connective tissue disease treated?
Most such diseases are treated by a specialist of a certain anatomical or physiological area, or pathology.
How many illnesses are connected to connective tissue?
There are more than 200 illnesses ‘connected’ to connective tissue. Some are the result of genetic disorders, some are caused by autoimmune processes. Connective tissue cancer occurs as the result of mutation in any associated cell type; sarcomas and leukemia begin in bone tissue, for example.
Which cells produce reticular fibers?
Reticular cells produce reticular fibers but play the role of fibrocytes in areas of tissue that contain reticular fibers.
What is the body's epithelial tissue?
Epithelial tissue covers our external surfaces (our skin) and lines internal organs and cavities. Muscles are also very visible thanks to their large volumes. The average muscle mass for an adult female of around 30 years is almost 30% of her body weight. Our nervous system flows through the entire body and includes the brain, spinal cord, and every single nerve. Connective tissue with a fluid matriix is often considered to be less important; however, it is found in large quantities and is essential.
What is connective tissue?
Connective tissue connects, supports, binds, and separates organs and tissues, forming a framework to support body tissues and organs, for structural and metabolic purposes. In connective tissue, cells are few and dispersed — they are not in close contact, as in epithelial tissue. Most connective tissues are vascularized (except cartilage ).
What are the components of connective tissue?
Connective tissue is made up of: 1 Fibrous components (collagen and elastin) 2 Glycosaminoglycans or GAGs (long chains of repeating disaccharide units; the main role is to support collagen) 3 Proteoglycans (GAGs attached to a core protein)
What is the type of connective tissue that consists of chondrocyte cells, collagen fibers, and?
Cartilage (a type of supporting connective tissue that consists of chondrocyte cells, collagen fibers, and elastic fibers; semi-solid or flexible matrix; includes hyaline cartilage , fibrocartilage , and elastic cartilage )
What type of connective tissue contains osteoblasts?
Bone (a type of supporting connective tissue contains osteoblasts or osteocytes; consists of collagen fibers and is rigid or calcified)
How many diseases are there in the connective tissue?
There are more than 200 diseases and conditions that affect connective tissue. Some connective tissue diseases are consequences of infection, injury, or due to genetic abnormalities. The cause of some connective tissue diseases remains unknown.
Which type of connective tissue stores excess fat and energy?
Adipose tissue (a type of supporting connective tissue that cushions, stores excess fat and energy; contains reticular cells and reticular fibers)
Where is loose irregular connective tissue found?
Dense connective tissue is found in joint capsules, muscle fascia, and the dermis layer of skin.
Where do connective tissues come from?
They are widely distributed in every part of the body. They originate from the mesoderm (the middle germinal layer of the embryo).
What type of cells are in connective tissue?
They secrete different types of fibres and matrices. Fibroblasts or adipose cells are stationary and macrophages, mast cells, monocytes, lymphocytes are migrating cells.
What is the term for a group of cells along with intercellular substances that perform a specific function?
Connective Tissue. A group of cells along with intercellular substances that perform a specific function is called tissue. There are mainly four different types of tissues present in our body. Epithelial- provides covering or lining. Muscular- helps in movement.
What is collagen made of?
Collagen fibres are the most widespread and made up of fibrous protein, collagen. Collagen fibres are flexible and have high tensile strength (comparable to steel).
Which connective tissue is responsible for maintaining correct posture?
Specialised Connective Tissue. Other than these, there are supportive connective tissues, that help in maintaining correct posture and support internal organs, e.g. cartilage and bone. Blood and lymph are fluid connective tissues that circulate in the body and help in interaction and communication among all the organs.
What is the other type of connective tissue disorder?
EB is characterised by skin oversensitivity. The other type of connective tissue disorder is autoimmune. When the immune system of the body starts attacking healthy tissues, it is known as an autoimmune disorder. Some of the autoimmune diseases of connective tissue are the following:
Which connective tissue is the hardest to maintain?
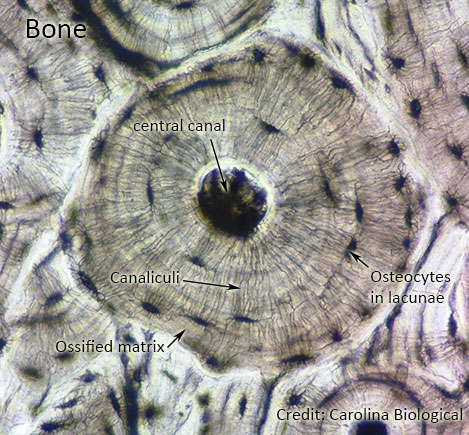
Bones: Bone is the hardest connective tissue and helps in maintaining the shape and posture of the body, it protects internal organs. They are rich in collagen fibres and calcium, which give strength. The cells of the bone are known as osteocytes. They are present in lacunae and secrete the matrix.
