"Utility maximization" is a term that is used to describe the efforts of the consumer to obtain the greatest degree of utility or value from a purchase, while keeping the cost of that purchase as low as possible.
How to calculate utility maximization?
b. utility maximizing rule: MBx = MUx/Px The MB of product X can be measured by finding the MU per dollar spent on product X Why divide by price? because you cannot compare a $1 beer with a $3 steak sandwich dividing by price means that we are comparing a dollar's worth of beer with a dollar's worth of a steack sandwich MCx = MUy/Py
What does maximize utility mean?
Utility maximization requires seeking the greatest total utility from a given budget. Utility is maximized when total outlays equal the budget available and when the ratios of marginal utility to price are equal for all goods and services a consumer consumes; this is the utility-maximizing condition.
How does money help in maximizing utility?
How does money help in maximizing utility? Money enables consumers in making payments for goods and services of their needs. It provides freedom of choice of consumption. On the basis of prices of various goods and services, consumers are able to allocate their income in such a way so that they can derive maximum utility from their consumption.
Why wealth maximization is better than profit maximization?
Wealth maximization involves the consideration of risks and uncertainty whereas profit maximization ignores all such factors. The main objective of company should of wealth maximization rather than profit maximization as there is always risk associated in achieving profit. The risk can be neglected in short run but cannot be ignored in long run.
What is a utility maximizing consumer?
Understanding Utility Maximization The consumer may consider purchasing more of one item and less of another. Through maximizing utility, the consumer will buy an item that produces the greatest marginal utility with the least amount of spending.
What is utility maximization example?
Utility maximization means making economic decisions that guarantee the highest level of consumer satisfaction (benefit). An example is when a consumer decides to purchase more of "Product A" and less of "Product B" because this combination guarantees more benefit (utility) per dollar.
What is consumer utility?
Economists use the term utility to describe the pleasure or satisfaction that a consumer obtains from his or her consumption of goods and services. Utility is a subjective measure of pleasure or satisfaction that varies from individual to individual according to each individual's preferences.
Where is the utility maximizing point found for a consumer?
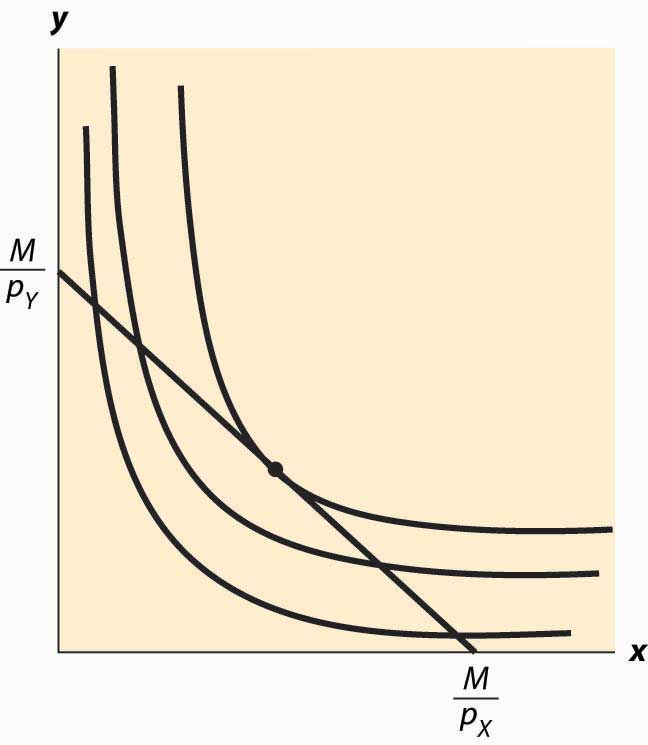
Utlity Maximization Given the goal of consumers is to maximize utility given their budget constraints, they seek that combination of goods that allows them to reach the highest indifference curve given their budget constraint. This occurs where the indifference curve is tangent to the budget constraint (combination A).
How do you do utility maximization?
A Rule for maximizing Utility If a consumer wants to maximize total utility, for every dollar that they spend, they should spend it on the item which yields the greatest marginal utility per dollar of expenditure.
What are the two conditions for maximizing utility?
