
Contiguous namespace for example, refers to the concept that Domains in an Active Directory all share a common namespace. You create a disjointed name space as you add trees into your AD instance. Each tree has its own contiguous namespace.
What is contiguous namespace in AD?
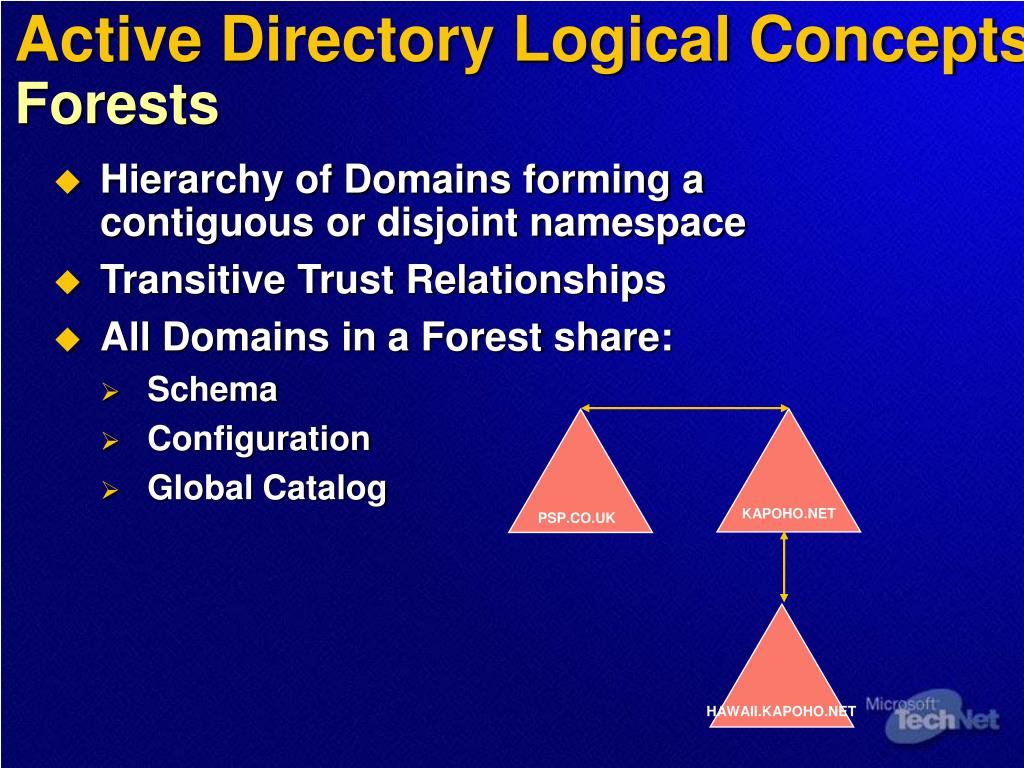
Contiguous namespace for example, refers to the concept that Domains in an Active Directory all share a common namespace. You create a disjointed name space as you add trees into your AD instance. Each tree has its own contiguous namespace. See example below that shows two trees in an Active Directory forest. Notice the namespace of each tree.
What is an active directory tree?
Active Directory uses trees and forests. Active Directory uses DNS domains to define its namespace. As we've seen, a standard LDAP hierarchy conforms to a contiguous namespace called a Directory Information Tree. An Active Directory namespace that follows a contiguous namespace is also called a tree (see Figure 6.11 ).
What is the difference between domain and forest in Active Directory?
– A forest is a group of trees that do not share a contiguous namespace. Domain: A domain is defined as a logical group of network objects (computers, users, devices) that share the same Active Directory database. – When you add a domain to an existing tree, the new domain is a child domain of an existing parent domain.
When are multiple domains in the same namespace considered to be?
When you have multiple domains in the same namespace (e.g., techdirect.local, zone.techdirect.local), they are considered to be in the same tree. The tree also supports multiple levels of domains.
What is contiguous DNS namespace?
A contiguous namespace links a child container to its parent by adding one and only one more identifier to the beginning of the DNS name. For example, if the parent Domain was named COMPANY and the child Domain was named AMERICA. COMPANY, then these two domains would form a contiguous namespace.
What is a namespace in Active Directory?
In Active Directory, a domain defines a separate namespace, a separate security structure, a separate management structure, and a separate naming context. The Active Directory database is hosted on domain controllers. Users and computers are members of a domain.
What is a set of Active Directory domains that share a contiguous namespace called?
tree. a group of related domains that share the same contiguous DNS namespace.
What is a disjointed namespace?
Disjoint namespace is a scenario in which a computer's primary domain name system (DNS) suffix doesn't match the DNS domain name where that computer resides. The word disjoint is a synonym for separate. The computer with the suffix that doesn't match is called the disjoint.
What are the two types of DFS namespace?
When creating a namespace, you must choose one of two namespace types: a stand-alone namespace or a domain-based namespace.
What is the purpose of a namespace?
A namespace is a declarative region that provides a scope to the identifiers (the names of types, functions, variables, etc) inside it. Namespaces are used to organize code into logical groups and to prevent name collisions that can occur especially when your code base includes multiple libraries.
What is tree and forest in Active Directory?
An Active Directory (AD) tree is a collection of domains within a Microsoft Active Directory network. The term refers to the fact that each domain has exactly one parent, leading to a hierarchical tree structure. A group of AD trees is known as a forest.
What is domain tree in Active Directory?
A domain tree is made up of several domains that share a common schema and configuration, forming a contiguous namespace. Domains in a tree are also linked together by trust relationships. Active Directory is a set of one or more trees.
What is the difference between domain tree and forest?
A forest is a collection of one or more domain trees. The domains in the movie.edu domain tree and the example.com domain tree could be part of the same forest. A domain tree is based on a common namespace, but a forest is not. A forest is named after the first domain created in the forest.
What is NetBIOS in Active Directory?
NetBIOS domain name: Typically, the NetBIOS domain name is the subdomain of the DNS domain name. For example, if the DNS domain name is contoso.com, the NetBIOS domain name is contoso. If the DNS domain name is corp.contoso.com, the NetBIOS domain name is corp.
What is NetBIOS name?
NetBIOS (Network Basic Input/Output System) is a network service that enables applications on different computers to communicate with each other across a local area network (LAN). It was developed in the 1980s for use on early, IBM-developed PC networks.
How do I find the NetBIOS name of a domain?
StepsLog into the Active Directory server.Navigate to Start > Programs > Active Directory Users and Computers.For the example below, paloaltonetworks. lab is the DNS domain name.Right-click the name, then select Properties.Under General, the Domain name displays the NetBIOS domain name.
What is namespace in domain?
A namespace is a context within which the names of all objects must be unambiguously resolvable. For example, the internet is a single DNS name space, within which all network devices with a DNS name can be resolved to a particular address (for example, www.microsoft.com resolves to 207.46.
What is namespace example?
Prominent examples for namespaces include file systems, which assign names to files. Some programming languages organize their variables and subroutines in namespaces. Computer networks and distributed systems assign names to resources, such as computers, printers, websites, and remote files.
What is a namespace server?
A namespace server is a domain controller or member server that hosts a namespace. The number of namespaces you can host on a server is determined by the operating system running on the namespace server.
How does DFS namespace work?
DFS Namespaces and DFS Replication are role services in the File and Storage Services role. DFS Namespaces Enables you to group shared folders that are located on different servers into one or more logically structured namespaces. Each namespace appears to users as a single shared folder with a series of subfolders.
What is domain in Active Directory?
In Active Directory, a domain defines a separate namespace, a separate security structure, a separate management structure, and a separate naming context. The Active Directory database is hosted on domain controllers. Users and computers are members of a domain.
How many objects can an Active Directory database hold?
Active Directory is capable of holding a billion objects. This is enough to hold account, computer, mailboxes, and group memberships for every person in the western hemisphere. A big Active Directory database is like an NBA center, though.
Why do domain controllers register SRV records?
They also return referrals to clients to ensure that clients use a local domain controller for authentication and LDAP queries. This “localization” feature is possible because each site is associated with one or more IP networks connected by Site Links. A domain controller can read the IP address of a client and determine the site it should designate when making DNS requests for SRV records.
Why is Sysvol on NTFS?
Sysvol must be on an NTFS volume because folders within Sysvol use reparse points, which are only supported by NTFS.
How does LDAP search work?
In a standard LDAP search involving multiple naming contexts hosted by multiple servers, the servers pass referrals to the client, and the clients walk the tree to get information from the various servers. This process of query and referral consumes time and bandwidth. And if one of those domain controllers is at the wrong end of a 56K line oversubscribed with users downloading MP3s, the search might take a while.
What is schema naming context?
The Schema naming context holds ClassSchema and AttributeSchema objects that represent the various classes and attributes in Active Directory. If this sounds like a circular definition, it's meant to be. Unlike some directory services that load the schema in a separate file, the Active Directory schema is completely self-referential.
What is the new feature in Windows Server 2003?
A new feature in Windows Server 2003 is the ability to create additional naming contexts that can be placed on specific domain controllers. Microsoft uses this feature to store DNS resource records for Active Directory Integrated zones.
What is an example of a company with an Active Directory domain?
An example of this is a company with an Active Directory domain of corp.contoso.com that uses DNS zones such as hr.corp.contoso.com, production.corp.contoso.com, and it.corp.contoso.com.
What are the disadvantages of using a disjoint namespace?
Using a disjoint namespace can have the following disadvantages: You must create and manage separate DNS zones for each Active Directory domain in the forest that has member computers that use a disjoint namespace. (That is, it requires an additional and more complex configuration.)
What is a domain member?
Domain member computers, including domain controllers, can function in a disjoint namespace. Domain member computers can register their host (A) resource record and IP version 6 (IPv6) host (AAAA) resource record in a disjoint DNS namespace. When domain member computers register their resource records in this way, domain controllers continue to register global and site-specific service (SRV) resource records in the DNS zone that is identical to the Active Directory domain name.
Why use a disjoint namespace?
Using a disjoint namespace can have the following advantages: Because the primary DNS suffix of a computer can indicate different information, you can manage the DNS namespace separately from the Active Directory domain name . You can separate the DNS namespace based on business structure or geographical location.
What is a disjoint DNS?
As previously mentioned, a disjoint namespace can cause problems for any applications and services that are written to assume that a computer primary DNS suffix is identical to the name of the domain name of which it is a member. Before you deploy a disjoint namespace, you must check applications for compatibility issues. Also, be sure to check the compatibility of all applications that you use when you perform your analysis. This includes applications from Microsoft and from other software developers.
What is the domain controller for a domain named na.corp.fabrikam.com?
For example, assume that a domain controller for the Active Directory domain named na.corp.fabrikam.com that uses a primary DNS suffix of corp.fabrikam.com registers host (A) and IPv6 host (AAAA) resource records in the corp.fabrikam.com DNS zone. The domain controller continues to register global and site-specific service (SRV) resource records in the _msdcs.na.corp.fabrikam.com and na.corp.fabrikam.com DNS zones, which makes service location possible.
Is DNS suffix the same as Active Directory?
Network applications that are written to assume that the Active Directory namespace is identical to the primary DNS suffix for all domain member computers do not function properly in a disjoint namespace.
What is a disjointed namespace?
Disjointed namespaces contain domains that are interrelated but that don't share common root names. For example, if you have related resources in ecg.com and ecg.net, the namespaces are considered disjointed.
What is the purpose of Active Directory?
Active Directory makes use of DNS to resolve network names and server locations. AD itself is based around and can use LDAP (Lightweight Directory Access Protocol) for the basis of its directory schema and access. Good things come in trees.
What is AD tree?
AD trees consist of a group of domains that share the same schema and configuration. Domains in a directory tree all have a contiguous namespace. In contrast, a forest contains one or more sets of trees that don't form a contiguous namespace.
What is the global catalog in AD?
The global catalog contains a list of all the objects from all the domains in the entire AD tree. It also contains a few of the properties from each object. (An administrator can change the index criteria.) This global catalog is then distributed to all servers in the AD.
What is AD in network?
AD has been designed to centralize all of the user, group, application, printer, and computer information on your network in one repository. Rather than having to administer many different domains and trust relationships between them, all network information can be placed in AD.
What is a site in Microsoft?
A site is a collection of workstations and servers along subnets with fast connections. Within a site, NT replicates information after a regularly defined time. Between sites, NT replicates data only at selected times or events to minimize WAN traffic.
What is domain model in Windows 2000?
AD drops the concept of Primary Domain Controllers (PDCs) and Backup Domain Controllers (BDCs) within domains. Instead, all domain controllers (DCs) act as peers with one another, allowing you to make changes to the database of any server in the tree. All changes are forwarded to all servers throughout the network in what Microsoft calls a multi-master replication. This can make for a lot of network traffic, and special consideration should be made for slow wide area network (WAN) links.
Why do proxy clients not require external name resolution?
Web proxy clients, for example, don't require external name resolution because the proxy server does this on their behalf. Overlapping internal and external namespaces aren't recommended.
What should be included in external DNS?
External servers should include only those names that you want to be visible to the Internet. Internal servers should contain names that are for internal use. You can set your internal DNS servers to forward requests that they can't resolve to external servers for resolution.
Is DNS already in place?
However, in some cases, the DNS namespace may already be in place . In such a configuration, the Active Directory environment should be designed independently and then implemented either as a separate namespace or as a subdomain of the existing namespace.
Can a root server be created unintentionally?
Make sure that root servers aren't created unintentionally. Root servers may be created by the Dcpromo Wizard, resulting in internal clients being able to reach external clients or to reach parent domains. If the "." zone exists, a root server has been created. It may be necessary to remove this for proper name resolution to work.
Can you use a subdomain of a company name?
Use different internal and external namespaces. Internally, you could use comp .com or a subdomain of the external name such as corp. company .com. The subdomain structure could be useful if you already have an existing DNS namespace. Different locations or organizations can be named with different subdomains such as nameone. corp. company .com or nametwo. corp. company .com to ease administration.
What are Active Directory Domain Services (AD DS)?
In addition to simplifying the management of groups of network objects, Active Directory also provides crucial security services in the form of AD DS. These services include:
What is the Active Directory framework?
In the Active Directory framework, objects are grouped into hierarchies that determine how they can be viewed, who can access them, and how they can be modified by the administrator.
What is trust in Active Directory?
Active Directory uses rules called Trusts to allow users in a given domain to access resources in another domain. There are many different types of trust rules that grant varying levels of access and permissions to users.
What is the unique identification associated with each network object?
The unique identification associated with each network object is also known as its characterization schema. These schemas determine how each object will be used in the network. When network administrators modify a schema in an active directory, the changes automatically propagate throughout the system.
Why create additional domains?
Reasons to create Additional domain: There will be many occasions in which you will need to create additional domains. Multiple domains are useful when you are dealing with - Different password requirements between organizations - Large numbers of objects - Different internet domain names - Better control of replication - Decentralized network administration
How are domains identified in deployment?
The objects for a single domain are stored in a single database (which can be replicated). Domains are identified by their DNS name structure, (namespace).
What is a domain in a tree?
Domain: A domain is defined as a logical group of network objects (computers, users, devices) that share the same Active Directory database. – When you add a domain to an existing tree, the new domain is a child domain of an existing parent domain. Tree: A tree is a collection of one or more domains and domain trees in a contiguous namespace, ...
How are parent and child domains linked?
Some other information to note. – Parent and child domains are automatically linked by a trust. Users in different domains can use these trusts to access resources in another domain assuming that they have access. Trees in the forest are linked together via a trust automatically.
What is the framework that holds objects?
The framework that holds the objects can be viewed at different levels namely forest, domain trees, and domains. An Active Directory framework can have more than one domain, and the above tiers are referred to a forest. See the following guides for other information.
What is an AD?
Active Directory (AD) is a directory service developed by Microsoft for the Windows domain environment. Active Directory forest is the top container in an Active Directory setup that contains domains, users, computers, and group policies. The Active Directory structure is built on the domain level. The framework that holds the objects can be viewed at different levels namely forest, domain trees, and domains. An Active Directory framework can have more than one domain, and the above tiers are referred to a forest. See the following guides for other information. What are the differences between Universal, Global, and Domain Local Group Scopes, and Differences between Active Directory Lightweight Directory Services and Active Directory Domain Services, What are Active Directory Forest, Trees, Domain, and Sites, and how to add a second Domain Controller to your environment?
Can you have multiple trees in an Active Directory domain?
Note: Under each domain, you can have as many trees as possible. Having an Active Directory environment of this nature can create autonomy and segregation of duty thereby increasing security and if not configured correctly, it can also lead to exploitation in the Active Directory environment.
What are the components of Active Directory?
The Active Directory structure is comprised of three main components: domains, trees, and forests.
What is Active Directory?
Active Directory is a Microsoft product and runs on Windows Server operating systems. It includes several services to manage permissions and provides access to resources in a network.
How Does Active Directory Work?
When you begin installing a Windows computer, all the systems are workgroups or standalone computers. There’s no domain present at this stage. Such an environment includes several systems, workstations, or servers with separate passwords and usernames.
Why is Active Directory important?
Active Directory is one of the most important IT infrastructure tools, and it helps admins manage user provisioning processes, security, and audits and provides access to each user’s account from a single location. With the help of Active Directory, users can be organized logically into groups and subgroups to provide access control.
How does Active Directory maintain consistency?
Large organizations normally have multiple domain controllers, so admins must ensure all the domain controllers contain the same information. To maintain consistency, Active Directory implements synchronization mechanisms to ensure all domain controllers have consistent data.
What is AD DS?
AD DS can be considered the main service of Active Directory; it stores directory information and takes care of the interaction between the user and the domain. When a user tries to connect to a device, server, or resource over a network, AD DS checks the login credentials and access permissions given to the user.
What is AD management?
AD management is also a part of the network or server monitoring and management processes. Active Directory monitoring can help automate Active Directory user provisioning processes, comply with regulations and audits, provide security, and grant access to users’ accounts from a central location.
Application Compatibility
Advantages of Disjoint Namespaces
- Using a disjoint namespace can have the following advantages: 1. Because the primary DNS suffix of a computer can indicate different information, you can manage the DNS namespace separately from the Active Directory domain name. 2. You can separate the DNS namespace based on business structure or geographical location. For example, you can separate...
Disadvantages of Disjoint Namespaces
- Using a disjoint namespace can have the following disadvantages: 1. You must create and manage separate DNS zones for each Active Directory domain in the forest that has member computers that use a disjoint namespace. (That is, it requires an additional and more complex configuration.) 2. You must perform manual steps to modify and manage the Active Directory at…
Planning A Namespace Transition
- Before you modify a namespace, review the following considerations, which apply to transitions from contiguous namespaces to disjoint namespaces (or the reverse): 1. Manually configured Service Principal Names (SPNs) may no longer match DNS names after a namespace change. This can cause authentication failures.For more information, see Service Logons Fail Due to Inc…
Planning For Disjoint Namespace Deployments
- Take the following precautions if you deploy computers in an environment that has a disjoint namespace: 1. Notify all software vendors with whom you do business that they must test and support a disjoint namespace. Ask them to verify that they support their applications in environments that use disjoint namespaces. 2. Test all versions of operating systems and appli…