What consumer surplus means?
consumer surplus, also called social surplus and consumer's surplus, in economics, the difference between the price a consumer pays for an item and the price he would be willing to pay rather than do without it.
What is consumer surplus measure quizlet?
Consumer surplus measures the benefit to buyers of participating in a market. It is measured as the amount a buyer is willing to pay for a good minus the amount a buyer actually pays for it.
What is consumer surplus and its formula?
Consumer surplus = Maximum price buyer is willing to pay – Actual price. The consumer surplus formula for multiple consumers can be expressed as follows: Consumer Surplus = ½ * Demand quantity at equilibrium * (Maximum price buyer is willing to pay – Market price)
What is producer surplus How is it measured?
Producer surplus is the total amount that a producer benefits from producing and selling a quantity of a good at the market price. The total revenue that a producer receives from selling their goods minus the marginal cost of production equals the producer surplus.
How surplus is measured?
The total surplus in a market is a measure of the total wellbeing of all participants in a market. It is the sum of consumer surplus and producer surplus. Consumer surplus is the difference between willingness to pay for a good and the price that consumers actually pay for it.
Which best describes consumer surplus?
Consumer surplus is the difference between the price a consumer pays for an item and the price he/she is willing to pay for the item.
How do you calculate consumer surplus from supply and demand?
3:3314:38Consumers' Surplus from a Demand Function - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipOkay now we will find uh the consumer surplus the formula for a consumer surplus is simply aMoreOkay now we will find uh the consumer surplus the formula for a consumer surplus is simply a consumer surplus is equal to that definite integral from zero to equilibrium quantity. Okay and taking
Why is consumer surplus?
A consumer surplus occurs when a consumer is willing and able to offer more for a particular product that is readily available at a given cost. This economic measurement of consumer benefits occurs when a consumer is paying less than he or she is willing to offer for a particular product at a given period.
How do you measure economic surplus?
How to calculate economic surplus? The easiest way to calculate total economic surplus is to subtract total benefits from total costs. It is equivalent to subtracting marginal benefits from marginal costs. The economic surplus graph depicts a triangle based on the y-axis, reaching equilibrium of supply and demand.
How do you calculate consumer surplus for an entire market?
when calculating consumer surplus for an entire market: calculate the area below the demand curve and above the equilibrium price, from zero to quantity traded.
What does consumer surplus and producer surplus measure?
Consumer Surplus (CS) = A measure of how well off consumers are. Willingness to pay minus the price actually paid. Producer Surplus (PS) = A measure of how well off producers are. Price received minus the cost of production.
How is surplus defined quizlet?
What is Surplus? A market condition existing at any price where the quantity supplied is greater than the quantity demanded.
What is surplus value quizlet?
-Surplus value is the value that remains after the subsistence wages are paid. Surplus value can be created by lengthening the working day: workers work part of the working day toward their subsistence and the rest creating surplus value. Also surplus value can be created by introducing more productive technologies.
What is the law of diminishing marginal utility?
The law of diminishing marginal utility states that as you consume a particular commodity more and more, the utility derived from it keeps on decreasing. For a particular commodity, there exists only one price in a market. For instance, you buy 10 coconuts. The price of a coconut in the market is $10. You pay the same price for all the units you buy. You pay $10 for the first coconut. Obviously, you do not pay $20 for the second. At the same time, the utility you derive from each coconut may differ.
What is consumer surplus?
Prof. Samuelson defines consumer’s surplus as “The gap between the total utility of a good and its total market value is called consumer’s surplus.” In the words of Hicks, “Consumer’s surplus is the difference between the marginal valuation of a unit and the price which is actually paid for it.”
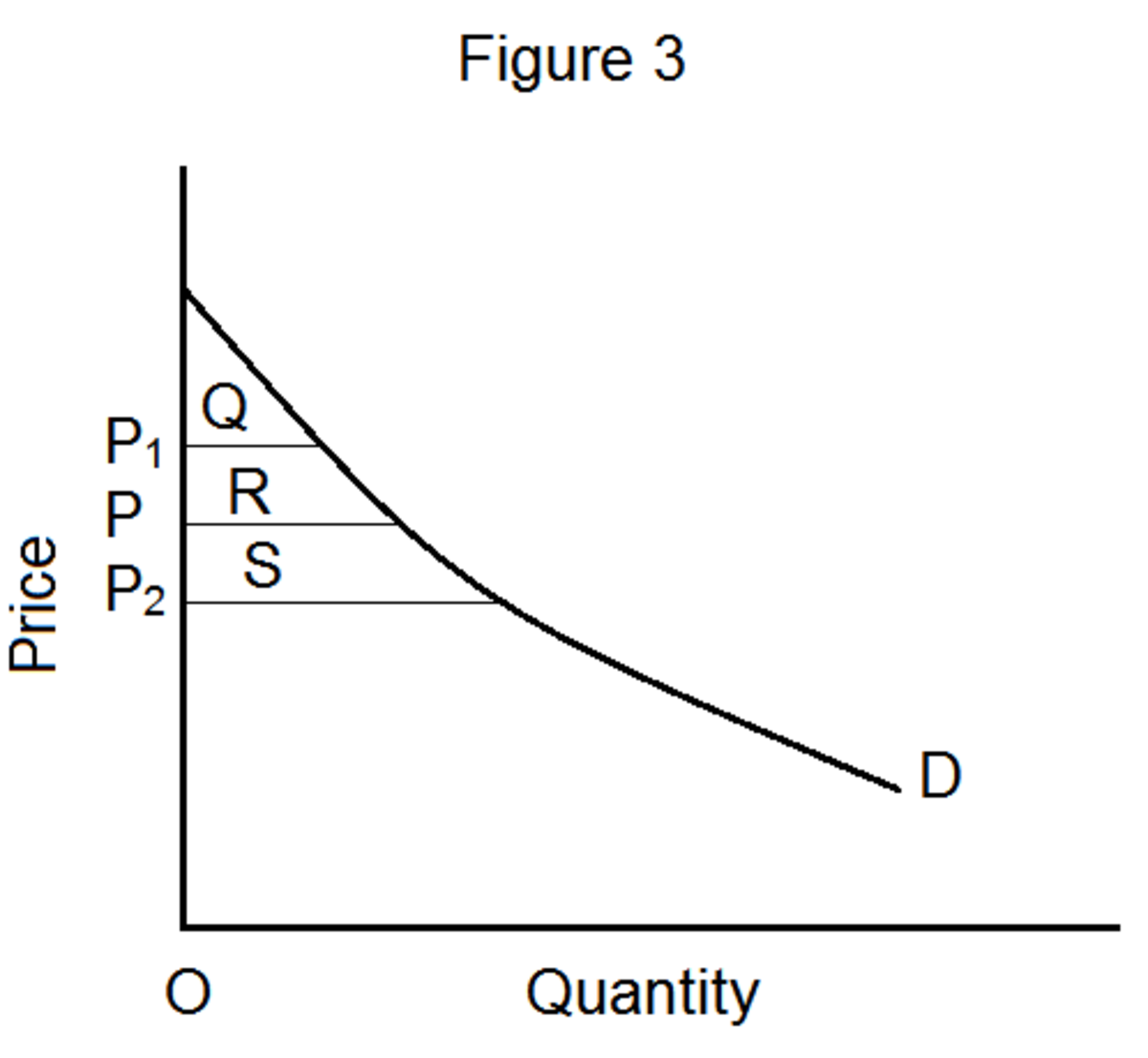
What is the area Q and R?
In figure 3, when the market price for the commodity under consideration is OP, the areas Q and R are consumer’s surplus. If there is an increase an increase in the market price (OP 1 ), the area Q will represent consumer’s surplus. Note that there is a loss of consumer’s surplus equivalent to area R. When the price decreases (OP 2 ), consumer’s surplus increases (area Q + area R + area S).
What does DD mean in a graph?
In figure 2, DD represents market demand curve. It shows the price that the market is willing to pay for the successive units of a commodity. The market offers lower prices for the successive units of the commodity because of the law of diminishing marginal utility. PB denotes market price line. PB is horizontal, which implies that the market price is same for all units of the commodity. The point E represents equilibrium position, where market demand curve intersects market price line. OQ represents the quantity of the commodity that the market purchases given the equilibrium position.
Why do you pay $10 for a commodity?
You are willing to pay $10 for the commodity because you feel that the commodity is worth $10. It implies that the total utility derived from the commodity is equal to $10. However, you are able to buy the commodity for $5.
What is the relationship between market price and consumer surplus?
An inverse relationship means that a decline in market price increases consumer’s surplus and vice-versa.
What is the second important assumption?
The second important assumption is that the commodity under consideration does not have substitutes.
.png)
What Is Consumer Surplus?
Producer Surplus vs. Consumer Surplus
Measuring Consumer Surplus
- There are many points where the price that consumers are ready to pay for a good is lower than the price at which producers are ready to sell before the intersection of the supply and demand curves. At the market price, both consumers and producers benefit from a surplus. Consumers who are willing to pay more only pay the market rate, but producers who are willing to sell at a lo…
Relationship Between Consumer Surplus and Demand
- When demand for a product is perfectly inelastic, consumer surplus is zero. This is because consumers are ready to match the price of the goods. When demand is highly elastic, consumer surplus is infinite because a change in the item price has little impact on demand. This may include necessities, such as food and water. Demand curves are typically downward sloping bec…
Assumptions of The Consumer Surplus Theory
- Here are some assumptions of the consumer surplus theory: 1. The utility is a quantifiable entity.The consumer surplus theory bases the notion that you can measure the value of utility by quantifying it. The usefulness of an apple, for example, is 15 units. 2. No substitutes are available.There are no viable alternatives to any of the goods in ques...