Utility is maximized when total outlays equal the budget available and when the ratios of marginal utilities to prices are equal for all goods and services.
How is consumer utility measured?
Total utility measures the satisfaction or benefits a person gets from the total consumption—including marginal utility—of a product or service. If consuming 10 units of a product yields 20 utils, and consuming one additional unit yields 1 util, the total utility is 21 utils. If consuming another unit yields .
What are the 4 types of utility in marketing?
The Four Components of the Utility Marketing ModelThe utility marketing model helps business owners design marketing campaigns that appeal to the psychological motivations that drive consumers to make purchases. ... Form Utility. ... Time Utility. ... Place Utility. ... Possession Utility.
What are the example of utilities?
Utility services include telecommunications, electrical utilities, natural gas, certain transportation services, and also water and wastewater treatment services provided by private companies.
What are the four assumptions about utility maximization?
In economics, utility theory governs individual decision making. The student must understand an intuitive explanation for the assumptions: completeness, monotonicity, mix-is-better, and rationality (also called transitivity).
How do you solve utility maximization problems?
0:315:40General Solution: Cobb-Douglas Utility Maximization - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipOr the marsh utility of good ax divided by the marsh utility of good Y that's the marginal rate ofMoreOr the marsh utility of good ax divided by the marsh utility of good Y that's the marginal rate of substitution. And that equals the ratio of the prices.
How does utility maximization affect the demand curve?
Choices that maximize utility—that is, choices that follow the marginal decision rule—generally produce downward-sloping demand curves.
Which scenario would be an example of the law of diminishing marginal utility?
For example, an individual might buy a certain type of chocolate for a while. Soon, they may buy less and choose another type of chocolate or buy cookies instead because the satisfaction they were initially getting from the chocolate is diminishing.
How does the utility maximizing rule work in household choice of products?
The Utility Maximization rule states: consumers decide to allocate their money incomes so that the last dollar spent on each product purchased yields the same amount of extra marginal utility.
What does utility mean in economics?
the usefulness or enjoymentUtility, in economics, refers to the usefulness or enjoyment a consumer can get from a service or good. Although the concept of utility is abstract, it is a useful way to explain how and why consumers make their decisions. "Ordinal" utility refers to the concept of one good being more useful or desirable than another.
How do you calculate utility maximizing bundles?
To find the consumption bundle that maximizes utility you need to first realize that this consumption bundle is one where the slope of the indifference curve (MUx/MUy) is equal to the slope of the budget line (Px/Py) in absolute value terms. You know MUx = Y and MUy = X, so MUx/MUy = Y/X. You know that Px/Py = 2/4=1/2.
What is maximization of utility?
The maximization of utility derived from the consumption of a given product is best understood with the understanding of the consumer demand as explained above. It should be understood that all consumers are rational in their choices especially those that directly affect their satisfaction during or after the consumption process.
How to maximize utility?
In order to maximize utility, consumers purchase a given product bundle (combination) as compared to the purchase of more of only one single product that would meet their needs. Therefore, instead of spending all the money on one product only, consumer usually spread their money on a number of products that have different utilities in order to maximize the outcome.
What is consumer utility?
211), consumer’s utility is the satisfaction that a consumer could derive from consuming a given set of products in the market. The concept is abstract rather than concrete or any other thing that could be observed.
Why does the threshold of satisfaction derived from consuming any additional unit of a product or service do not receive similar?
In summary, the total utility of the consumer would increase at a reducing pace as the consumption of the product/service increases.
What is total utility?
Therefore, as noted by Wayne & Hoyer (2008, p, 75), the total utility of a consumer corresponds to the total satisfaction derived from the consumption of a given product or service. Another economic concept related to this is the marginal utility, which is used to denote the additional fulfillment that a consumer derives from a given extra unit-consumption of a given product.
Why are consumers rational?
All consumers of any product and services are also considered rational as they always seek to maximize their utility given their budget constraints. The forces of demand and supply are significant in our understanding of the utility of a consumed derived from consumption of a given product or service.
How is the demand curve determined?
