What are the diagnostic criteria for severe preeclampsia?
Severe preeclampsia must include 1 of the following: >300 mg protein per 24-hour urine collection Protein:creatinine ratio >30 mg/mmol: In the absence of severe hypertension, features of severe preeclampsia include mild/moderate hypertension and proteinuria with ≥1 of the following: Severe headache Problems with vision such as blurring or ...
What is preeclampsia and how dangerous is it?
The blood supply to the placenta might be decreased in preeclampsia, and this can lead to problems for both you and the fetus. Poor nutrition or high body fat might also contribute to the development of preeclampsia. A lack of blood flow to the uterus or genes could also be a factor.
What is diffence between mild and severe preenclampsia?
Typically, preeclampsia is categorized by its severity, and distinguishing between mild and severe preeclampsia is important because the management strategies are very different. 0.3g of protein is collected in a 24-hour urine sample or persistent 1+ protein measurement on urine dipstick Severe preeclampsia is a more serious problem.
What are some signs and symptoms of worsening preeclampsia?
Warning Signs of Preeclampsia
- High blood pressure. Hypertension, or high blood pressure, is a cardinal symptom of preeclampsia. ...
- Headaches. Everyone gets headaches on occasion, but a headache that occurs suddenly or doesn’t go away despite rest could signal a bigger problem.
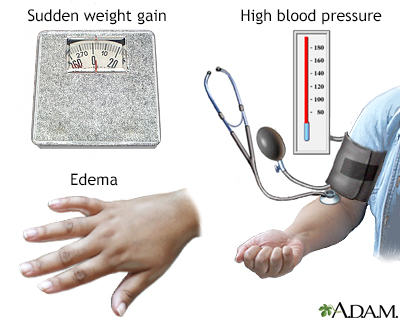
- Swelling of the hands or face. ...
- Visual changes. ...
- Sudden weight gain. ...
- Protein in the urine. ...
See more

What confirms severe preeclampsia?
Severe preeclampsia occurs when a pregnant woman has any of the following: Systolic blood pressure of 160 mmHg or higher or diastolic blood pressure of 110 mmHg or higher on two occasions at least 4 hours apart while the patient is on bed rest.
What is the difference between mild and severe preeclampsia?
Preeclampsia can be categorized as mild or severe. You may be diagnosed with mild preeclampsia if you have high blood pressure plus high levels of protein in your urine. You are diagnosed with severe preeclampsia if you have symptoms of mild preeclampsia plus: Signs of kidney or liver damage (seen in blood work).
How high is too high preeclampsia?
How is preeclampsia diagnosed? Your health care provider will check your blood pressure and urine at each prenatal visit. If your blood pressure reading is high (140/90 or higher), especially after the 20th week of pregnancy, your provider will likely want to run some tests.
When should I go to the ER for preeclampsia?
Seek urgent, immediate medical care at the hospital if: Your blood pressure is very high, such as 160/110 or higher. You have symptoms of pre-eclampsia, such as: Sudden swelling of your face, hands, or feet. New vision problems (such as light sensitivity, blurring, or seeing spots).
How high does BP have to be for preeclampsia?
Signs of preeclampsia in a pregnant woman include: Blood pressure of 140/90. Systolic blood pressure that rises by 30 mm Hg or more even it if is less than 140. (This is the highest level of blood pressure during the heart's pumping cycle.)
What are signs of worsening preeclampsia?
As pre-eclampsia progresses, it may cause:severe headaches.vision problems, such as blurring or seeing flashing lights.pain just below the ribs.vomiting.sudden swelling of the feet, ankles, face and hands.
Does baby move more with preeclampsia?
Decreased fetal movements are seen in cases of chronic fetal distress such as preeclampsia, hypertension in pregnancy, etc. It was shown that in these cases a pronounced decrease up to cessation of fetal movements occurred before fetal death in utero while fetal heart beats were still audible for at least 12 hours.
What is the biggest risk factor for preeclampsia?
The most significant risk factors for preeclampsia are:Previous history of preeclampsia.Multiple gestation (i.e., pregnant with more than one baby)History of chronic high blood pressure, diabetes, kidney disease or organ transplant.First pregnancy.Obesity, particularly with Body Mass Index (BMI) of 30 or greater.More items...
Do you have to stay in the hospital with preeclampsia?
If your preeclampsia is severe, you may need to stay in the hospital to be monitored closely. If the preeclampsia remains severe, the baby may need to be delivered. If your preeclampsia is mild, you may be able to stay at home on bed rest. You will need to have frequent checkups and tests.
Do you have to go on bed rest with preeclampsia?
In its most severe form (blood pressure of 160/110 or higher), preeclampsia can threaten the life of the mother and her baby. Women with the condition must be closely monitored, and bed rest is often recommended.
How long can I be hospitalized for preeclampsia?
Length of stays varied from a few hours to several weeks and depended on a number of factors: how many weeks pregnant they were, whether they were admitted because they had started to go into labour, the severity of their pre-eclampsia, and whether they had any other health concerns affecting their pregnancy (such as ...
How do hospitals treat preeclampsia?
Treatment in the hospital may include: Close monitoring of the mother and baby. Medicines to control blood pressure and prevent seizures and other complications. Steroid injections for pregnancies under 34 weeks gestation to help speed up the development of the baby's lungs.
How serious is mild preeclampsia?
Preeclampsia is a serious pregnancy condition that can affect every internal organ, says the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG). 1 This potentially dangerous condition is classified as either mild or severe. Mild preeclampsia is characterized by high blood pressure and protein in the urine.
How often does mild preeclampsia turn severe?
Pre-eclampsia can range from mild to severe. Mild pre-eclampsia affects up to 6% of pregnancies. Severe cases are rarer and develop in about 1 to 2% of pregnancies.
What happens if I have mild preeclampsia?
Most women with mild preeclampsia are delivered by 37 weeks of pregnancy . If you have mild preeclampsia before 37 weeks: Your provider checks your blood pressure and urine regularly. She may want you to stay in the hospital to monitor you closely.
Can you go full term with mild preeclampsia?
As inpatients mothers are monitored frequently for evidence of maternal or fetal compromise until 38 weeks gestation when delivery is accomplished. If a patient with mild preeclampsia labors after 34 weeks, no attempt is made to stop labor and delivery is undertaken.
What are the symptoms of preeclampsia?
Other signs and symptoms of preeclampsia may include: Excess protein in your urine (proteinuria) or additional signs of kidney problems. Severe headaches.
How to prevent preeclampsia?
Researchers continue to study ways to prevent preeclampsia, but so far, no clear strategies have emerged. Eating less salt, changing your activities, restricting calories, or consuming garlic or fish oil doesn't reduce your risk. Increasing your intake of vitamins C and E hasn't been shown to have a benefit.
What is the name of the disorder that causes high blood pressure during pregnancy?
Preeclampsia is classified as one of four high blood pressure disorders that can occur during pregnancy. The other three are: Gestational hypertension. Women with gestational hypertension have high blood pressure but no excess protein in their urine or other signs of organ damage.
How long does it take for preeclampsia to occur?
Preeclampsia usually begins after 20 weeks of pregnancy in women whose blood pressure had been normal.
Why is blood pressure important during pregnancy?
Monitoring your blood pressure is an important part of prenatal care because the first sign of preeclampsia is commonly a rise in blood pressure. Blood pressure that exceeds 140/90 millimeters of mercury (mm Hg) or greater — documented on two occasions, at least four hours apart — is abnormal.
How to take care of a baby when you are pregnant?
Once you're pregnant, take care of yourself — and your baby — through early and regular prenatal care. If preeclampsia is detected early, you and your doctor can work together to prevent complications and make the best choices for you and your baby. By Mayo Clinic Staff.
Where does preeclampsia start?
Experts believe it begins in the placenta — the organ that nourishes the fetus throughout pregnancy. Early in pregnancy, new blood vessels develop and evolve to efficiently send blood to the placenta. In women with preeclampsia, these blood vessels don't seem to develop or function properly.
Why is preeclampsia called preeclampsia?
Preeclampsia is so named because it was originally identified as a disorder preceding eclampsia, although it is now known that eclamptic seizures are only one of the several potential complications of the disease. Eclamptic seizures usually occur as a later complication of severe preeclampsia, but may also arise without any prior signs of severe disease.
How to manage preeclampsia?
Many factors guide a healthcare provider’s decision about how to manage preeclampsia, including the gestational age and health of the baby, overall health and age of the mother, and a careful assessment of how the disease is progressing. This includes monitoring blood pressure and assessing the results of laboratory tests that indicate the condition of the mother’s kidneys, liver, or the ability of her blood to clot. Other tests monitor how well the unborn baby is growing and/or if he or she seems in danger. When the pregnancy is less than 37 weeks the caregiver usually tries to gain some time, but if 37 weeks or later, the provider will often opt to deliver the baby.
What is the name of the condition that causes high blood pressure during pregnancy?
Preeclampsia is persistent high blood pressure that develops during pregnancy or the postpartum period and is often associated with high levels of protein in the urine OR the new development of decreased blood platelets, trouble with the kidneys or liver, fluid in the lungs, or signs of brain trouble such as seizures and/or visual disturbances.
How does preeclampsia affect the body?
Preeclampsia affects the blood flow to the placenta, often leading to smaller or prematurely born babies. Ironically, sometimes the babies can be much larger, but scientists are not certain that preeclampsia was the cause. While maternal death from preeclampsia is rare in the developed world, it is a leading cause of illness and death globally for mothers and infants.
What is the medical term for pregnancy induced hypertension?
You may encounter other names like toxemia, PET (pre-eclampsia/toxemia) and PIH (pregnancy induced hypertension) EPH gestosis (edema, proteinuria, hypertension), but these designations are all outdated terms and no longer used by medical experts.
When is preeclampsia diagnosed?
It is diagnosed by the elevation of the expectant mother’s blood pressure usually after the 20th week of pregnancy. According to guidelines released by the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists, the diagnosis of preeclampsia no longer requires the detection ...
Can preeclampsia kill a baby?
Preeclampsia and other hypertensive disorders of pregnancy can be devastating diseases, made worse by delays in diagnosis or management, seriously impacting or even killing both women and their babies before, during or after birth.
What are the risks of preeclampsia?
Risks of preeclampsia can include: Seizures in the mother. Stroke or bleeding in the brain. Temporary kidney failure. Liver problems. Blood clotting problems. Placental abruption: The placenta pulls away from the wall of the uterus, causing distress to the baby and bleeding in the mother. Poor growth of the baby.
What is the complication of preeclampsia?
Eclampsia is a life-threatening complication that develops in approximately 1% of women with preeclampsia and results in seizures or coma. Warning signs to watch for can include:
Why does preeclampsia occur?
Preeclampsia is thought to arise from a problem with the health of the placenta (the organ that develops in the uterus during pregnancy and is responsible for providing oxygen and nutrients to the baby). It is thought that the blood supply to the placenta is decreased in preeclampsia, and this can lead to problems with both the mother and baby.
What is HELLP syndrome?
HELLP syndrome is a severe form of preeclampsia that develops in 4 to 12% of cases. The name stands for:
What is the condition that occurs during pregnancy?
Preeclampsia is a condition unique to pregnancy that complicates up to 8% of all deliveries worldwide. It's characterized by high blood pressure (hypertension) and high levels of protein in the urine (proteinuria) in the mother. Preeclampsia typically happens in first-time mothers and in the later part of pregnancy (after 20 weeks gestation).
How to diagnose preeclampsia?
Preeclampsia is often diagnosed during routine prenatal appointments, when your healthcare provider checks your weight gain, blood pressure and urine protein. If preeclampsia is suspected, additional blood tests may be ordered. In some cases, blood pressure readings will be observed in the hospital and a 24-hour urine collection is performed to check for proteinuria (protein in the urine). An ultrasound and fetal monitoring may also be used to provide more information about the baby.
How to treat preeclampsia?
Your healthcare provider will advise you on the best way to treat preeclampsia. Preeclampsia can only be cured with delivery. If you're at term (37 weeks gestational age or greater), the baby will be delivered. If preeclampsia develops earlier in pregnancy, you can be monitored closely in the hospital in an effort to prolong the pregnancy and allow for the baby to grow and develop. If the preeclampsia worsens or becomes more severe, the baby will be delivered. Women with preeclampsia can have a vaginal delivery through induction of labor — which is more likely to be successful if you're closer to term — or planned cesarean section. During labor and following delivery, women with preeclampsia are often given magnesium intravenously (directly into the vein) to prevent development of eclampsia.
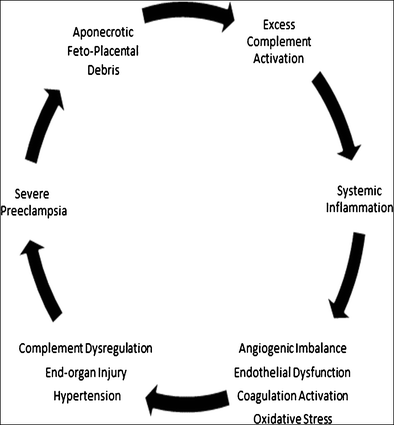
What is severe preeclampsia?
Severe preeclampsia is new onset hypertension in pregnancy after 20 weeks gestation with proteinuria. Treatment is usually delivery to prevent maternal and fetal complications, but delayed delivery can be considered under certain circumstances.
What is the diagnosis of preeclampsia?
Diagnosis/definition: Preeclampsia is the new onset of hypertension in pregnancy after 20 weeks gestation with proteinuria in a previously normotensive woman. Severe features of preeclampsia include any of the following findings: Systolic blood pressure of 160mm Hg or higher, or diastolic blood pressure of 110mm Hg or higher on 2 occasions ...
When to start aspirin for preeclampsia?
Prevention :For women with a medical history of early-onset preeclampsia and preterm delivery at <34 weeks gestation or preeclampsia in more than one prior pregnancy, initiating daily low-dose (60-80mg) aspirin beginning in the late first trimester is suggested.
Does expectant management cause maternal morbidity?
For women with severe preeclampsia before the limit of viability, expectant management has been associated with frequent maternal morbidity with minimal or no benefits to the newborn.
Is preeclampsia a risk factor?
Risk factors/associations: The likelihood of severe preeclampsia is substantially increased in women with a history of preeclampsia, diabetes mellitus, chronic renal disease, anti-phospholipid antibodies, obesity, chronic hypertension, or multifetal gestation.
How much is the risk of pre-eclampsia during pregnancy?
The risk of recurrence of pre-eclampsia during a subsequent pregnancy has to be considered. This risk is estimated to be less than 10% for all cases of pre-eclampsia,37but is greater when pre-eclampsia is discovered before 28 weeks.
What is the incidence of pre-eclampsia?
The incidence of pre-eclampsia ranges from 3% to 7% for nulliparas and 1% to 3% for multiparas. Pre-eclampsia is a major cause of maternal mortality and morbidity, preterm birth, perinatal death, and intrauterine growth restriction. Unfortunately, the pathophysiology of this multisystem disorder, characterized by abnormal vascular response ...
What happens to spiral arteries during pregnancy?
During normal pregnancy, the villous cytotrophoblast invades into the inner third of the myometrium, and spiral arteries lose their endothelium and most of their muscle fibers. These structural modifications are associated with functional alterations, such that spiral arteries become low-resistance vessels, and thus less sensitive, or even insensitive, to vasoconstrictive substances.
What is the pre-eclampsia age?
The criteria that define pre-eclampsia have not changed over the past decade.1,2These are: onset at >20 weeks’ gestational age of 24-hour proteinuria ≥30 mg/day or, if not available, a protein concentration ≥30 mg (≥1+ on dipstick) in a minimum of two random urine samples collected at least 4–6 hours but no more than 7 days apart, a systolic blood pressure >140 mmHg or diastolic blood pressure ≥90 mmHg as measured twice, using an appropriate cuff, 4–6 hours and less than 7 days apart, and disappearance of all these abnormalities before the end of the 6th week postpartum. Nonetheless, some presentations of pregnancy-related hypertension combined with clinical or laboratory abnormalities or intrauterine growth restriction should also be considered as potential pre-eclampsia.1
What is the sole curative treatment for pre-eclampsia?
The sole curative treatment being delivery, management must continuously balance the risk–benefit ratio of induced preterm delivery and maternal–fetal complications. Screening women at high risk and preventing recurrences are also key issues in the management of pre-eclampsia.
What are the risk factors for pre-eclampsia?
Other risk factors have been identified, including a medical history of chronic hypertension, kidney disease, diabetes, obesity, birthplace in Africa, age ≥35 years, and pregnancy characteristics, such as twin or molar pregnancy, previous pre-eclampsia, or fetal congenital abnormality.6,7High altitude has also been shown to increase the incidence of pre-eclampsia, and is attributed to greater placental hypoxia, smaller uterine artery diameter, and lower uterine artery blood flow.8
Why is pre-eclampsia important?
This examination is important because pre-eclampsia may unmask previously undiagnosed systemic or kidney disease or thrombophilia. It should include a specific set of questions, blood pressure measurement, a clinical examination looking for signs of autoimmune conditions, and a urinary dipstick test.
What is the diagnosis of severe preeclampsia?
Thus, one of the following findings is also necessary for a diagnosis of severe preeclampsia: 1 . At least twice the normal measurements of certain liver enzymes on a blood test.
Why is it important to distinguish between mild and severe preeclampsia?
Typically, preeclampsia is categorized by its severity, and distinguishing between mild and severe preeclampsia is important because the management strategies are very different.
What are the symptoms of high blood pressure during pregnancy?
Preeclampsia is one of numerous disorders related to high blood pressure during pregnancy, including: 3 1 Chronic hypertension, high blood pressure that was documented prior to pregnancy or that occurs before 20 weeks gestation. 2 Chronic hypertension with superimposed preeclampsia, which is diagnosed in women who had chronic hypertension prior to pregnancy and then develop an exacerbation of their high blood pressure along with protein in the urine or other signs of preeclampsia during pregnancy. 3 Gestational hypertension, which features high blood pressure during pregnancy but not excess protein in their urine or signs of damage to other organs. However, some women with gestational hypertension will go on to develop preeclampsia.
What are the symptoms of preeclampsia?
The main features of preeclampsia are high blood pressure, protein in the urine and swelling of the extremities. 2 Patients may notice sudden weight gain, headaches and changes in vision, but many women experience no symptoms at all. An Overview of Pregnancy Complications.
What is the blood pressure of a pregnant woman?
Blood pressure is greater than 140 systolic or 90 diastolic. Pregnancy is greater than 20 weeks. There are no other signs of problems with the mother or the baby. Severe preeclampsia is a more serious problem. Diagnosis of severe preeclampsia requires the basic features of mild preeclampsia as well as some indication of additional problems ...
Is there a cure for preeclampsia?
There is no treatment for preeclampsia; the only cure is delivery of the baby. Therefore, the more severe the condition is and the earlier it occurs in a pregnancy, the more difficult it is to manage. Balancing the needs of continued gestation for the baby and the risks the disease poses to both mother and baby is the challenge for women with ...
Can hypertension cause preeclampsia?
Chronic hypertension with superimposed preeclampsia, which is diagnosed in women who had chronic hypertension prior to pregnancy and then develop an exacerbation of their high blood pressure along with protein in the urine or other signs of preeclampsia during pregnancy.
What does a health care provider look for in a preeclampsia test?
