What are the solutions to negative externalities?
Remedies for Negative Externalities One of the solutions to negative externalities is to impose taxes to change people’s behavior. The taxes can be imposed to reduce the harmful effects of certain externalities such as air pollution, smoking, and drinking alcohol.
How do you deal with externalities in a market economy?
We can either set the appropriate quantity directly through a quota, price floor, or price ceiling. More commonly, governments address the externality through a tax or subsidy. In this case, the government introduces a tax that will make market participants act as if they care about participants outside the market.
What is an example of internalizing the externality?
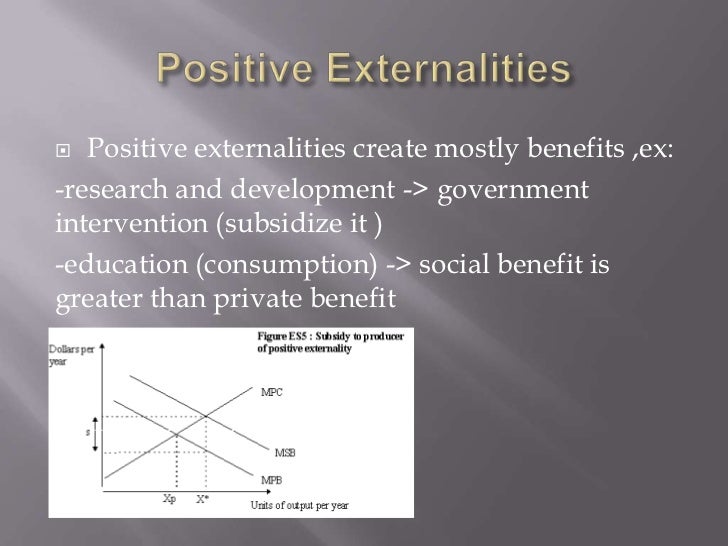
In economic jargon, this is called internalizing the externality. A tax that addresses a negative externality by taxing the good instead of the actual external cost is called a Pigouvian Tax. We work through an example below. Consider the following diagram of a perfectly competitive market with a negative externality present.
What are the different types of externalities?
Generally, externalities are categorized as either negative or positive. 1. Negative externality A negative externality is a negative consequence of an economic activity experienced by an unrelated third party.

What methods does the government use to correct for externalities?
Negative externalities often cause markets to fail. When that happens, the government can respond by using one of three types of policies: regulation, Pigovian taxes, and tradable pollution permits. Regulation allows the government to reduce externalities by passing new laws that directly regulate problematic behavior.
Why do we need to correct positive externalities?
Positive externalities also result in inefficient market outcomes. However, goods that suffer from positive externalities provide more value to individuals in society than is taken into account by those providing the goods.
What are examples of externalities?
Light pollution is an example of an externality because the consumption of street lighting has an effect on bystanders that is not compensated for by the consumers of the lighting.
How do you deal with externalities in economics?
Taxes are one solution to overcoming externalities. To help reduce the negative effects of certain externalities such as pollution, governments can impose a tax on the goods causing the externalities. The tax, called a Pigovian tax—named after economist Arthur C.
What externalities mean?
Definition: Externalities refers to situations when the effect of production or consumption of goods and services imposes costs or benefits on others which are not reflected in the prices charged for the goods and services being provided.
What are positive externalities examples?
A positive externality is a benefit of producing or consuming a product. For example, education is a positive externality of school because people learn and develop skills for careers and their lives. In comparison, negative externalities are a cost of production or consumption.
What are the 4 types of externalities?
There are four main types of externalities – positive consumption externalities, positive production externalities, negative consumption externalities, or negative production externalities. Externalities create a social cost where goods are undersupplied or create damage to the environment.
What causes externality?
The primary cause of externalities is poorly defined property rights. The ambiguous ownership of certain things may create a situation when some market agents start to consume or produce more while the part of the cost or benefit is inherited or received by an unrelated party.
What is another word for externalities?
What is another word for externality?corollaryconsequenceeffectaftermathupshotproductissuesequelaftereffectoutgrowth100 more rows
How do you solve negative externalities?
One of the solutions to negative externalities is to impose taxes to change people's behavior. The taxes can be imposed to reduce the harmful effects of certain externalities such as air pollution, smoking, and drinking alcohol.
When a market is fully corrected for externalities it?
When a market is fully corrected for externalities, it: maximizes surplus.
How do you measure externalities?
The two prominent quantitative methods used by economists to assess externalities are cost of damages and cost of control. For example, in the case of an oil spill, the cost of damages method puts a number to the cost of cleanup necessary to clear the pollution and restore the habitat to its original state.
How can a positive externality be corrected?
Government can discourage negative externalities by taxing goods and services that generate spillover costs. Government can encourage positive externalities by subsidizing goods and services that generate spillover benefits.
How do you overcome positive externalities?
Dealing with positive externalitiesRules and regulations – minimum school leaving age.Increasing supply – the government building of council housing to increase the stock of good quality housing.Subsidy to reduce price and encourage consumption, e.g. government subsidy for rural train services.
Why do positive externalities cause market failure?
Externalities lead to market failure because a product or service's price equilibrium does not accurately reflect the true costs and benefits of that product or service.
What impact do positive externalities have on production?
Due to the positive externalities, the social marginal cost of production is less than the private marginal cost. It leads to the under-production of the good or service as the external benefit accruing to society is not taken into account by the market-driven processes of price determination.
