/cloudfront-us-east-1.images.arcpublishing.com/gray/WHQ5RRY2DRAKFE5MOLH34KBMBY.jpg)
What is another name for Corrigan pulse?
Synonym (s): aortic regurgitation Corrigan pulse - the collapsing or water-hammer-type pulse in aortic regurgitation or peripheral arterial dilation, characterized by an abrupt rise and rapid fall away. Want to thank TFD for its existence?
What is Corrigan disease of the heart?
Corrigan disease - reflux of blood through an incompetent aortic valve into the left ventricle during ventricular diastole. Synonym (s): aortic regurgitation Corrigan pulse - the collapsing or water-hammer-type pulse in aortic regurgitation or peripheral arterial dilation, characterized by an abrupt rise and rapid fall away.
What is Corrigan's pulse and Watson's water hammer pulse?
"Corrigan's pulse" is named for Sir Dominic Corrigan, the Irish physician, who characterized it in 1832. "Watson's water hammer pulse" is named for Thomas Watson, who characterized it in 1844. ^ a b cSuvarna JC (2008).
What is the meaning of wiry pulse?
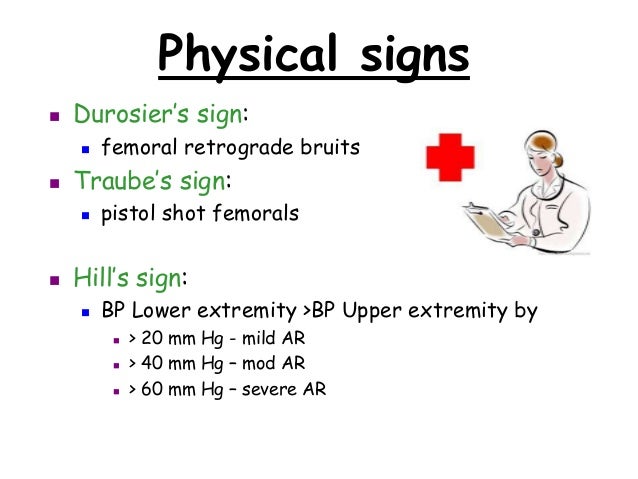
A pulse with a powerful upstroke and then sudden disappearance; a hallmark of aortic regurgitation. Synonym: triphammer pulse; Corrigan's pulse wiry pulse A tense pulse that feels like a wire or firm cord. Medical Dictionary, © 2009 Farlex and Partners Corrigan's pulse
What is Corrigan pulsation?
Corrigan pulse: A pulse that is forceful and then suddenly collapses. It is usually found in patients with aortic regurgitation, a condition caused by a leaky aortic valve. The left ventricle of the heart ejects blood under high pressure into the aorta.
Why it is called water hammer pulse?
The water hammer pulse is a physical exam finding with many different etiologies. However, it is commonly associated with aortic regurgitation. It will feel like a tapping impulse through the patient's forearm due to the rapid emptying of blood from the arm during diastole.
What do you feel in collapsing pulse?
Collapsing pulse can be thought of as a palpably widened pulse pressure; in the context of aortic regurgitation or PDA it is often possible to feel a markedly water hammer pulse on lifting the arm up.
How do you examine a Corrigan's pulse?
The Corrigan's pulse is a bounding carotid pulse, characterized by a rapid systolic rise and a rapid diastolic collapse. To detect the Corrigan's sign, inspect the base of the patient's neck, right where the carotids are. Click here to see an example of the Corrigan's sign.
What are the 3 types of pulse?
Types of PulseTemporal: It is felt in the head.Carotid: It is felt in the neck.Branchial: It is felt in the elbow.Femoral: It is felt at the groin.Radial: It is felt on the wrist.Popliteal: It is felt on the knee.Dorsalis pedis: It is felt on the foot.
How do you fix water hammer?
You can cure water hammer by turning off the water behind the waterlogged chamber, opening the offending faucet and permitting the faucet to drain thoroughly. Once all the water drains from the chamber, air will fill it again and restore the cushion.
Can collapsing pulse be normal?
Collapsing pulse is possible only in cases where there is a strong, bounding pulse due to the increased stroke volume in all conditions causing it. 1 Lifting of the arm of the patient may be needed, if at all, to confirm a collapsing pulse, when it is suspected to be present on routine examination.
How do you treat a bounding pulse?
Worrying about your irregular heartbeat only adds additional stress to your life. Limiting your alcohol and caffeine consumption can also help to keep your pulse from bounding. Some herbs (such as those used in energy drinks), medications, and even tobacco smoke can act as stimulants and should be avoided.
What are thrills and heaves?
A thrill is a palpable murmur whereas a heave can be a sign of right ventricular hypertrophy. A thrill feels like a vibration and a heave feels like an abnormally large beating of the heart. Feel for these all over the precordium. Palpate for any heaves or thrill.
What is quincke's pulse?
Definition/Introduction. Quincke's sign, also known as Quincke's pulse, represents the visualization of capillary pulsations upon light compression applied to the tip of the fingernail bed.
What is Hyperdynamic pulse?
Hyperdynamic individuals were defined as individuals who had the uppermost 25% of both pulse rate and pulse pressure distributions. Hypodynamic individuals were defined as individuals who had the lowest 25% of both pulse rate and pulse pressure distribution.
What is Bisferiens pulse?
Pulsus bisferiens is a single central pulse wave with two peaks separated by a distinct mid-systolic dip. An early component percussion wave results from rapid left ventricular ejection. A late component tidal wave represents a reflected wave from the periphery due to an artery's recoil effect.
What is water hammer sound?
Water hammer is a loud bang coming from the pipes after a fill valve shuts off. This type of plumbing noise is typically due to worn or damaged faucet washers. A buildup of minerals and rust inside the shut-off valves may also cause this sound.