As indicated above, the demand of a given product is determined by the needs to be fulfilled. Goods are exchanged in the market using a given medium of exchange that is in most cases money. Due to their unlimited nature, needs create the demand curve that indicates the quantity of goods that consumers demand in a given market at given prices.
What is utility maximization?
This approach allows the company to secure items essential to the operation, but at a lower cost. In this manner, the utility maximization involves saving money while still securing enough of the products to make the effort cost-effective for the business.
Why is automobile marketing so focused on utilities?
Automobile marketing may be focused on added utilities, because consumers are willing to pay extra for features they will use.
What is utility maximizing?
Choices that maximize utility—that is, choices that follow the marginal decision rule—generally produce downward-sloping demand curves. This section shows how an individual’s utility-maximizing choices can lead to a demand curve.
Why is it important to distinguish the effects of the demand curve?
First, the reduction in the price of apples made them cheaper relative to oranges . Before the price change, it cost the same amount to buy 2 pounds of oranges or 1 pound of apples.
How to determine Mary Andrews' demand curve?
Mary Andrews’s demand curve for apples, d, can be derived by determining the quantities of apples she will buy at each price. Those quantities are determined by the application of the marginal decision rule to utility maximization. At a price of $2 per pound, Ms. Andrews maximizes utility by purchasing 5 pounds of apples per month. When the price of apples falls to $1 per pound, the quantity of apples at which she maximizes utility increases to 12 pounds per month.
Why do consumers substitute inferior goods for other goods?
Consumers will substitute more of the inferior good for other goods because its price has fallen relative to those goods. The quantity demanded increases as a result of the substitution effect.
What does individual demand curves mean?
Individual demand curves, then, reflect utility-maximizing adjustment by consumers to various market prices. Once again, we see that as the price falls, consumers tend to buy more of a good. Demand curves are downward-sloping as the law of demand asserts.
What is substitution effect?
The substitution effect always involves a change in consumption in a direction opposite that of the price change. When a consumer is maximizing utility, the ratio of marginal utility to price is the same for all goods. An income-compensated price reduction increases the extra utility per dollar available from the good whose price has fallen; a consumer will thus purchase more of it. An income-compensated price increase reduces the extra utility per dollar from the good; the consumer will purchase less of it.
What is utility maximization?
In utility maximization, consumers strive to spend money in ways that provide the greatest amount of resources and satisfaction for the least cost. Learn about budget constraints and consumer choices in the context of utility maximization, review utility as it pertains to consumers, and understand why consumers care about this and the impact if they ignore it. Updated: 11/05/2021
Why Do Consumers Care?
In the example above, your basic needs are taken care of, but that doesn't mean that you don't have to care about utility. Say that the choice for Friday night is between a show of student bands put on by the college activities council and a concert by your favorite band. The student show is free, but the concert is $50 a ticket. Unless you have a really good reason to go to the student show, chances are you will be inclined to spend that $50 on concert tickets. Now, you couldn't do that if you earlier skipped through the quad throwing money at random people, could you? By paying attention to the utility that your resources can bring you, you can make sure you're at the concert where you want to be.
How are spending decisions determined?
Your spending decisions are determined by the amount of utility, or usefulness, you'll find in a given activity. As you may remember, economists assume that people act to maximize their utility with their resources, and in this case, your version of resources is your paycheck.
Is it bad to ignore utility?
Ignoring utility isn't bad for consumers because it leads to people throwing money in the air while at a nightclub - it is bad because it leads to disappointment and unrealized maximization of utility. In this lesson, we focused on the importance of utility for consumers.
Who developed the utility maximization problem?
Utility maximization was first developed by utilitarian philosophers Jeremy Bentham and John Stewart Mill. In microeconomics, the utility maximization problem is the problem consumers face: "How should I spend my money in order to maximize my utility ?" It is a type of optimal decision problem. It consists of choosing how much of each available good or service to consume, taking into account a constraint on total spending (income), the prices of the goods and their preferences .
What is the relationship between the utility function and Marshallian demand in the utility maximisation problem?
The relationship between the utility function and Marshallian demand in the utility maximisation problem mirrors the relationship between the expenditure function and Hicksian demand in the expenditure minimisation problem. In expenditure minimisation the utility level is given and well as the prices of goods, the role of the consumer is to find a minimum level of expenditure required to reach this utility level.
What happens to the consumer's budget line when income is increased?
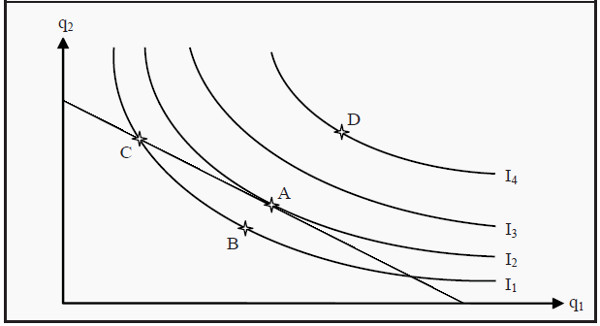
If the consumers income is increased their budget line is shifted outwards ands they now have more income to spend on either good x, good y, or both depending on their preferences for each good. if both goods x and y were normal goods then consumption of both goods would increase and the optimal bundle would move from A to C (see figure 5). If either x or y were inferior goods, then demand for these would decrease as income rises (the optimal bundle would be at point B or C).
What happens to the consumption of goods when prices change?
When the prices of goods change, the optimal consumption of these goods will depend on the substitution and income effects. The substitution effect says that if the demand for both goods is homogenous, when the price of one good decreases (holding the price of the other good constant) the consumer will consume more of this good and less of the other as it becomes relatively cheeper. The same goes if the price of one good increases, consumers will buy less of that good and more of the other.
What is utilitarian social choice?
The utilitarian social choice rule is a rule that says that society should choose the alternative that maximizes the sum of utilities. While utility-maximization is done by individuals, utility-sum maximization is done by society.
Why do consumers pick bundles?
Because consumers are rational , they seek to extract the most benefit for themselves. However, due to bounded rationality and other biases , consumers sometimes pick bundles that do not necessarily maximize their utility.
What is utility maximizing choice?
This argument can be written as another rule: the utility-maximizing choice between consumption goods occurs where the marginal utility per dollar is the same for both goods, and the consumer has exhausted his or her budget.
What is consumer equilibrium?
The problem of finding consumer equilibrium, that is, the combination of goods and services that will maximize an individual’s total utility, comes down to comparing the trade-offs between one affordable combination (shown by a point on the budget line in Figure 1, below) with all the other affordable combinations.
Does a sensible economist pay twice as much for something?
A sensible economizer will pay twice as much for something only if, in the marginal comparison, the item confers twice as much utility. Notice that the formula for the table above is

Utility Maximization and Scarcity
Demand
- As indicated above, the demand of a given product is determined by the needs to be fulfilled. Goods are exchanged in the market using a given medium of exchange that is in most cases money. Due to their unlimited nature, needs create the demand curve that indicates the quantity of goods that consumers demand in a given market at given prices. The demand schedule is used …
Supply
- The supply is determined by the availability of economic resources that are scarce. Suppliers also supply products in a market given the compensation to be received in terms of price that is usually in monetary terms. Based on the compensation received, a demand schedule can be used to develop a demand curve that indicates the amount of goods that suppliers are able and willin…
Utility
- According to Kehoe & Prescott (2007, P. 211), consumer’s utility is the satisfaction that a consumer could derive from consuming a given set of products in the market. The concept is abstract rather than concrete or any other thing that could be observed. Therefore, the amount of units assigned to the utility of consuming a given product in the market are given arbitrarily rath…
Utility Maximization
- The maximization of utility derived from the consumption of a given product is best understood with the understanding of the consumer demand as explained above. It should be understood that all consumers are rational in their choices especially those that directly affect their satisfaction during or after the consumption process. In order to maximi...
List of References
- Blackwell, D, Miniard W & Engel F 2006, Consumer behavior,Thompsons publishers, South Western. Kehoe, T & Prescott, E 2007, Great Depressions of the Twentieth Century,Federal Reserve Bank of Minneapolis, Minneapolis. Vance, D 2003, Financial Analysis & Decision Making, McGraw-Hill, New York. Wayne, D & Hoyer, M 2008, Consumer behavior,Cangage Learning, Sout…