What is externality in economics?
Now we know that an externality is a form of market failure that arises because market participants do not account for factors external to the market. This makes the market quantity is too low or too high relative to the socially optimal level of production. Fortunately, in Topic 3 and 4, we learned a variety of policies that influence the number of goods exchanged in a market. We can use these to set quantity where MSB =MSC. If we create policy correctly, we can bring the market back to the social surplus maximizing level of output.
How does the government address externality?
More commonly, governments address the externality through a tax or subsidy. In this case, the government introduces a tax that will make market participants act as if they care about participants outside the market. In economic jargon, this is called internalizing the externality.
Does external cost impact market participants?
Recognizing that externalities do exist, our market no longer naturally optimizes, since external costs do not impact market participants and thus are not taken into account for their decision.
What are externalities in the economy?
Externalities are the indirect effects that a decision has on something else. In this case, the economy. Governments look to minimize negative externalities by creating penalties in the forms of taxes or fines to reduce the incentive to make such decisions.
How do externalities affect the economy?
In this case, the economy. Governments look to minimize negative externalities by creating penalties in the forms of taxes or fines to reduce the incentive to make such decisions. For example, a gas guzzler tax on large inefficient cars was created to reduce the incentive to buy a large vehicle, which produces more pollution than it's smaller counterparts. The pollution is the externality in this case when someone buys a large vehicle.
How can negative externality be overcome?
Pigou negative externality can be overcome and socially efficient level of output can be achieved by way of improving taxes on producing units, By imposing a tax equal to the level of the externality generated (MSC-MPC) public policy forces manufactures to fully account for all resources used in production.
What are the three policies that correct negative externalities?
This article throws light upon the top three policies taken by government that will correct negative externalities. The policies are: 1. Taxation 2. Subsides 3. Regulation. Type # 1. Taxation: Corrective taxation of negative externality, forces market participants to account for the opportunity costs of all resources allocated in private market.
What is regulation policy?
Regulation is very different from tax and subsidy policies. Regulation sets in minimum environmental quality levels or maximum allowable levels of externalities. For e.g., rules and regulations of civic authorities regarding garbage disposal and recycling. Regulation also requires enforcement.
How does marginal opportunity cost affect profit?
Since marginal opportunity costs exceed marginal benefits of Qa, firms increases profit by cutting back production to the point where marginal opportunity cost are equal to marginal benefits . This equality is attained at point T 2 which is the socially efficient level of production. A firm lower production to socially efficient levels and receives subsidies equal to dcfh.
Can rubber be used for scarce air space?
No property rights are issued for the air space, and therefore neither the rubber manufacturer nor the households may charge the other for use of scarce air space. The rubber manufacturer who use free air may produce at point T 1 and charge a per unit price of P 1 because at this point MPC = MSB.
What are negative externalities?
Negative consumption externalities arise during consumption and result in a situation where the social cost of consuming the good or service is more than the private benefit. Private benefits refer to the positive factors rewarded to the producer or the consumer involved in a transaction. Social costs are negative factors impacting third parties. For example, when a person consumes alcohol and becomes drunk, he/she causes social disorder, disturbing the peace of non-drinkers.
What are negative externalities in manufacturing?
Negative production externalities occur when the production process results in a harmful effect on unrelated third parties. For example, manufacturing plants cause noise and atmospheric pollution during the manufacturing process.
How do negative externalities affect public resources?
Negative externalities commonly affect public resources where it is difficult to hold parties accountable such as in a case of environmental pollution. Producers or consumers may create a negative externality without worrying about lawsuits or fines.
What is an ordinary transaction?
An ordinary transaction involves two parties, i.e., a consumer and the producer, who are referred to as the first and second parties in the transaction. Any other party that is not related to the transaction is referred to as a third party.
What are the remedies for externalities?
PUBLIC SECTOR REMEDIES FOR EXTERNALITIES: REGULATION In an ideal world, Pigouvian taxation and quantity regulation would be identical Quantity regulation seems more straightforward, hence, it has been the traditional choice for addressing environmental externalities In practice, there are complications that may make taxes a more effective means of addressing externalities. The only way to reduce an externality, e.g., pollution, is not to cut down on production. Think of a “pollution reduction” technology (many examples).
Why is Ronald Coase's insight that externalities can sometimes be internalized useful?
It provides the competitive market model with a defense against the onslaught of market failures. It is also an excellent reason to suspect that the market may be able to internalize some small-scale, localized externalities. It won’t help with large-scale, global externalities, where only a “government” can successfully aggregate the interests of all individuals suffering from externality
What are the problems with the Coasian solution?
PROBLEMS WITH COASIAN SOLUTION 3) Transaction Costs and Negotiating Problems: The Coasian approach ignores the fundamental problem that it is hard to negotiate when there are large numbers of individuals on one or both sides of the negotiation. This problem is amplified for an externality such as global warming, where the potentially divergent interests of billions of parties on one side must be somehow aggregated for a negotiation.
What is the second part of the outline course?
OUTLINE Second part of course is going to cover market failures and show how government interventions can help 1) Externalities and public goods 2) Asymmetric information (social insurance)
What is the holdout problem?
2) The holdout problem: Shared ownership of property rights gives each owner power over all the others (because joint owners have to all agree to the Coasian solution) As with the assignment problem, the holdout problem would be amplified with an externality involving many parties.