Why are my water pipes pulsating?
Whenever the faucet is open or the toilet is filling, you may hear a pulsing or whooshing noise coming out of the main supply line. It means the pipes are beginning to accumulate calcium and mineral deposits from the inside. Such sounds occur in plumbing systems made of galvanized or copper pipes.
What is the water hammer effect?
Water hammer is a phenomenon that can occur in any piping system where valves are used to control the flow of liquids or steam. Water hammer is the result of a pressure surge, or high-pressure shockwave that propagates through a piping system when a fluid in motion is forced to change direction or stop abruptly.
What is the character of pulse?
The pulse amplitude, or character, refers to how strong, forceful, or full the pulse is. A weak, thready, or feeble pulse is typically considered an emergency and could be an indication of low blood pressure, like when a client is hemorrhaging, as well as a serious heart problem or a blockage of a blood vessel.
What is a corrigan pulse?from litfl.com
Corrigan pulse describes the excessive visible pulsations of arteries in patients with aortic valve insufficiency, most obvious in the head and superior extremity arteries when the patient is upright; in particular, the subclavian, carotid, temporal, brachial, and palmar arteries.
What did Sir Corrigan observe?from litfl.com
He observed the visible abrupt distension and collapse of the carotid, head, and superior extremity arteries in patients with permanent patency of the aortic mouth. Sir Corrigan explained that in aortic valve insufficiency, the ascending aorta and branching arteries lessen in diameter as blood regurgitates back into the left ventricle, which then suddenly and greatly dilates with ventricular contraction.
What is the pulse of aortic regurgitation?from litfl.com
The pulse of aortic regurgitation is sometimes at least very striking and peculiar: sudden like the blow of a hammer without any prolonged swell of an artery. It always reminds me of the well-known chemical toy, formed by including a small quantity of liquid in a glass tube exhausted of air and hermetically sealed. On reversing the tube the liquid falls from one end of it to the other with a hard, short knock, as if it were a mass of lead. The sensation given by the pulse, when there is much regurgitation through the aortic valves, is very similar to this.
Who is the Corrigan aorta named after?from litfl.com
It is named after Sir Dominic John Corrigan, who described the visible arterial pulsations of aortic regurgitation, while comprehensively explaining the pathophysiology, diagnosis, management, and prognosis of the disease in his 1832 publication ‘On permanent patency of the mouth of the aorta, or inadequacy of the aortic valves’. ...
Who first used the water hammer pulse?from litfl.com
However, the water-hammer description was first used by Sir Thomas Watson in his lecture on aortic valve insufficiency (1837; published in 1842).
Who described the exaggerated visible pulsations of the head and upper extremity arteries?from litfl.com
Hodgkin 1829. 1832 – Sir Dominic John Corrigan (1802 – 1880) described the exaggerated visible pulsations of head and upper extremity arteries, in addition to ‘Bruit de soufflet’ and ‘frémissement’ as the three physical signs of aortic regurgitation in the Edinburgh Medical and Surgical Journal. He also briefly mentioned the ‘full pulse’ ...
What is alternating pulseone?
alternating pulseone with regular alteration of weak and strong beats without changes in cycle length. Called also pulsus alternans.
What is anadicrotic pulseone?
anadicrotic pulseone in which the ascending limb of the tracing shows two extra small waves or notches.
What does it mean when your pulse is weaker?
If a pulse is noted to be weaker during inhalation and stronger during exhalation (pulsus paradoxus), this could indicate either greater reduction in the flow of blood to the left ventricle than is normal, as in constrictive pericarditisor pericardial effusion, or a grossly exaggerated inspiratory maneuver, as in tracheal obstruction, asthma, or emphysema.
Why is the examiner's thumb never used to take a pulse?
The examiner's thumb is never used to take a pulse because its own pulse is likely to be confused with that of the patient. Pressure should be light; if the artery is pressed too hard, the pulse will disappear entirely. The number of beats felt in exactly 1 minute is the pulse rate.
How many expansions are there in tricrotic pulseone?
tricrotic pulseone in which the tracing shows three marked expansions in one beat of the artery.
What is the instrument used to measure the movement of an arterial pulse?
An instrument for registering the movements, form, and force of the arterial pulse is called a sphygmograph. The sphygmographic tracing (or pulse tracing) consists of a curve having a sudden rise (primary elevation) followed by a sudden fall, after which there is a gradual descent marked by a number of secondary elevations.
Where is the carotid pulse felt?
carotid pulsethe pulse felt over the carotid artery, which lies between the larynx and the sternocleidomastoid muscle in the neck; frequently used to assess effectiveness of cardiac massage during cardiopulmonary resuscitation. It can be felt by pushing the muscle to the side and pressing against the larynx, or, if the patient is dyspneic, by palpating the pulse at the groove in the muscle.
What is the difference between Watson's water hammer pulse and Corrigan's pulse?
"Watson's water hammer pulse" and "Corrigan's pulse" refer to similar observations. However, the former usually refers to measurement of a pulse on a limb, while the latter refers to measurement of the pulse of the carotid artery.
What is a collapsing pulse?
Watson's water hammer pulse, also known as Corrigan's pulse or collapsing pulse, is the medical sign (seen in aortic regurgitation) which describes a pulse that is bounding and forceful, rapidly increasing and subsequently collapsing, as if it were the sound of a water hammer that was causing the pulse.
Why does a water hammer pulse happen?
This happens because the blood that is pumped to the arm during systole is emptied very quickly due to the gravity effect on the raised arm.
What causes a water hammer pulse?
Water hammer pulse is commonly found when a patient has aortic regurgitation. It can also be seen in other conditions which are associated with a hyperdynamic circulation. A more comprehensive list of causes follows: