The definition of contraction is the lengthening or shortening of a muscle fiber or a word formed by combining the sounds of two longer words. An example of a contraction is the action of the uterus during the birth process.
What are the signs of contractions?
Mar 24, 2020 · The definition of contraction is the lengthening or shortening of a muscle fiber or a word formed by combining the sounds of two longer words. An example of a contraction is the action of the uterus during the birth process.
What are common contractions?
Concentric contraction is a type of muscle activity that generates tension and force to move an object as the muscle shortens. Cross-bridge cycling between actin and myosin myofilaments and shortening of sarcomeres occur in concentric contraction. This is the most common type of muscle contraction in our body.
What is the scientific definition of contraction?
Sep 01, 2020 · A muscle contraction is an increase in the tension or a decrease in the length of a muscle. Muscle tension is the force exerted by the muscle on a bone or other object. A muscle contraction is isometric if muscle tension changes, but muscle length remains the same. An example of isometric muscle contraction is holding a book in the same position.
When will that expansion or contraction end?
Dec 05, 2021 · The definition of contraction is the lengthening or shortening of a muscle fiber or a word formed by combining the sounds of two longer words. An example of a contraction is the action of the uterus during the birth process. An example of a contraction is the word doesn’t from does not. noun.

What does contraction in science mean?
Scientific definitions for contraction The shortening and thickening of a muscle for the purpose of exerting force on or causing movement of a body part. See more at muscle.
What is contraction in very short answer?
Contractions, which are sometimes called 'short forms', commonly combine a pronoun or noun and a verb, or a verb and not, in a shorter form. Contractions are usually not appropriate in formal writing.6 days ago
What is contraction process?
Abstract. Muscle contraction occurs when the thin actin and thick myosin filaments slide past each other. It is generally assumed that this process is driven by cross-bridges which extend from the myosin filaments and cyclically interact with the actin filaments as ATP is hydrolysed.
What is contraction in cells?
Muscle contraction thus results from an interaction between the actin and myosin filaments that generates their movement relative to one another. The molecular basis for this interaction is the binding of myosin to actin filaments, allowing myosin to function as a motor that drives filament sliding.
What is contraction and example?
A contraction is a shortened form of a word (or group of words) that omits certain letters or sounds. In most contractions, an apostrophe represents the missing letters. The most common contractions are made up of verbs, auxiliaries, or modals attached to other words: He would=He'd. I have=I've.
What is contraction words list?
Here are some common contractions and the groups of words that they represent.aren't → are not.there's → there is; there has.can't → can not.they'd → they had; they would.couldn't → could not.they'll → they will; they shall.didn't → did not.they're → they are.More items...
What is muscle contraction physiology?
Muscle contraction is the activation of tension-generating sites within muscle cells. In physiology, muscle contraction does not necessarily mean muscle shortening because muscle tension can be produced without changes in muscle length, such as when holding a heavy book or a dumbbell at the same position.
How do you explain muscle contraction?
Muscle contraction is the tightening, shortening, or lengthening of muscles when you do some activity. It can happen when you hold or pick up something, or when you stretch or exercise with weights. Muscle contraction is often followed by muscle relaxation, when contracted muscles return to their normal state.Oct 25, 2021
What is muscle contraction Class 11?
During the muscle contraction, the thin actin and thick myosin filaments slide past each other. The process is done by cross-bridges which is extended from the myosin filaments. The contractile unit of muscle is said to be the sarcomere. At the end of the sarcomere, actin filaments are attached to the Z disc.Jan 16, 2021
What allows movement in a cell?
In addition to playing this structural role, the cytoskeleton is responsible for cell movements. These include not only the movements of entire cells, but also the internal transport of organelles and other structures (such as mitotic chromosomes) through the cytoplasm.
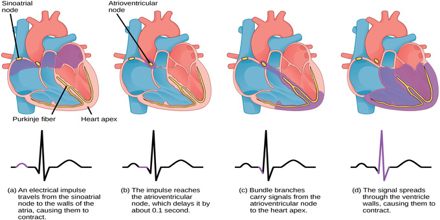
What are the heart muscles?
The muscle layer of the heart is termed the myocardium and is made up of cardiomyocytes. The myocardium is found in the walls of all four chambers of the heart, though it is thicker in the ventricles and thinner in the atria.Sep 18, 2021
How muscles contract and relax?
When the stimulation of the motor neuron providing the impulse to the muscle fibers stops, the chemical reaction that causes the rearrangement of the muscle fibers' proteins is stopped. This reverses the chemical processes in the muscle fibers and the muscle relaxes.
What is the name of the area where the testicles are drawn up?
In males, the testicles are drawn up into the scrotum. Some individuals may experience muscle spasms in the hands, feet or face as muscle tension increases. Heart rate continues to quicken, blood pressure rises and the individual becomes closer to orgasm.
What are social activities that reflect the complexities of intimate human interaction?
In addition to the physiological intricacies, sexual desire, arousal and orgasm are often social activities that reflect the complexities of intimate human interaction.
Where are the Bartholin glands located?
The Bartholin glands are two pea-sized glands located on the left and right sides of the vaginal opening. Historically, these glands were thought to produce compounds that lubricated the vagina; however, current research shows that the secretions of the Bartholin glands may be relatively minute.
What muscles are involved in ejaculation?
In females, the muscles of the vagina and uterus also produce powerful, rhythmic contractions. These contractions are the source of pleasure during orgasm, as they release muscle tension built up during ...
What happens to the heart rate when you have a pelvic nerve stimulation?
For many individuals, the heart rate quickens, skin may become flushed and muscle tension increases.
What causes a male to erection?
A penile erection is caused by the release of nitric oxide from neurons into the arterial blood supply of the penis. This chemical compound causes the blood vessels to relax and allows the tissue to become engorged with blood.
What is the bonding theory?
The Pair Bonding Theory. This theory relies on the rush of feel-good chemicals released during orgasm, such as dopamine and oxytocin. Oxytocin, in particular, is thought to produce feelings of intimacy and bonding while dopamine simulates the brain’s reward center. Basically, this theory postulates that males and females who orgasm together, ...
Excitement
Plateau
- During this stage, many of the functions of the excitement stage are maintained, such as erection and lubrication. The clitoris may become highly sensitive and retract under the clitoral hood to avoid direct simulation; in addition, the vaginal walls turn dark purple. In males, the testicles are drawn up into the scrotum. Some individuals may experience muscle spasms in the hands, feet …
Orgasm
- After excitation and the plateau stages comes the phase of sexual arousal that, for many individuals, serves as the primary motivation for sexual interaction. Typically lasting just a few seconds, this phase is by far the shortest. In males, contractions of the prostate and seminal glands produce secretions that enter the urethra and mix with sperm...
Resolution
- After orgasm, heart rate, blood pressure and breathing return to normal. Many individuals experience a relaxed feeling during this period and fatigue is common. During the resolution stage, most males will not be able to achieve sexual arousal and orgasm, although some females are able to. WHY WE ORGASM As we’ve seen, from a physiological stand point sexual arousal is …
The By-Product Theory
- Is the female orgasm simply a by-product of the female’s embryological similarity to males (like why males have nipples that serve no pragmatic function)? This was—and to some extent, still is—a widely believed theory until a 2011 paper titled “Genetic analysis of orgasmic function in twins and siblings does not support the by-product theory of female orgasm” contested this beli…
The Up Suck/Sperm Retention Theory
- In the early 1900’s, it was widely believed that the female orgasm was necessary for fertilization, according to the popular up suck theory. In the 1950’s William Masters and Virginia Johnson tested this hypothesis—which postulated that orgasmic contractions sucked semen into the uterus—by applying artificial semen mixed with a radio-opaque substance, which showed on an …
The Pair Bonding Theory
- This theory relies on the rush of feel-good chemicals released during orgasm, such as dopamine and oxytocin. Oxytocin, in particular, is thought to produce feelings of intimacy and bonding while dopamine simulates the brain’s reward center. Basically, this theory postulates that males and females who orgasm together, stay together. And when you’re raising an infant—whether in anci…
The Mate Selection Theory
- This theory states that the female orgasm was developed as a tool for selecting high-quality mates. In an interview with The Guardian, Tim Spector, a researcher at St. Thomas’s hospital in London, explains it like this: “If a man is considered powerful enough, strong enough, or thoughtful enough in bed or in the cave, then he’s likely to hang around as a long-term partner and be a bett…