Health care providers look for an increase in blood pressure and either protein in the urine, fluid buildup, or both for a diagnosis of superimposed preeclampsia. In addition to tests that might diagnose preeclampsia or similar problems, health care providers may do other tests to assess the health of the mother and fetus, including:
What is the term for a woman who has seizures?
Eclampsia occurs when women with preeclampsia develop seizures. The seizures can happen before or during labor or after the baby is delivered. HELLP syndrome is diagnosed when laboratory tests show hemolysis (burst red blood cells release hemoglobin into the blood plasma), elevated liver enzymes, and low platelets.
What does a health care provider check during pregnancy?
En Español. A health care provider will check a pregnant woman's blood pressure and urine during each prenatal visit. If the blood pressure reading is considered high (140/90 or higher), especially after the 20th week of pregnancy, the health care provider will likely perform blood tests and more extensive lab tests to look for extra protein in ...
When does gestational hypertension occur?
Gestational hypertension occurs when women whose blood pressure levels were normal before pregnancy develop high blood pressure after 20 weeks of pregnancy. Gestational hypertension can progress into preeclampsia. 1.
Can gestational hypertension cause preeclampsia?
Gestational hypertension can progress into preeclampsia. 1. Mild preeclampsia is diagnosed when a pregnant woman has: 2, 3. Systolic blood pressure (top number) of 140 mmHg or higher or diastolic blood pressure (bottom number) of 90 mmHg or higher and either.
When was the last update for preeclampsia?
Preeclampsia Tests. Last Updated on July 12, 2021. Making sense of preeclampsia tests. Preeclampsia, in all of its forms, can mean a lot of testing, both during and after pregnancy.
How long does it take for preeclampsia to show up?
If you do this be sure to record the date and time of each reading. Remember, preeclampsia can appear up to six weeks after delivery even if you haven’t had symptoms during your pregnancy.
What is the blood pressure of a pregnant woman?
High blood pressure is traditionally defined as blood pressure of 140/90 or greater, measured on two separate occasions six hours apart. Severe high blood pressure, which is a reading at or greater than 160/110, requires treatment right away both during pregnancy and in the first weeks after delivery. Urinalysis.
What is a biomarker test for preeclampsia?
There are many biomarker tests being developed to predict or diagnose preeclampsia. While none of these have been widely accepted into practice in the U.S., your provider may use such a test to augment their clinical judgment. One of these tests measures levels of a protein called PAPP-A.
Can preeclampsia cause anemia?
In severe forms of preeclampsia (such as HELLP syndrome), your red blood cells can be damaged or destroyed to produce a type of anemia. Your liver enzymes (the AST and ALT) can rise substantially, and your platelets can fall below the normal range (most often 150,000-400,000) as determined by the laboratory.
Can you do a protein spot check for preeclampsia?
However, the amount of protein doesn’t define how severe the preeclampsia is or may get. Alternatively, your provider may do a "spot check" to immediately check levels of protein compared to creatinine, also an indicator of kidney health.
Is it normal to have a lot of swelling while pregnant?
Weight. Most providers also routinely weigh you to assess whether your weight gain is within the normal range. Although swelling can be normal in pregnancy, swelling in your face and hands and sudden weight gain (three to five pounds or more in a week) sometimes precedes signs of preeclampsia. Optional screening tests.
Overview
Symptoms
Causes
Risk Factors
Complications
- Preeclampsia is a complication of pregnancy. With preeclampsia, you might have high blood pressure, high levels of protein in urine that indicate kidney damage (proteinuria), or other signs of organ damage. Preeclampsia usually begins after 20 weeks of pregnancy in women whose blood pressure had previously been in the standard range. Left untreated...
Prevention
- The defining feature of preeclampsia is high blood pressure, proteinuria, or other signs of damage to the kidneys or other organs. You may have no noticeable symptoms. The first signs of preeclampsia are often detected during routine prenatal visits with a health care provider. Along with high blood pressure, preeclampsia signs and symptoms may include: 1. Excess protein in u…