What is connective tissue?
Overview and types of connective tissue. Connective tissue is the tissue that connects, separates and supports all other types of tissues in the body. Like all tissue types, it consists of cells surrounded by a compartment of fluid called the extracellular matrix (ECM). However connective tissue differs from other types in ...
What are the different types of connective tissue?
Based on the cells present and the ECM structure, we differ two types of connective tissue: 1 Connective tissue proper; further divided into loose and dense connective tissues 2 Specialised connective tissue; reticular, blood, bone, cartilage and adipose tissues
Why is connective tissue important?
We know that there are way cooler histology topics than connective tissue, like muscle tissue or neural tissue. But as the connective tissue is the glue that holds all other tissues together, it has the important function of ensuring that our body systems work in harmony.
What is the compartment of connective tissue?
Like all tissue types, it consists of cells surrounded by a compartment of fluid called the extracellular matrix ( ECM). However connective tissue differs from other types in that its cells are loosely, rather than tightly, packed within the ECM. Based on the cells present and the ECM structure, we differ two types of connective tissue:
Where is dense irregular connective tissue located?
It is usually located in the capsules and walls of the organs, the dermis of the skin and glands.
Where is loose connective tissue found?
Loose connective tissue is the most widely distributed type of connective tissue, found in the lining of the body's inner surfaces.
Which type of connective tissue has collagen fibers aligned parallel to each other?
Dense regular connective tissue has the collagen fibers aligned parallel to each other. This arrangement provides the tissue with high unidirectional resistance to stress. The best dense regular connective tissue examples are the tendons and ligaments.
What is the function of connective tissue?
a fibrous type of body tissue with varied functions; it supports and connects internal organs, forms bones and the walls of blood vessels, attaches muscles to bones, and replaces tissues of other types following injury. Connective tissue consists mainly of long fibers embedded in noncellular matter, the ground substance.
Why is connective tissue important?
Inclusive health: methods of tissue preservation: connective tissue plays an important role in maintaining health; an inclusive model of care can contribute to whole body wellness
What are the three main groups of connective tissue?
Such tissues fall into three main groups: ‘true’ connective tissue (ADIPOSE TISSUE, AREOLAR TISSUE, yellow elastic tissue (LIGAMENTS) and white fibrous tissue (TENDONS); skeletal tissue: BONE and CARTILAGE;
What makes connective tissue soft and rubbery?
The density of these fibers and the presence or absence of certain chemicals make some connective tissues soft and rubbery and others hard and rigid. Compared with most other kinds of tissue, connective tissue has few cells. The fibers contain a protein called collagen.
What is the tissue that forms the supporting and connecting structures of the body?
Tissue arising chiefly from the embryonic mesoderm that is characterized by a highly vascular matrix and includes collagenous, elastic, and reticular fibers, adipose tissue, cartilage, and bone. It forms the supporting and connecting structures of the body.
What is the connective tissue of the animal body?
con·nec·tive tis·sue. Physical or functional supporting tissue of the animal body, a major constituent of which ( in addition to various kinds of cells) is an extracellular matrix of ground substance, protein fibers, and structural glycoproteins; derived from the mesenchyme, which in turn is derived mainly from mesoderm.
What is the term for the supporting or framework tissue of the animal body?
con·nec·tive tis·sue. The supporting or framework tissue of the animal body, formed of fibers and ground substance with more or less numerous cells of various kinds. It is derived from the mesenchyme, and this in turn from the mesoderm.
What is the purpose of connective tissue?
Connective tissue, as the name implies, is a term given to several different tissues of the body that serve to connect, support and help bind other tissues in the body. Connective tissue can further be broken down into three categories: loose connective tissue, dense connective tissue, and specialized connective tissue. Loose connective tissue works to hold organs in place and is made up of extracellular matrix and collagenous, elastic and reticular fibers. Dense connective tissue is what makes up tendons and ligaments and consist of a higher density of collagen fibers. Examples of specialized connective tissues are adipose tissue, cartilage, bone, blood, and lymph.
Which connective tissue has a variable blood supply?
Different types of connective tissue have a variable blood supply. Tendons and ligaments, in particular, appear partially avascular. They are compromised mainly of densely packed collagen fibers which undergo no metabolic activity and don’t require a blood supply. There are living cells hidden within these collagen fibers which require blood supply; however, their volume is minimal as compared to the tendons as a whole. [3]
What is collagen fiber?
Collagen fibers are made up of closely packed thin collagen fibrils that run a wavy course in tissues. These parallel fibrils are bundles with flexible proteoglycans to offer an essential mechanical property. They offer flexible but powerful resistance to pulling force. Specifically, in loose connective tissue, collagen runs in a parallel course and then joins to form a larger bundle. They split from each other and join back together at varying locations creating a three-dimensional meshwork. Dense connective tissue such as ligaments and tendons are compromised mainly of densely packed collagen fibers. [1]
How are muscle cells connected?
Connective tissue exists between every muscle cell, fiber, and fascicle. At a molecular level, each muscle cell is connected to other muscle cells by a collagenous basement membrane called an endomysium. The fascicles are surrounded by perimysium which further connects to the epimysium which encompasses the entire skeletal muscle and is continuous with the tendon. The collagenous network beginning at the level of the endomysium is continuous with the perimysium and the tendon, which allows for an effective and powerful muscle contraction. [5]
What is mixed connective tissue disease?
Mixed connective tissue disease (MCTD) is an autoimmune connective tissue disorder characterized by an autoantibody to ribonucleoprotein (RNP). It presents clinically as SLE, systemic sclerosis, and polymyositis. Diagnostic criteria are based on anti-RNP serology with myositis or synovitis plus two of the following: edema of hands, Raynaud’s phenomenon, sclerodactyly/acrosclerosis. Pulmonary symptoms are prevalent in patients with MCTD. Patients may complain of cough, dyspnea or pleuritic chest pain. Pulmonary hypertension is the most severe pulmonary consequence and often leads to premature death. [6]
What is the outermost layer of connective tissue that encloses the entire peripheral nerve?
All peripheral nerve fibers consist of three connective tissue layers which serve as a protective connective sheath. Epineurium is the outer most layer of dense connective tissue that encloses the entire peripheral nerve. Within the epineurium , there are several nerve fascicles which are individually enclosed by the perineum. These fascicles are made up of myelinated individual nerve fibers that are surrounded by endoneurium. [4]
Where are reticular fibers found?
They are primarily present in basement epithelial tissue, adipose cells, Schwann and muscle cells, lymphoid tissue and endothelium of hepatic sinusoids. Under microscopy, these reticular fibers are fine, dark fibrils that are continuous with the college fibers described above. The arrangement of these fibers forms a network that underlies the basal lamina layer. There is a firm attachment of these fibers to the basal lamina that indicates that, along with the collagen fibers, these fibers create a functional and structural unit that serves to support tissues. The loose arrangement of these fibers also provides space for molecular movement within the extracellular fluid. [1]
What are the two proteins that make up connective tissue?
Connective tissues are made up of two proteins: collagen and elastin. Collagen is a protein found in the tendons, ligaments, skin, cornea, cartilage, bone and blood vessels. Elastin is a stretchy protein that resembles a rubber band and is the major component of ligaments and skin.
How many types of connective tissue diseases are there?
There are more than 200 different types of connective tissue diseases. They may be inherited, caused by environmental factors, or most often, are of unknown cause. Connective tissue diseases include, but are not limited to: Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA): Rheumatoid arthritis is one of the most common connective tissue diseases and can be inherited.
What is an undifferentiated connective tissue disease?
Undifferentiated connective tissue disease (s): Conditions that have characteristics of connective tissue diseases but don't meet the guidelines as defined at a particular time. Some people with these conditions will eventually go on to develop a specific type of connective tissue disease, but most will not.
What are the diseases that connect the body?
Connective tissue diseases include autoimmune diseases like rheumatoid arthritis, scleroderma and lupus.
What tests are done to determine if you have connective tissue disorder?
The doctor will first ask for your medical history, a family history, and will do a physical examination. Further tests may include: Imaging tests, such as X-rays and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scans.
What parts of the body are affected by connective tissue disease?
Body parts that may be affected include: Bones. Joints.
What is the condition that causes scar tissue to form in the skin, internal organs, and small blood vessels?
Scleroderma: An autoimmune condition that causes scar tissue to form in the skin, internal organs (including the GI tract), and small blood vessels. It affects women three times more often than men throughout life, occurring at a rate of 15 times greater for women during childbearing years.